Job description for a carpenter at a technical school. Job description for a carpenter in a hospital. Professional and personal qualities
Although a carpenter-joiner is a universal specialist, the basis of his work is woodworking. What's included job responsibilities joiner-carpenter and how difficult is this work? Let's find out!
In general, the good thing about the profession of a carpenter is that you can not only masterfully perform woodwork, but there are also many related professions that a carpenter can master - concrete worker, mechanic, roofer, parquet floorer and many others. But the most logical continuation of the carpentry profession is the profession of a joiner.
What are the responsibilities of a carpenter?
The work responsibilities of a carpenter-joiner include a wide range of work with wood, both rough and fine. Often, not even everyone will be able to distinguish where the carpenter’s work ends and the carpenter’s work begins, both of whom make various products, parts and structures from wood.
A joiner-carpenter knows the types of timber that exist and are used in work, the basic properties of wood, he knows methods of manual rough processing of materials, methods of work and the design of electrified tools.
Job description of a carpenter-joiner
According to the instructions, the job responsibilities of a carpenter-joiner include rough trimming, cross-sawing, and planing of timber. A carpenter knows how to handle hand tools, knows how to sharpen them correctly, how to care for them, and knows how to repair them.
A carpenter-joiner is able to do complex carpentry work, including general construction and formwork. The master knows and puts into practice all methods of processing wood with various tools.
Wood processing in any form is the responsibility of a carpenter. He makes all the necessary parts, assembles them and installs them. A carpenter can make office, cabinet, upholstered and other types of furniture, windows, trim, doors, railings, cladding, interior items made of wood and much more. Even, for example, cross-country skiing. He can install door locks and other fittings, and line walls, floors, and ceilings with wood panels.
But this is not a complete list of job responsibilities of a carpenter-joiner. The work of this specialist is multifaceted, just like the work of a carpenter.
A carpenter, like a carpenter, is a very popular profession. It is difficult to list all the types of industries where timber workers can find high-paying jobs.
They are needed in woodworking, furniture factories, in restoration, in factories for the production of wood products and parts, in construction, mechanical engineering, in schools, housing departments, repair organizations.
Carpenters/joiners can work independently, be freelance artists, make unique things from wood, build original houses according to special projects. The scope of application of the skills is very wide.
Requirements for carpenters
The following requirements are required for a woodworker: qualification requirements when applying for a job in an organization. Firstly, it is desirable to have a secondary specialized vocational education.
Although this requirement is not mandatory always and everywhere, it is still a good idea to have it. Also, in some cases, they may hire you without work experience, or offer training, but rich and varied experience will be your ticket to a good job.
In addition to the fact that a joiner-carpenter must be excellent with working tools and perform high-quality carpentry work, he must understand drawings, understand the types of wood and be able to determine its quality.
The responsibilities of a carpenter also include some skills in working with woodworking equipment, and such personal qualities, like, accurate eye, spatial thinking, endurance, accuracy, attentiveness, accuracy. Also, a carpenter must have the necessary physical strength sufficient to work with heavy timber.
Anyone who can perfectly perform the duties of a carpenter has a good chance of making some kind of career in the profession and even becoming famous. This is the case if he does not stop at simple things mastered during training, but tries to learn something new, come up with a method, and make something unique and beautiful.
There are famous master joiners and carpenters in our country. There are many designer workshops in Moscow that offer their products, and, among other things, you can come to work in them and evaluate your skills.
Even though at first glance, the job responsibilities of a carpenter may look boring, such work is akin to the work of an artist and, in general, it is creative and artistic. Elite furniture made of valuable wood, original stairs, windows, doors, Wall panels, elegant log houses, gazebos, baths - the list of what a carpenter can do with high quality is very wide.
A woodworker's income depends on where he works. The salary of a well-known freelancer can reach very high figures; the salary of a carpenter at a construction site starts from 50,000 rubles.
1. Is the performer of work on technical operation and current repair of wooden structures and is directly subordinate to the foreman (technician or foreman).
2. In its activities, it is guided by these instructions, the rules of operation of the housing stock, technical regulations established for the production and acceptance of general construction repair work, safety regulations and fire safety, as well as orders and instructions from superiors and immediate superiors, transmitted through the foreman (technician or foreman).
