Presentation "Calcium and its compounds" (Grade 9). Calcium Presentation about the chemical element calcium
Calcium
Chemistry teacher GBOU school No. 644
St. Petersburg Novosadova N.I.


CALCIUM(lat. Calcium), Ca, chemical element Group IIA of the periodic system, atomic number 20, atomic mass 40.078; refers to alkaline earth metals .
Name: the name is from the Latin "calx", genitive "calcis" (lime).

The structure of the atom
1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2
p20, n20, e20
St. ok. +2, alkaline earth metal

Finding in nature:
in terms of prevalence in the earth's crust, calcium occupies 5th place
(minerals: calcite, chalk, marble,
limestone - (CaCO 3 ) ,
phosphorites, apatites - (Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 ),
dolomites - (CaCO 3 *MgCO 3 ),
fluorite (CaF 2), gypsum (CaSO 4 * 2H 2 O)
and other calcium compounds.

CaF 2 - fluorite
CaCO 3 - a piece of chalk
CaSO 4 2H 2 O- gypsum
CaSO 4 - anhydrite

Physical properties: silver-white metal, density 1.54 g / cm 3, t pl \u003d + 852 ° С. At normal temperatures, it easily oxidizes in air.


2Ca+O 2 = 2CaOCa0 - 2 e Ca +2 reducing agent 2 O 0 +4e 2 O -2 oxidant

II. interaction with complex substances
1) with water
Ca + 2H 2 O \u003d Ca (OH) 2 + H 2
2) with acids C a + 2HC l \u003d C a C l 2 + H 2





- he controls the beating of our heart,
- at his command, our muscles relax or contract,
- calcium transmits signals through the nervous system,
- participates in the process of blood clotting,
- in the processes of digestion, excretion, nervous processes, affects the immune system and the reproductive system.

OUTPUT: CALCIUM IS NEEDED FOR OUR BODY!
900game.net

The hardness of water is due to the presence of Ca and Mg ions in it.
Carbonate - temporary Ca (HCO 3) 2, Mg (HCO 3) 2, Fe (HCO 3) 2.
Removal ("water softening"):
Boiling Ca (HCO 3) 2 \u003d CaCO 3 + CO 2 + H 2 O
Adding soda
Ca (HCO 3) 2 + Na 2 CO 3 \u003d CaCO3 + 2NaHCO 3
Non-carbonate - constant CaCl 2, CaSO 4, MgCl 2, MgSO 4
Removed: by adding soda
CaSO 4 + Na 2 CO 3 \u003d CaCO 3 + Na 2 SO 4
MgSO 4 + Na 2 CO 3 + H 2 O \u003d (Mg (OH)) 2 CO 2 + CO 2 + Na 2 SO 4


2. Physical properties of Ca:
Calcium is a silvery white and rather hard metal, light. The melting and boiling points are higher than those of the alkali metals. Natural calcium consists of a mixture of six isotopes with mass numbers 40 (the main isotope), 42, 43,44,46 and 48. In nature: CaCO 3 - chalk, marble, limestone; CaSO 4 * 2H 2 O - gypsum; Ca 3 (PO 4) 2 - phosphorite.

3. Obtaining Ca.
- Electrolysis of molten salts CaCl 2 =Ca+Cl 2 ;
- From oxides 2 Cao+2Al=2Ca+Al 2 O 3 ;
In industry, calcium is obtained by electrolysis of a mixture of molten salts: 6 parts of calcium chloride CaCl 2 and 1 part of calcium fluoride CaF 2. The latter is added to lower the melting point of calcium chloride at which electrolysis is carried out.

4.Chemical properties Ca.
With simple substances:
- Ca + H 2 \u003d CaH 2
- 3Ca + Cl 2 \u003d CaCl 2 (halides)
3) 2Ca+O 2 \u003d 2CaO (brick red flame)
Ca + O 2 \u003d CaO 2 (peroxides)
4) 3 Ca + N 2 \u003d Ca 3 N 2
- Ca+2C=CaC (car BIT)
Ca + 2 H 2 O \u003d Ca (OH) 2 + H 2
Ca + 2HCl \u003d CaCl 2 + H 2
Ca + 2NH 3 \u003d Ca (NH 2) 2 + H 2

