The importance of soils for human life. The role of soil in human life What role does soil play in human life
The soil cover of the Earth seems to us ordinary and eternally existing in nature. However, it is not. Nature created soil over 4.5 billion years! The basis for the formation of soil was the weathering products of rocks. Weathering is a complex process, the result of the combined action of many physical, chemical and biological factors. Video 37.
Conventionally, this is reflected in the formula:Rocks + Sun + air + water + living organisms = soil.
The process of soil formation never stops; of course, it continues today, but very slowly. The soil is in a constant process of development - formation or destruction. The duration of the process of formation of the Earth's soil cover is determined by many factors. It takes many millennia for soil to form. At the same time, irrational environmental management, which is detrimental to the soil, can destroy it in just a few years.
Do you think soil should be classified as a renewable or non-renewable natural resource? Is it possible to give a definite answer to this question?
The soil cover of the Earth provides life for plants, animals and humans. Soil is the most important component of all terrestrial ecological systems of the Earth and is itself a unique ecosystem (see topics 2 and 3 for more details). It communicates living organisms with the lithosphere, atmosphere and hydrosphere. Soil is an object of study for a separate science - soil science. The founder of soil science - an outstanding Russian scientist Vasily Vasilievich Dokuchaev. In St. Petersburg there is the Central Museum of Soil Science named after. V.V. Dokuchaev, which is one of the world's largest soil-ecological museums. In the museum you can get answers to the questions - What is soil? How is it formed? What grows on this soil? Who lives in this soil? The museum is the custodian of the richest collection of soils from various natural areas of the world.
Currently, scientists identify about one hundred types of soils. Why are there different types of soil?
The diversity of soils is, of course, associated with the diversity of conditions in which they were formed. The climate and properties of the rocks from which the soil is formed are especially important.

Look at the picture and compare chernozem, soddy-podzolic and tundra podzolic soils.
Do you know what types of soil are typical for your area? The soil has several layers connected to each other. Video 38. Among them, a distinction is made between bedrock, which undergoes weathering when it reaches the surface, and parent rock, from which the top layer of soil is formed. The underlying layer is called subsoil.
A unique property of soil is fertility. This is what ensures the existence of life on Earth. Soil fertility is determined by the content of humic substances (humus) in it. Humus is an accumulation of organic substances that were formed during the decay of plant and other living remains. It gives the soil a black color and ensures the growth and development of plants (i.e. life on Earth). The more humus in the soil, the more fertile it is. Most humus is found in chernozem soils. Video 39.
What is soil made of?
Approximately 50% of the space in the soil is occupied by air, filling the spaces between solid particles. About 45% of the soil mass comes from mineral substances, about 5% from organic substances. However, this information about the composition of the soil does not give a real idea of it.
We are accustomed to thinking that the soil is sparsely populated, that the bulk of living organisms are on its surface. But this is not true at all! It is a habitat for many animals. Everyone knows that earthworms, insect larvae, and insects themselves live in the soil. The soil serves as a nesting and housing site for many birds and other animals. Scientists' calculations show that the mass of living things in the soil is? masses of living forest inhabitants and more? masses of living steppe vegetation.
It has been established that the smaller the size of the organisms, the greater their number in the soil. Thus, in 1 m 3 of soil there are several tens of millions of worms and insects. And 1 gram of soil contains more than a million protozoan microorganisms. In general, scientists estimate the number of soil microorganisms on Earth to be approximately one billion tons!However, the importance of living organisms in soil processes is determined not by their mass, but by the enormous work they perform. Video 40.
We do not notice the work of soil bacteria, which continuously process dying parts of plants and other organisms. But if it stopped, the surface of the Earth would be littered with these remains. It’s hard to imagine what would happen to our beautiful Planet in just a hundred years! And earthworms, as you know, swallow soil when feeding. If about 140 thousand earthworms live in one hectare of soil, then their mass is 500 kg! This means that in one year they pass about ten tons of soil mass through their bodies!

What is the biosphere function of soil?
It is important to understand that to characterize a soil, it is not enough to know its composition. Scientific knowledge about soil is associated with the understanding that it is a complex natural body that has a certain structure. Let us remember: Soil is not a mechanical mixture of various substances. Soil is a complex system of interaction between minerals, organic substances and living organisms.
Thanks to their interaction, the soil performs its biosphere functions. But, we repeat, it is provided not only by the composition, but also by the structure of the soil.