3. A carpenter-joiner performs the following duties:
Produces regular deliveries in accordance with schedule technical inspections wooden roof structures, walls, window and wooden fillings, floors, ceilings and other building elements - twice a year (spring and autumn);
Performs extraordinary inspections of wooden structures of walls and roofs, windows and doors filled after heavy rains and snowfalls, as well as ceilings and floors after leaks;
Strengthens and partially repairs rafters with installation and fastening of struts and supports, repairs dormers, overhangs, valleys, etc.;
Perform work on partial replacement of wooden (board and shingle) roofs;
Conducts minor and medium repairs of window and door fillings, including all parts (window sashes, door panels, vents, transoms, window and door frames);
Changes door panels, individual window sashes (up to 5% of the total);
Places temporary wooden supports, fastening structures of floor beams, balconies, walls, rafters, etc.);
Opens up clean floors and changes the backfill in certain areas of the floor, adds backfill in the attic floors;
Repairs wooden structures of partitions, stairs, canopies, walls with partial replacement of the lower frames of the crowns, racks;
Replaces wooden chairs of columnar foundations with digging holes, backfilling and compacting soil.
Agreed: Chairman of the trade union committee, lawyer.
1.1 This job description defines functional responsibilities, rights and responsibilities of a carpenter.
1.2 A carpenter belongs to the category of technical performers.
1.3 A carpenter is appointed to a position and dismissed from a position as established by the current labor legislation order by order of the director of the enterprise on the recommendation of the head of the woodworking shop.
1.4 Relationships by position:
|
1.4.1 |
Direct subordination |
Head of the woodworking shop |
|
1.4.2. |
Additional Subordination |
To the director of the enterprise |
|
1.4.3 |
Gives orders |
|
|
1.4.4 |
The employee is replaced |
Person appointed to in the prescribed manner |
|
1.4.5 |
The employee replaces |
- Qualification requirements for a carpenter:
|
2.1 |
education |
Primary vocational education |
|
2.2 |
experience |
no work experience requirements |
|
2.3 |
knowledge |
types and designs of manufactured joinery; rules for reading drawings; basic physical mechanical properties wood and its defects; rules for sharpening and setting up carpentry tools; installation of mechanical wires and wires with HDTV heating; requirements for the quality of products and materials; technical specifications for processing parts; working techniques for planing, cleaning parts and applying glue; types, properties of glue and methods of its preparation; types of carpentry joints; assembly and facing works; requirements for the quality of work; requirements for the use of protective equipment; methods and techniques for performing work safely; the procedure for notifying the manager of all deficiencies discovered during work; rules for providing first (pre-medical) aid to victims of injury, poisoning and sudden illness; internal rules labor regulations; rules of labor protection, industrial sanitation and personal hygiene, fire safety; |
|
2.4 |
skills |
work in specialty |
|
2.5 |
Additional requirements |
--- |
- Documents regulating the activities of a carpenter
3.1 External documents:
Legislative and regulations related to the work being performed.
3.2 Internal documents:
Charter of the enterprise, Orders and instructions of the director of the enterprise (head of the woodworking shop); Regulations on the woodworking workshop, Job description carpenter, Internal labor regulations.
- Job responsibilities of a carpenter
4.1. Carpenter before starting the working day:
Undergoes periodic medical examinations in accordance with the established procedure;
Receives instructions on labor protection and safety in accordance with the established procedure;
Accepts workplace;
Prepares workplace and facilities personal protection;
Checks the serviceability of equipment, tools and devices;
4.2. During the work process, the carpenter:
Complies with personal hygiene and industrial sanitation requirements;
Uses personal protective equipment;
Complies with the rules of use technological equipment, devices and tools, methods and techniques for performing work safely;
Immediately notifies his immediate supervisor of any deficiencies discovered during work;
Provides first (pre-medical) aid to victims of injury, poisoning emergency situations and sudden illness;
4.3. During the working day, the carpenter:
Performs the full range of work on the production of carpentry structures according to drawings and sketches;
Carry out planing, cleaning and grinding of product blanks;
Performs all types of work on basic woodworking machines;
Prepares and installs parts on unfinished units and products using glue and screws;
Cleans glue drips from solid wood parts;
Prepares the surfaces of parts of various products for cladding;
Produces stickers on upholstery materials;
Cleans and polishes coated parts and assemblies;
Carries out fitting and fastening of parts with glue and screws to assemblies and finished products;
Installs fastening fittings in assemblies and parts;
Repairs parts and assemblies or surfaces of products, repairs and restoration of assembled products;
Performs related duties;
4.4. Carpenter at the end of the working day:
Cleans woodworking machines;
Cleans the workplace;
Removes waste to designated place;
Rents out a workplace;
- Carpenter's rights
The carpenter has the right:
5.1. Submit proposals for improvement of work related to those provided for by this instructions and duties.
5.2. Within your competence, inform your immediate supervisor about all shortcomings identified in the course of your activities and make proposals for their elimination.