Ca compounds
Calcium oxide CaO - "quicklime"
Getting: CaCO 3 \u003d CaO + CO 2 (roasting)
Chemical properties: CaO is a basic oxide.
- CaO + H 2 O \u003d Ca (OH) 2 - slaked lime
- CaO + SiO 2 \u003d CaSiO 3
- CaO + CO 2 \u003d CaCO 3
- CaO+2HCl = CaCl2+H2O
- CaO+3C=CaC2 +CO (heating)
Calcium hydroxide Ca (OH) 2 - "slaked lime".
Getting: CaO+H2O=Ca(OH)2
Physical properties: solid white color, insoluble in water.
Qualitative reaction for Ca
Ca(OH)2 +CO2 =CaCO3+H2O - the solution becomes cloudy, with further passage of CO2 the solution becomes transparent: CaCO3 +CO2 +H2O=Ca(HCO3)2
Application of Ca compounds: CaCl2 – water absorbent; CaS - for dressing leather; Ca(OH)2 - in agriculture, construction.

Application
For the manufacture of lead-calcium alloys required in the production of bearings.


- Describe the physical properties of Ca.
- Obtaining calcium in industry.
1 slide

2 slide
The hardness of water is due to the presence of Ca and Mg ions in it. Carbonate - temporary Ca (HCO3) 2, Mg (HCO3) 2, Fe (HCO3) 2. Removal ("water softening"): - by boiling Ca(HCO3)2 =CaCO3 +CO2 +H2O - adding soda Ca(HCO3)2 +Na2CO3 =CaCO3+2NaHCO3 +Na2CO3 = CaCO3 +Na2SO4 MgSO4 +Na2CO3 +H2 O=(Mg(OH))2 CO2 +CO2+Na2SO4

3 slide
Finding in nature. Calcium is one of the common elements. its total content in the earth's crust is 3.6%. In nature, the following calcium compounds are most widely distributed: the mineral calcite CaCO3 (limestone, marble and chalk arrays are formed from it), gypsum CaSO4 * 2H 2O anhydrite CaSO 4. Calcium in the form of phosphate Ca3 (PO4)2 is present in apatites, phosphorites and animal bones. It is found in natural waters and soils.

4 slide
2. Physical properties of Ca: Calcium is a silvery white and rather hard metal, light. The melting and boiling points are higher than those of the alkali metals. Natural calcium consists of a mixture of six isotopes with mass numbers 40 (the main isotope), 42, 43,44,46 and 48. In nature: CaCO3 - chalk, marble, limestone; CaSO4 * 2H2O - gypsum; Ca3(PO4)2 - phosphorite.

5 slide
3. Obtaining Ca. Electrolysis of molten salts CaCl2=Ca+Cl2; From oxides 2Cao+2Al=2Ca+Al2O3; In industry, calcium is obtained by electrolysis of a mixture of molten salts: 6 parts of calcium chloride CaCl2 and 1 part of calcium fluoride CaF 2. The latter is added to lower the melting point of calcium chloride, at which electrolysis is carried out.

6 slide
4. Chemical properties of Ca. With simple substances: Ca + H2 \u003d CaH2 3Ca + Cl2 \u003d CaCl2 (halides) 3) 2Ca + O2 \u003d 2CaO (brick-red flame) Ca + O2 \u003d CaO2 (peroxides) 4) 3Ca + N2 \u003d Ca3N2 Ca + 2C \u003d CaC (carbite) Ca+2H2O=Ca(OH)2 +H2 Ca+2HCl=CaCl2+H2 Ca+2NH3=Ca(NH2)2 +H2