Soil is made up of very fine particles. Microscopic organisms live in the film of water that envelops soil particles. Larger ones settle between soil particles, as in caves. Both of them form a single formation with the soil. Those that live on the surface of particles require air, and those that are inside the particles are able to live without air.
Nutrition, respiration and all other life processes of living organisms lead to many changes in the composition of the soil. At the same time, they involve substances contained in the air and dissolved in water into these processes, and they themselves release new substances formed in the process of their life activity.
Thus, the soil fulfills its biosphere function as the final link ensuring the creation of the entire biomass of the Planet.
Soil destruction can occur both as a result of natural processes and under the influence of irrational human actions.

Destruction of soil cover at a forest cutting site
Natural processes such as the advance of glaciers, volcanic eruptions, the formation of mountains, earthquakes, hurricanes, tornadoes or floods cannot but influence the state of the earth's crust and soil formation processes. But natural soil erosion (destruction and removal of the upper most fertile layers as a result of the action of water and wind) is a slow continuous process, at the same time as a new soil layer is formed. Unlike natural, anthropogenic soil erosion is caused by human intervention in the natural environment for economic purposes. Irrational use of fields and pastures, deforestation, drainage of water bodies and the like - all this can destroy soil fertility in a very short time.

For example, the first settlers in America exploited the land so mercilessly that in 100 years they destroyed 20% of arable land. The soil is also destroyed due to waterlogging and desertification.


Bitter evidence of man's reckless exploitation of nature is the deserts of North Africa, the Baltic dunes, and eroded spaces in Australia, Pakistan, India and Canada. In the European part of our country alone there are up to 2 million ravines, which were formed mainly as a result of plowing the land. Every year, land loses a layer of fertile soil, which nature spent thousands of years creating. Soil scientists call erosion a real tragedy.
Scientists believe that in order to maintain the ecological sustainability of the territory, each natural zone must maintain a certain ratio of arable land, pastures and forests. So, for example, in the forest-steppe, according to research by V.V. Dokuchaev, forests should be 10-18%. Now, due to excessive plowing, there are significantly fewer of them left.
According to modern data, humanity has already lost about 2 billion hectares of once fertile lands over the historical period, turning them into anthropogenic deserts. This is more than the area of all modern arable land in the world, amounting to 1.5 billion hectares. At the end of the twentieth century, it became obvious that soil degradation had acquired alarming proportions and was one of the main threats to the global environmental crisis. This is especially alarming given that, according to recent estimates, there are more than one billion hungry people in the world, that is, one in six people on the planet. This means that more people are suffering from hunger and malnutrition than at any time in human history, while soil fertility and the area suitable for agriculture are declining.
Do we ever think about what soil means in our lives? Perhaps very rarely. It seems to us that since soil is not a flower, not an insect, not an animal, what can happen to it? It will always lie under your feet. And at the same time, the world-famous ecologist Jean Pierre Dorsta said: “Soil is our most precious capital. The life and well-being of the entire complex of terrestrial biocenoses, natural and artificial, ultimately depends on the thin layer that forms the uppermost cover of the Earth.”
By underestimating the role of this greatest natural wealth, humanity jeopardizes its very existence.
Protecting the soil from destruction and combating the decline in its fertility is a major environmental problem that requires the urgent attention of the world community.
You can often hear the expression “the earth is the breadwinner,” but people often do not attach any meaning to it. But it would be more correct to say that grass and trees grow, wheat sways in the field and forests rustle only because we have soil.
The soil began to form along with the very first living beings appearing on the planet, so we owe our lives to them, and not only in genetic terms. For a long time, humanity has known that the surrounding reality has an incredible property, which was called “fertility.”
The earth's soil, to which the animal and plant world owes its existence, manifested this property more closely, more noticeably and clearly. It is an indispensable condition for the life of animals, plants and humans. While cultivating all kinds of agricultural crops, man turned his attention to the fact that fruits grown from the seeds of the same plant turn out to be different in different areas of the earth.
Soil also plays a significant role in the natural habitat of people. Soil, being part of the group of natural resources of a non-renewable nature, is the most important means of agricultural production. All kinds of international agreements and declarations on issues related to environmental management affirm the importance of soil as a real human asset, which absolutely all people are obliged to rationally use and protect.
At the moment, the problem of human interaction with nature has become particularly acute. It becomes clear that solving problematic issues related to maintaining the level of quality of human life is unimaginable without understanding current environmental problems. It is the soil that determines a large number of processes that occur in the biosphere. The great importance of soil lies in the reliable accumulation of organic matter, various chemical elements and energy.