5.3. Demand that the management of the enterprise provide assistance in the performance of its official duties and rights.
- Carpenter's responsibility
The carpenter is responsible:
6.1. For improper performance or failure to fulfill one’s official duties as provided for in this job description - within the limits determined by the current labor legislation of Ukraine.
6.2. For offenses committed in the course of carrying out their activities - within the limits determined by the current administrative, criminal and civil legislation of Ukraine.
6.3. For causing material damage- within the limits determined by the current labor and civil legislation of Ukraine.
- Working conditions for a carpenter
7.1. The work schedule of a carpenter is determined in accordance with the internal labor regulations established at the enterprise.
- Terms of payment
The terms of remuneration for a carpenter are determined in accordance with the Regulations on remuneration of personnel.
9 Final provisions
9.1 This Job Description is drawn up in two copies, one of which is kept by the Company, the other by the employee.
9.2 Tasks, Responsibilities, Rights and Responsibilities can be clarified in accordance with changes in the Structure, Tasks and Functions of the structural unit and workplace.
9.3 Changes and additions to this Job Description are made by order general director enterprises.
|
Head of structural unit |
|||
|
(signature) |
(surname, initials) |
||
AGREED: |
|||
|
Head of the legal department |
|||
|
(signature) |
(surname, initials) |
||
|
00.00.0000 |
|||
|
I have read the instructions: |
|||
|
(signature) |
|||
We bring to your attention typical example job description for a 4th grade carpenter, sample 2019/2020. A person with education and work experience can be appointed to this position. Don’t forget, each instruction for a 4th grade carpenter is handed out against a signature.
Typical information about the knowledge that a 4th category carpenter should have is presented. About duties, rights and responsibilities.
This material is part of the huge library of our website, which is updated daily.
1. General Provisions
1. A carpenter of the 4th category belongs to the category of workers.
2. A carpenter of the 4th category is accepted to be a person who has: ________ (requirements for education, experience)
3. A carpenter of the 4th category is hired and dismissed by _______ organization on the recommendation of _______. (director, manager) (position)
4. A carpenter of the 4th category must know:
a) special (professional) knowledge:
— the main elements of wooden parts of buildings and wooden structures and the requirements for their quality;
— methods of constructing wall frames, sheathing and temporary structures;
— methods of preparing sheet piles;
— methods of connecting parts using simple cuts;
— dry antiseptic methods; methods of impregnation of wooden structures and parts with antiseptic and fire retardant compounds in bathtubs;
— methods of marking and covering roofs;
— requirements for the quality of piece roofing materials and coatings;
— design of mounting piston guns and rules of their operation.
— instructions for use, operation, storage of devices, tools, measuring instruments and others technical means used in their work.
— sketches and drawings directly used in the process of work.
— requirements for the quality of work in related construction processes;
— professional requirements requirements for a worker in a given profession of a lower category;
b) general knowledge of an employee of the organization:
— rules on labor protection, industrial sanitation and fire safety;
— rules for using personal protective equipment;
— requirements for the quality of work (services) performed and for the rational organization of labor in the workplace;
— range and labeling of materials used, consumption rates of fuels and lubricants;
— rules for moving and storing goods;
— types of defects and ways to prevent and eliminate them;
— production alarm.
5. In his activities, a 4th category Carpenter is guided by:
— legislation of the Russian Federation,
— Charter (regulations) of the organization,
- orders and instructions of the ________ organization (general director, director, manager)
- this job description,
— Internal labor regulations of the organization.
6. A 4th grade carpenter reports directly to _________ (a worker with a higher qualification, the head of production (site, workshop) and the director of the organization)
7. During the absence of a Carpenter of the 4th category (business trip, vacation, illness, etc.), his duties are performed by a person appointed _______ organization (manager position) upon the recommendation of _________ (position) in the prescribed manner, who acquires the corresponding rights, responsibilities and bears responsibility for the performance of his assigned duties.
2. Job responsibilities of a 4th grade carpenter
The responsibilities of a 4th category Carpenter are:
a) Special (professional) responsibilities:
— Carpentry and formwork work.
— Covering roofs with piece roofing materials.