7 slide
Compounds Ca Calcium oxide CaO - "quicklime" Obtaining: CaCO3 = CaO + CO2 (roasting) Chemical properties: CaO - basic oxide. CaO + H2O \u003d Ca (OH) 2 - slaked lime CaO + SiO2 \u003d CaSiO3 CaO + CO2 \u003d CaCO3 CaO + 2HCl \u003d CaCl2 + H2O CaO + 3C \u003d CaC2 + CO (heating) Calcium hydroxide Ca (OH) 2 - “slaked lime ". Preparation: CaO+H2O=Ca(OH)2 Physical properties: white solid, slightly soluble in water. Qualitative reaction for Ca Ca(OH)2 +CO2 =CaCO3+H2O - the solution becomes cloudy, with further transmission of CO2 the solution becomes transparent: CaCO3 +CO2 +H2O=Ca(HCO3)2 Application of Ca:CaCl2 compounds - water absorbent; CaS - for dressing leather; Ca(OH)2 - in agriculture, construction.
Description of the presentation on individual slides:
1 slide
Description of the slide:
Calcium and its compounds KSU "Research Specialized Center-School-Complex of Developmental Education "Vostok" for Gifted Children" of the Education Department of the East Kazakhstan region Kupriyanova Irina Vasilievna, teacher of higher chemistry qualification category Ust-Kamenogorsk
2 slide
Description of the slide:
L. TOLSTOY Au Os Cs Hg Li W Fe Al Ag Champion Metals Who advised: "Try to give the mind as much food as possible"? The toughest. The most common in nature. The easiest. The most electrically conductive. The most active. Most plastic. The most space. The lightest. The heaviest. The slide is used to update knowledge.
3 slide
Description of the slide:
4 slide
Description of the slide:
5 slide
Description of the slide:
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE CHEMICAL ELEMENT calcium Periods 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Rows 1 2 3 4 10 9 8 7 5 6 Oxidation state Electronic formula Home 40 +20 0 To work with a slide, you need to click the mouse - the item characteristics of the element open.
6 slide
Description of the slide:
being in nature 5th place in terms of content in the earth's crust. Mass fraction in the earth's crust - 3.6%. active Moderate activity noble Calcium is an active metal, found in nature only in the form of compounds. In nature, in the form of salts: sulfates, carbonates, phosphates, fluorides. Is an integral part bones and blood in humans and animals. ACTIVITY SERIES OF METALS / ELECTROCHEMICAL VOLTAGE SERIES Li Rb K Ba Sr Ca Na Mg Al Mn Zn Cr Fe Cd Co Ni Sn Pb (H) Bi Cu Hg Ag Pt Au To work the slide, you need to click the mouse - the text will appear sequentially.
7 slide
Description of the slide:
the presence of calcium in nature SULPHATES, CARBONATES, PHOSPHATES, FLUORIDES, etc. Only in the form of salts CaCO3 chalk CaCO3 marble CaCO3 limestone CaCO3 * MgCO3 dolomite CaSO4 * 2H2O gypsum CaF2 fluorite Ca5 (PO4) 3F fluorapatite Ca5 (PO4) 3OH apatite Ca3 (PO4) 2 Phosphorite For the slide to work, you need to click the mouse to make the text appear.
8 slide
Description of the slide:
Deposits in Kazakhstan PHOSPHORITES (in the Karatau mountains, in the Aktobe region) PINK SHELL (on Mangyshlak) GYPSUM (in the Zhambyl region) CEMENT CLAYS (near Shymkent and Semey)
9 slide
Description of the slide:
OBTAINING CALCIUM obtaining Electrolysis of the salt melt СaCl2 → Сa2+ + 2Cl- СaCl2 → Сa + Cl2 1808 – English. chemist Humphrey Davy obtained the metal and named it “calcium” 1896 – an industrial method for producing calcium was developed in Germany 1904 – the first calcium production plant started operating Сa2+ Сa2+ Cl- Cl- Cl- Cl- showing the electrolysis process.
10 slide
Description of the slide:
11 slide
Description of the slide:
Chemical properties of calcium Chemical properties of Ca Interaction with simple substances Ca + H2 = CaH2 hydride Ca + 2C = CaC2 carbide 3Ca + N2 = Ca3N2 nitride 3Ca + 2P = Ca3P2 phosphide 2Ca + O2 = 2CaO oxide Ca + S = CaS sulfide Ca + Cl2 = CaCl2 chloride t° t° Interaction with complex substances Ca + 2H2O = Ca(OH)2 + H2 Ca + 2HCl = CaCl2 + H2 Ca + BeO = CaO + Be 2Ca + CO2 = 2CaO + C 2Ca + SiO2 = 2CaO + Si For for the slide to work, you need to click on the red rectangle.
12 slide
Description of the slide:
13 slide
Description of the slide:
Calcium compounds Calcium oxide Calcium hydroxide Calcium salts Hygroscopic content CaO + H 2O \u003d Ca (OH) 2 CaO + CO2 \u003d CaCO3 (for the release of gases from CO2, H2O) Obtaining: roasting limestone CaCO3 \u003d CaO + CO2 CaSO4 * 2H2O gypsum \u003d CaSO4 * 0.5H2O + 1.5H2O alabaster CaCO3 + H 2O + CO2 \u003d Ca (HCO3) 2 calcium bicarbonate CaCO3 - calcium carbonate limestone, marble, chalk CaO - basic oxide Ca (OH) 2 - alkali CaCO3, CaSO4 quicklime lime slaked lime lime water lime milk For the slide to work, you need to click the mouse to display the text.