Soil performs the functions of a biological destroyer, absorber and effective neutralizer of various contaminants. In addition, soil cover is the most significant natural formation. Its importance in the life of human society can be determined by the fact that soil cover is the primary source of various foods, which provides about 95-97 percent of all food resources for the world's population.
We hear the words “the earth is the nurse” so often that we hardly attach any meaning to them. But it would be more correct to say that trees and grass grow, forests rustle and wheat sways in the field only because we have land, or rather soil. The formation of soil began with the appearance of the first living creatures on Earth, so it is to them that we owe life, and not only genetically. “From ancient times, people knew that the world around them has an amazing property, which was called fertility. The most noticeable, most everyday close and understandable thing for people was the soil, to which the modern flora and fauna owe their existence and development. It is a necessary condition for the life of plants, animals, and humans. While cultivating agricultural crops, people noticed that the crop grown from the seeds of the same plant turns out to be different on different plots of land.
Soil also plays an important role in the natural human environment. Soil, classified as a non-renewable natural resource, is the main means of agricultural production. International declarations and agreements on environmental issues (“World Conservation Strategy”, “World Soil Charter”, “Foundations of World Soil Policy”) affirm the importance of soil as the universal heritage of humanity, which should be rationally used and protected by all people of the Earth.
Currently, the problem of interaction between human society and nature has become particularly acute. It becomes indisputable that solving the problem of preserving the quality of human life is unthinkable without a certain understanding of modern environmental problems. The Earth's soil cover is the most important component of the Earth's biosphere. It is the soil shell that determines many of the processes occurring in the biosphere. The most important importance of soils is the accumulation of organic matter, various chemical elements, and energy. Soil cover functions as a biological absorber, destroyer and neutralizer of various pollutants. In addition, soil is the most important natural formation.
Its role in the life of society is determined by the fact that soil is the main source of food, providing 95-97% of food resources for the planet's population. The world's land area is 129 million km2 or 86.5% of the land area. Arable land and perennial plantings as part of agricultural land occupy about 15 million km2 (10% of the land), hayfields and pastures - 37.4 million km2 (25% of the land). The total arable suitability of land is estimated differently by different researchers: from 25 to 32 million km2.
If this link of the biosphere is destroyed, then the existing functioning of the biosphere will be irreversibly disrupted. The modern soil cover was formed over thousands of years, under conditions that have now completely changed. Hence, the importance of the correct and effective use and conservation of soil resources increases immeasurably.
We hear the words “the earth is the nurse” so often that we hardly attach any meaning to them. But it would be more correct to say that trees and grass grow, forests rustle and wheat sways in the field only because we have land, or rather soil. The formation of soil began with the appearance of the first living creatures on Earth, so it is to them that we owe life, and not only genetically. “From ancient times, people knew that the world around them has an amazing property, which was called fertility. The most noticeable, most everyday close and understandable thing for people was the soil, to which the modern flora and fauna owe their existence and development. It is a necessary condition for the life of plants, animals, and humans. While cultivating agricultural crops, people noticed that the crop grown from the seeds of the same plant turns out to be different on different plots of land.
Soil also plays an important role in the natural human environment. Soil, classified as a non-renewable natural resource, is the main means of agricultural production. International declarations and agreements on environmental issues (“World Conservation Strategy”, “World Soil Charter”, “Foundations of World Soil Policy”) affirm the importance of soil as the universal heritage of humanity, which should be rationally used and protected by all people of the Earth.
Currently, the problem of interaction between human society and nature has become particularly acute. It becomes indisputable that solving the problem of preserving the quality of human life is unthinkable without a certain understanding of modern environmental problems. The Earth's soil cover is the most important component of the Earth's biosphere. It is the soil shell that determines many of the processes occurring in the biosphere. The most important importance of soils is the accumulation of organic matter, various chemical elements, and energy. Soil cover functions as a biological absorber, destroyer and neutralizer of various pollutants. In addition, soil is the most important natural formation.
Its role in the life of society is determined by the fact that soil is the main source of food, providing 95-97% of food resources for the planet's population. The world's land area is 129 million km2 or 86.5% of the land area. Arable land and perennial plantings as part of agricultural land occupy about 15 million km2 (10% of the land), hayfields and pastures - 37.4 million km2 (25% of the land). The total arable suitability of land is estimated differently by different researchers: from 25 to 32 million km2.