- Civil works:
Installation of wooden partitions. Assembly and installation of wooden parts, elements and structures of residential and industrial buildings. Preparation, assembly, installation, disassembly and replacement of mauerlats and rafters. Chopping interior walls from logs. Construction of temporary structures: terraces, verandas, vestibules, porches, as well as sheds, sheds, guard booths, offices, passages, storage rooms, showers, latrines. Installation and replacement of wooden bases and chairs. Construction of frame walls. Clean walls and ceilings. Arrangement, relaying and joining of upper plank coverings (clean floors) from individual boards. Installation of floors from bars, glued panels, fibreboards, end blocks, from chipboards with sealing of joints. Fastening joinery to reinforced concrete parts using mounting piston guns. Installation of window and door frames, blocks and window sill boards, plastic and roof windows. Installation of laminated doors with a telescopic frame. Installation of plasterboard partitions. Installation of clean fences. Dry antiseptic. Antiseptic and fire-retardant impregnation of wooden structures and parts in bathtubs. Installation of bandages on poles and chairs. Manufacturing, laying, disassembling and changing joists, beams and purlins. Replacement of interfloor and attic floors. Construction of scaffolding, scaffolding and overpasses without building up racks. Installation of block scaffolding. Repair of frame walls, floors and plank roofing. Arrangement of angled connections using notches, plate dowels and keyed connections. Construction of wooden ice cutters and slipways. Construction of sleeper cages for heavy structures and equipment. Alignment and wedging of rolling tracks when sliding bridge spans. Manufacturing and staging of contractions on piles or racks, liners and ties, struts, braces and ice cutter rafters. Manufacturing of crossbars and installation of key beams on piles. Installing the ice cutter blade. Laying thrust beams and securing them with attachments. Manufacturing and laying of mauerlat beams on supports, crossbars and security and wheel guard beams. Preparation of wooden sheet piles and packages. Manufacturing and installation of headstocks (cuts). Laying nozzles on lighthouse piles and sheet piles. Preparation and assembly of A-shaped, three-post and U-shaped wooden supports for communication and power lines. Covering and repair of three- and four-slope hipped, attic, hip, T- and L-shaped roofs with asbestos-cement sheets and tiles (slate). Lining of overhangs, abutments, ridges, ribs and dormer windows. Construction of wooden frames for suspended ceilings of all types and wall cladding. Installation of suspended ceilings on wooden frames made of acmigran tiles, aluminum slabs, AGT slabs, etc. Covering walls and ceilings with wood fiber and particle boards (except for decorative ones). Installation of small molds manufactured in the factory.
— Formwork work:
Construction of scaffolding supporting the formwork. Installation of formwork for columns, beams, floor slabs, walls and partitions, foundations, massifs, frame posts and purlins. Manufacturing and installation of jacking frames, caps, panels for sliding formwork and working flooring. Production and repair of formwork panels for arrays of offshore hydraulic structures with longitudinal and transverse hatches and large-panel formwork panels with ribs. Installation of flooring in flexible joints from boards and beams. Dismantling the formwork of arches, domes, vaults, shells, reservoirs, tanks, bunkers, spiral chambers, suction and supply pipes, as well as scaffolding supporting the formwork. Installation of suspended formwork for floors.
— Carrying out the work of lower-skilled workers in a given profession.
— Management of workers of lower ranks of the same profession.
b) General Responsibilities employee of the organization:
— Compliance with the internal labor regulations and other local regulations of the organization, internal rules and regulations of labor protection, safety precautions, industrial sanitation and fire protection.
— Execution within employment contract orders of the employees to whom it was repaired in accordance with these instructions.
— Carrying out work on acceptance and delivery of shifts, cleaning and washing, disinfection of serviced equipment and communications, cleaning of the workplace, devices, tools, as well as maintaining them in proper condition.
— Maintaining established technical documentation.
3. Rights of a carpenter of the 4th category
A carpenter of the 4th category has the right:
1. Submit proposals for management’s consideration:
— to improve work related to the responsibilities provided for in this instruction,
— on bringing to material and disciplinary liability workers who violated production and labor discipline.
2. Request from structural divisions and employees of the organization information necessary for him to perform his job duties.
3. Get acquainted with the documents defining his rights and responsibilities for his position, criteria for assessing the quality of performance of official duties.
4. Get acquainted with the draft decisions of the organization’s management relating to its activities.
5. Require the management of the organization to provide assistance, including ensuring organizational and technical conditions and execution of the established documents necessary for the performance of official duties.