14 slide
Description of the slide:
PROPERTIES of CALCIUM compounds Chemical properties of calcium oxide and hydroxide CaO - basic oxide + water CaO + H2O = Ca(OH)2 2) + acid oxide 3CaO + P2O5 = Ca3(PO4)2 3) + acid CaO + H2SO4 = CaSO4 + H2O Hydroxide calcium Ca (OH) 2 - a strong base 1) + acid oxide Ca (OH) 2 + CO2 \u003d CaCO3 + H2O 2) + acid Ca (OH) 2 + 2HCl \u003d CaCl2 + 2H2O 3) + salt Ca (OH) 2+ СuCl2 = CaCl2 + Cu(OH)2 For the slide to work, you need to click on the red rectangle with the mouse.
15 slide
Description of the slide:
The biological role of calcium It is necessary to click with the mouse - first the role of calcium appears (in blue boxes), then signs of its deficiency (in blue boxes).
16 slide
Description of the slide:
The biological role of calcium For muscle contraction, including the heart muscle For normal blood clotting The main component of the bones of the skeleton and teeth Participates in the regulation of more than 300 Ca2+ enzymes Daily requirement - 1 g Excess calcium: excitability, dehydration, urolithiasis Calcium deficiency: pain in joints, muscle cramps Lack of calcium: in children - rickets, in adults - osteoporosis To work the slide, you need to click the mouse - blue rectangles open (the role of calcium), then blue rectangles (signs of lack and excess of calcium).
17 slide
Description of the slide:
application Calcium compounds answer answer answer answer Lime water CaO Quicklime Ca(OH)2 Hydrated lime CaCO3*MgCO3 Dolomite CaCO3 Limestone CaSO4*2H2O Gypsum Home Gypsum is used in medicine, in construction work, for the manufacture of stucco, figurines. Limestone and marble are used in construction and art. Lime water - for detecting CO2, milk of lime - for whitewashing, a mixture of slaked lime with sand and water - a binder for brickwork and plaster. What mass (kg) of limestone with a content of 5% impurities must be taken to obtain 112 kg of quicklime? 210.526 kg The body of an adult contains 2% calcium, 99% of which is in the bones and teeth. Calculate how many grams of calcium are in the bones and teeth of a person weighing 75 kg. 1.485 kg A person at rest emits 0.19 lCO2(N.C.) per minute. How much calcium hydroxide is needed to completely absorb CO2 exhaled during 8 hours of sleep? 301.3 g Do you know the formulas? Ca(OH)2 For the slide to work, you need to click on the blue rectangles. In 1-3 cells of the table - tasks. In the 4th cell - a test of knowledge of the formulas of substances. The slide is convenient for organizing the work of students in groups, pairs when consolidating and testing knowledge.
18 slide
Description of the slide:
A solution of Ca (OH) 2 stains phenolphthalein in a crimson color. Calcium belongs to the alkaline earth metals. Calcium belongs to the s-elements. A calcium atom has 2 electrons in its outer level. A calcium atom has 2 electrons in its outer level. In PSCE, calcium is located in period 4, group IVB. Calcium belongs to the s-elements. Calcium belongs to the alkaline earth metals. Calcium oxide does not interact with water. Calcium hydroxide is highly soluble in water. A solution of Ca (OH) 2 stains phenolphthalein in a crimson color. Calcium salts color the flame purple. REMOVE THE FURTHER 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 4 A slide is used to consolidate knowledge on a topic. It is necessary to click on the "extra", i.e. incorrect statement.
19 slide
Description of the slide:
Questions: Ca does not occur in nature in the form of a Method for producing Ca in industry Ca is stored under a layer of kerosene, since CaO reacts with all substances of the group He is CaCO3 CaF2 Ca(OH)2 CaCO3 CaSO4 electrolysis of molten salts by CO reduction by H2 reduction by Al reduction strongly smells explodes spreads oxidizes Na, H2O, Cl2 CO2, H2S, H2O CO2, H2, CO KOH, O2, S chalk marble gypsum limestone Answers: When completing this task, you must select the correct answer and click on it with the left mouse button.
MUNICIPAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION OF THE BELOYARSKY DISTRICT "SECONDARY EDUCATIONAL SCHOOL OF THE P. LYKHMA" Theme of the project: "Calcium - a biogenic element" CC aa Author of the project: Kalugina Veronika Arsenovna Class 8B project leader: Byzova Natalia Valentinovna 20152016 academic year

MUNICIPAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION OF THE BELOYARSKY DISTRICT "SECONDARY EDUCATIONAL SCHOOL OF THE P. LYKHMA" Object of study: food products vegetable and animal origin for the presence of calcium. Relevance: due to the increase in diseases of the skeletal system, in order to prevent the occurrence of the above diseases, you should know foods rich in calcium and eat them in the required daily rate. Theme of the project: "Calcium - a biogenic element"

MUNICIPAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION OF THE BELOYARSKY DISTRICT "SECONDARY EDUCATIONAL SCHOOL OF THE P. LYKHMA" Direction of study of materials on the topic Direction of study of materials on the topic "Calcium - a biogenic element" 1. Calcium and its role in the human body 2. Calcium - a chemical element 3. Calcium - a regulator of physiological processes in the human body 4. Bioavailability of Calcium 5. Causes and signs of deficiency and excess of calcium in the human body 6. Products that adversely affect the absorption of calcium 7. Products containing calcium Theme of the project: "Calcium is a biogenic element"

MUNICIPAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION OF THE BELOYARSKY DISTRICT "SECONDARY EDUCATIONAL SCHOOL OF LYKHMA village" Calcium and its role in the human body Calcium and its role in the human body Biological role Ca is the most important biogenic element. It is part of every living organism. The biological role of Ca is known: its phosphates are part of the bone tissue of all vertebrate organisms, giving it strength and hardness. Ca in the human body is mainly found in bones, teeth and blood (provides its clotting). Theme of the project: "Calcium - a biogenic element"

MUNICIPAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION OF THE BELOOYARSK DISTRICT "SECONDARY EDUCATIONAL SCHOOL OF THE P. LYKHMA" Calcium - a chemical element Calcium - the chemical element Ca is necessary for the formation of a number of cellular structures, maintaining normal permeability of outer cell membranes, for fertilization of eggs of fish and other animals, activation of a number of enzymes. Ca2+ ions transmit excitation to the muscle fiber, causing its contraction, increase the strength of heart contractions, increase the phagocytic function of leukocytes, activate the system of protective blood proteins, and participate in its coagulation. In cells, almost all Ca is in the form of compounds with proteins, nucleic acids, phospholipids, in complexes with inorganic phosphates and organic acids. Theme of the project: "Calcium - a biogenic element"

MUNICIPAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION OF THE BELOYARSK DISTRICT "SEVERAGE EDUCATIONAL SCHOOL, LYKHMA" , breakdown of glycogen, maintaining proper acid-base balance inside the body and normal permeability of the walls of blood vessels. In addition, a long-term lack of calcium in food undesirably affects the excitability of the heart muscle and the rhythm of heart contractions. reserve polysaccharide Theme of the project: "Calcium - a biogenic element"

MUNICIPAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION OF THE BELOYARSK DISTRICT "SECONDARY EDUCATIONAL SCHOOL OF LYKHMA village" Calcium bioavailability Calcium bioavailability There is a question of calcium bioavailability, that is, the ability of our body to assimilate this element. Therefore, calcium-rich foods must be combined with foods that contain a significant amount of vitamin D (this vitamin is present in butter, dairy products, egg yolk, fatty fish) and ascorbic acid (the main source of its intake is vegetables). In addition, calcium has been absorbed by bone tissue, enough magnesium should be supplied to the body (it is abundant in bran, wholemeal bread and nuts) and phosphorus salts (found in fish). Theme of the project: "Calcium - a biogenic element"

MUNICIPAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION OF THE BELOOYARSK DISTRICT "SECONDARY EDUCATIONAL SCHOOL OF THE P. LYKHMA" Causes and signs of deficiency and excess Causes and signs of deficiency and excess of calcium in the human body Calcium in the human body Despite the fact that calcium reserves in the body are replenished every day, its daily loss in sweat, urine and feces. If calcium is not supplied with food in sufficient quantities, the body begins to take it from hard tissues, which is safe at the initial stage. If its deficiency persists for a long time, it can lead to serious problems. Lack of calcium in the body will lead to the following symptoms: increased nervous excitability, irritability, insomnia; high blood pressure; rapid heartbeat; numbness and tingling in the arms and legs, nervous tics and deterioration in pain tolerance, sore gums, joint pain, cramps; fragility of nails; tooth decay; cessation of growth. Theme of the project: "Calcium - a biogenic element"

MUNICIPAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION OF THE BELOOYARSK DISTRICT "SECONDARY EDUCATIONAL SCHOOL OF THE P. LYKHMA" Products that negatively affect the absorption of calcium The same happens when eating a large amount of food containing protein: meat, fish, poultry, peas, beans. But this does not mean that protein foods should be excluded from the diet. In small amounts, protein increases the absorption of calcium. Also, excess and lack of fat can slow down the absorption of calcium. Coarse-fiber food containing fiber is necessary for the body. But with its excess, calcium absorption in the intestine decreases. Excessive consumption of coffee, cocoa, Coca-Cola, sweet carbonated and alcoholic drinks, as well as smoking negatively affects the absorption of calcium. A similar result is observed with the consumption of sweets and other sweets. Theme of the project: "Calcium - a biogenic element"

MUNICIPAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION OF THE BELOYARSK DISTRICT "SEVERAGE EDUCATIONAL SCHOOL OF LYKHMA" natural products nutrition. Many people think that calcium is found exclusively in animal products, but this is not so. Moreover, among plant products there are those that are confidently leading in terms of the content of this mineral. For example, 100 g of poppy contains almost 1.5 g of calcium, 100 g of sesame - 800 mg, 100 g of almonds - 250 mg, and 100 ml of milk contains no more than 120 mg. Eggshell contains 90% of easily digestible calcium and is another rich source of this mineral Project theme: “Calcium is a nutrient”

MUNICIPAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION OF THE BELOYARSK DISTRICT "SECONDARY EDUCATIONAL SCHOOL OF LYKHMA village" List of used literature 1. Bardinova Zh. S., Smetanin V. A. Laboratory work on selected chapters of biochemistry. ., Journal of Analytical Chemistry, No. 17 (1962), p.560 3. Lakin G. F. Biometrics, M., Higher School, 2009. 4. Frumina N. S., Kruchkova E. S., Mushtakova S. . P. " Analytical chemistry calcium." M., Nauka, 1974, p.102103. 5. Encyclopedic dictionary of a young biologist, Moscow: Pedagogy, 1990. 6. http://slovari.yandex.ru 7. http://wikipedia.com 8. http://slovari.yandex.ru Topic project: "Calcium - a biogenic element"

MUNICIPAL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION OF THE BELOYARSKY DISTRICT "SEVERAGE EDUCATIONAL SCHOOL OF THE P. LYKHMA" CC aa biogenic nutrient element Thank you for your attention Thank you for your attention
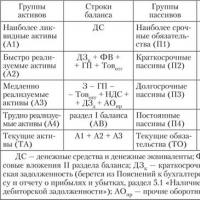 The essence and significance of the liquidity and solvency of the enterprise
The essence and significance of the liquidity and solvency of the enterprise Thesis work Improving the sales management system at Fap LLC The sales department does not have a sales process scenario
Thesis work Improving the sales management system at Fap LLC The sales department does not have a sales process scenario Object and subject of personnel management
Object and subject of personnel management How glass is blown
How glass is blown How to plan enterprise sales: methods and analysis
How to plan enterprise sales: methods and analysis How does a veterinary clinic work - home veterinary care How to open your own veterinary clinic
How does a veterinary clinic work - home veterinary care How to open your own veterinary clinic Selling candy as a business
Selling candy as a business