If this link of the biosphere is destroyed, then the existing functioning of the biosphere will be irreversibly disrupted. The modern soil cover was formed over thousands of years, under conditions that have now completely changed. Hence, the importance of the correct and effective use and conservation of soil resources increases immeasurably.
THE ROLE OF SOIL IN HUMAN LIFE AND ACTIVITY Soil also plays an important role in the natural human environment. First of all, because soil is the main means of agricultural production, classified as a non-renewable natural resource. International declarations and agreements on environmental issues (“World Conservation Strategy”, “World Soil Charter”, “Foundations of World Soil Policy”) affirm the importance of soil as the universal heritage of humanity, which should be rationally used and protected by all people of the Earth. Therefore, land use issues affect a complex of complex problems of a socio-economic nature: issues of land ownership, land legislation, land law, economic valuation of land, etc. In relation to the environment and humans, soil plays another important role - protective. Having the ability to absorb and retain various pollutants, including radionuclides, binding them chemically and physically, the soil thereby serves as a kind of filter that prevents the entry of these compounds into natural waters, plants and further along the food chain into animal organisms and humans . However, the possibilities of the soil in this regard are not unlimited, and the level of technogenic pressure is increasing, so cases of dangerous soil contamination and subsequent poisoning of people are increasingly observed. Human health is largely determined by the environment in which he is forced to live, and, as it turns out, soil plays an important role in this matter. Some diseases, the causes of which were previously unknown, are associated with certain soil conditions: an excess or deficiency of chemical elements, a violation of their ratio. The most widely known examples from this area are diseases of the thyroid gland (goiter and Graves' disease), lesions of tooth enamel (caries and fluorosis), but their list is very large and continues to expand. Thus, there is information about the connection with the characteristics of the soil cover and cancer. A study by oncologists of the geographic distribution of stomach cancer showed that in Tunisia, Egypt, and Afghanistan, the incidence of stomach cancer is significantly lower than in England, France, and the USA. Clinical studies have suggested an increased risk of this disease with insufficient magnesium in food (and therefore in water and soils), as well as with a violation of the ratio in the soil solution between Ca, Mg, Mn ions. This pattern was confirmed using the example of the Rostov region in the joint work of soil scientists (V.V. Akimtsev) and oncologists (Z.M. Mitlin). Such diseases, according to the proposal of A.P. Vinogradov were called endemic, and territories with abnormal contents of chemical elements were called endemic provinces. V.V. Kowalski compiled a map of biogeochemical zones and provinces of the USSR. On it, he identified areas of distribution of a number of human and animal diseases caused by the biogeochemical properties of soils and waters. The solution to the origin of endemic diseases made it possible to develop measures to neutralize these phenomena. Soils are populated by myriads of microorganisms. Some of them are isolated from soils and are used to produce valuable medicinal drugs - antibiotics. The soil microflora also contains pathogenic forms that cause severe diseases, for example, the causative agents of tetanus (b. tetani), anthrax (b. anthracis), malignant edema (b. oedematis maligni) and some others. Some human and animal diseases are associated with animals living only in certain soil conditions. For example, rodents and insects living in sandy and sandy loam soils of semi-deserts and dry steppes carry diseases such as tularemia and plague. Thus, many important issues in medicine and veterinary medicine cannot be resolved without taking into account the characteristics of the soil cover. That is why in 1986 the working group “Soils and Geomedicine” was organized within the framework of the International Society of Soil Sciences. This created
 Professional and personal qualities of a sales manager
Professional and personal qualities of a sales manager How to quit without working for two weeks, step-by-step instructions Why you need to work for 2 weeks when leaving
How to quit without working for two weeks, step-by-step instructions Why you need to work for 2 weeks when leaving Advances of modern natural science
Advances of modern natural science Entrepreneurial environment and its structure Entrepreneurial environment as a system of relations
Entrepreneurial environment and its structure Entrepreneurial environment as a system of relations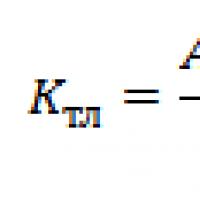 Theoretical aspects of analyzing the creditworthiness of an enterprise
Theoretical aspects of analyzing the creditworthiness of an enterprise Violation of the period of temporary import of goods
Violation of the period of temporary import of goods Is an ecologist a profession of the 20th century?
Is an ecologist a profession of the 20th century?