6. Other rights established by current labor legislation.
4. Responsibility of a 4th grade carpenter
A carpenter of the 4th category is responsible in the following cases:
1. For improper performance or failure to fulfill one’s job duties provided for in this job description - within the limits established by the labor legislation of the Russian Federation.
2. For offenses committed in the course of their activities - within the limits established by the current administrative, criminal and civil legislation of the Russian Federation.
3. For causing material damage to the organization - within the limits established by the current labor and civil legislation of the Russian Federation.
Job description for a 4th grade carpenter - sample 2019/2020. Job responsibilities of a 4th grade carpenter, rights of a 4th grade carpenter, responsibilities of a 4th grade carpenter.
The carpenter is one of the most famous construction specialties. The profession of a carpenter is associated with machining wood and subsequent production of components, structures and parts. A carpenter takes part in the construction of houses, bridges, installs window frames, ceilings, doors, builds scaffolding, and lays floors.
The profession is related to working at heights and indoors. Can be team or individual. In the process of work, a carpenter uses the following tools: an axe, a tape measure, chisels, a plumb line, a miter box, a drill, a screwdriver, a hammer, various saws, hacksaws, a jigsaw, an adze, woodworking machines, and hand-held electrical measuring instruments.
General provisions and responsibilities
- A carpenter is hired by order of the head of an enterprise or organization.
- The carpenter reports to the workshop foreman or site manager.
- A person without professional education or with vocational education, or with work experience depending on the required qualifications.
The carpenter must know:

Depends on the complexity of the work specialist rank. They come from 2 to 6
Description of categories
Worker 2 digits must know:
- Methods for dismantling and cleaning simple structures.
- Types of timber.
- Methods primary processing wood.
- Rules for transportation and storage of goods.
- Types of coating materials.
Be able to:
- Perform simple formwork and other work.
- Help with roofing work.
- Sort coating materials.

A carpenter 3 digits must know:
- The device of a power tool.
- Methods for finishing wood materials, preparing piles and supports.
- The main differences between wood, its disadvantages and advantages.
- Methods for constructing plank sheathing, decking and roof parts.
- Properties of coating materials.
- Methods for marking and covering simple roofs.
Be able to:
- The roof covering has a simple shape.
- Install boardwalks and baseboards.
- Trim logs and board edges.
- Cover the walls with boards.
- Prepare single piles and supports.
- Finish surfaces.
- Cover pitched roofs.
- Harvest simple forests.
- Disassemble formwork, ceilings, columns, beams.
A carpenter 4 digits must know:
- Basic wooden building structures.
- Construction of wooden wall frames.
- Dry antiseptic methods.
- Methods for impregnating wooden structures with antiseptics and fire retardants.
- Rationalization of labor.
- Methods for covering roofs and marking them are of medium complexity.
- TU works.
- Rules for moving goods.
Be able to:
- Perform formwork and carpentry work of medium complexity.
- Prepare the necessary tools, use measuring instruments and fixtures, read working sketches and drawings, and perform utility work.

A carpenter 5 ranks must know:
- Methods for manufacturing and marking complex wooden blocks and joints.
- Composition of rigging devices.
- Specifications for work, operating rules production equipment, and instrument.
- Specifications for acceptance and production of work, assortment and labeling of materials, parts, semi-finished products.
- Rules for moving goods.
- Safety regulations.
Be able to:
- Perform complex formwork and professional work.
A carpenter 6 digits must know:
- Especially complex engineering buildings.
- All possible formwork designs.
- Methods for making the necessary inventory templates.
- Organization of labor in its place, and in the case of a brigade form - organization of labor of the brigade.
- Technological process.
- MPRTS management rules.
- Features of the state's economy, the results of production plans of a construction team, site, organization.
- Ways to improve production efficiency - increasing labor productivity, quality construction products, energy savings and material resources, labor intensity of products and cost reduction, application of cost accounting.
- Specifications for work execution, marking and assortment.
- Rules for storing and moving goods.
- Safety standards.
Be able to:
- Perform particularly complex formwork and roofing work.
Differences in requirements for duties performed in enterprises and organizations
Special knowledge in construction:
- Methods for connecting and installing the most complex wooden floors.
- Basic design methods and design different types formwork.
- Possibility of producing templates for large engineering types of building structures.
- Technical instructions for operation, storage, use of tools, devices, measuring instruments.
- Sketches and drawings that are used in the work process.
- Necessary requirements to achieve maximum quality of work.
- Professional requirements for a given profession for a low-level worker.
Carpenter in housing and communal services sector need to know:
- Requirements for the quality of roofing materials.
- Methods for marking and roofing roofs of varying complexity.
- The front parts of the roofs are made of sheet steel.
- Basic physical and mechanical properties of wood.
- Tolerances and allowances for processing.
- Simple sketches and drawings.
- Design, purpose of tools, mechanisms, devices and equipment when using them.
- Assembly of all structural parts.

Duties of a carpenter in the hospital includes:
- Rough trimming, transverse and longitudinal sawing of lumber.
- Manufacturing and renovation work construction equipment.
- Carpentry and general construction work.
- Processing wood manually and using power tools.
- Simple carpentry work.
- Making and using simple carpentry products.
- Production and packaging of mail, goods and luggage boxes, pallets, lathing.
- Execution of collective works.
A carpenter At school deals with:
- Maintaining buildings on the school grounds in good condition.
- Maintaining water supply, heat supply, central heating systems, drains, and other similar equipment in working order.
- Carrying out repair work.
- Not complicated repairs in classrooms.
- Seasonal preparation of maintained structures, buildings, equipment.
- Elimination of damage and malfunctions at the request of the school director.
- Carrying out routine repairs including soldering and plumbing work.
The work of a carpenter is associated with an increased risk of injury. Depending on the business, this may be either outdoor or indoor. Working at heights, fire hazards, the use of varnishes, compositions and mixtures for impregnating wood, and allergenicity require particularly close monitoring of the safety of the labor process.
Safety
 Training of workers in safe labor methods is carried out in all organizations and enterprises, regardless of the degree and nature of the production hazard. The organization of training for the enterprise is entrusted to a special commission created by order of the head of the enterprise.
Training of workers in safe labor methods is carried out in all organizations and enterprises, regardless of the degree and nature of the production hazard. The organization of training for the enterprise is entrusted to a special commission created by order of the head of the enterprise.
Control over the timeliness of training and its quality is carried out by the labor protection department. Registration of training for each new arrival at the enterprise is carried out in special magazine.
Workers who have undergone special training and instruction, as well as safety training and medical examination are allowed to work.
Exist medical contraindications nominated for the profession of carpenter:
- neuropsychiatric disorders;
- allergy;
- musculoskeletal disorder;
- hypertension, other cardiovascular diseases;
- eye diseases.
Rights and responsibilities
The carpenter has the right:
- For all social rights and guarantees provided by law.
- Act to prevent and correct any problems or irregularities
- Require compliance with industrial labor protection.
- Perform your official duties and require assistance in this.
- enjoy project documentation, to perform work duties.
- Increase your qualification level.
- Make proposals to eliminate violations.
- Get acquainted with administrative documents, by orders of the workshop management.
- Make proposals to management for improving work related to the performance of job duties.
- Inform the workshop foreman about shortcomings identified by him during the work process.
He is responsible for:
- Low labor and production discipline.
- Failure to fulfill official duties.
- Violation of safety regulations.
- Failure to comply with management orders within the law.
- Material damage.
- Illegal use of official powers for personal gain.
- Violation of labor discipline.
- Delay in medical examinations.
You can see how a carpenter makes a table in this manual.
 Business Analyst - IT1410: Software Requirements Development - Business Informatics
Business Analyst - IT1410: Software Requirements Development - Business Informatics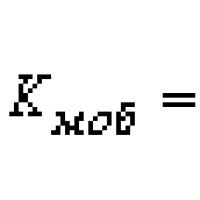 Assessment of the efficiency of use of fixed capital Analysis and assessment of the efficiency of use of fixed capital
Assessment of the efficiency of use of fixed capital Analysis and assessment of the efficiency of use of fixed capital The motive for learning activity refers to all the factors that determine the manifestation of learning activity: needs
The motive for learning activity refers to all the factors that determine the manifestation of learning activity: needs Job Description for Seller of Non-Food Products of Category I
Job Description for Seller of Non-Food Products of Category I The severity and intensity of labor: classification, indicators, factors. The criteria for the severity of labor under dynamic load are
The severity and intensity of labor: classification, indicators, factors. The criteria for the severity of labor under dynamic load are OKVED “tourism activities” - decoding New OKVED tourism activities
OKVED “tourism activities” - decoding New OKVED tourism activities What kind of profession is a laboratory assistant for chemical and bacteriological analysis?
What kind of profession is a laboratory assistant for chemical and bacteriological analysis?