sap products what. Description of SAP ERP system components. Description of SAP R3
Despite the fact that SAP has been present in Russia for 22 years and is difficult to find big business, in which the products of this manufacturer are not used in one way or another - this question is asked with enviable regularity and persistence. 🙂
Let's try to figure out what stands behind the abbreviation SAP.
A little history.
The story of SAP begins with five “fugitive” German IBM engineers.
More precisely, it all started with the fact that XEROX ordered IBM software for IBM mainframes. 🙂
But in 1972, the project team (Claus Wellenreuther, Hans-Werner Hector, Klaus Tschira, Dietmar Hopp and Hasso Plattner) were told that their work was no longer needed; and the project they were working on goes to another department.
After consulting, the entire team quit and founded the company in June 1972 "Systemanalyse und Programmentwicklung" (German)(“System analysis and program development”). Later the decoding changes to "Systeme, Anwendungen und Produkte in der Datenverarbeitung"(German) - “Systems, Applications and Products in Data Processing.”
The first client is the German division of Imperial Chemical Industries in the city of Ostringen, for which SAP developed an accounting and payroll system. Instead of storing data on punch cards, they decided to store it locally. SAP called its system a “real-time system” because it no longer had to wait overnight for punch cards to be processed.
In honor of “real time” (“Real-time”), the letter “R” was added to the name of the system, which remained until the end of the 90s (the system was called R/1, R/2, R/3).
Name confusion
For an uninitiated person, the abundance of SAP product names makes one feel a little dizzy.
Here you need to understand the following - there are several major areas of development:
- Technology platform
- Enterprise management systems or SAP Business Suite
- Data management
- New technologies
- Integration solutions
Since the corporation is huge, there are even competing solutions. An example is the presence of two reporting tools in SAP BI: SAP Business Explorer and SAP Business Objects. The first tool was originally developed by the company during work on SAP BI; the second was obtained as a result of the acquisition of a third-party company.
Technology platform.
Most SAP solutions are developed and executed on the same technology platform − SAP NetWeaver Application Server(SAP NW AS). In versions of SAP R/3 up to 4.6 inclusive, the technological part was called “basis”; later the basis became part of SAP NW AS.
I already mentioned that in the title " R/3"there is a mention of three-level architecture. Since 1992, the technology platform has been divided into three parts: database server(all system data is stored in it), application server(programs are executed on them; there may be several of them in the system) and the client part - SAP GUI(installed on the computers of system users).
Almost any combination can be used as a database and operating system for the SAP technology platform. Typically, this combination is chosen at the time of purchase of SAP software, based on existing licenses/cost of new ones, convenience, and cost of administration and support.
SAP NetWeaver Application Server includes:
- system core;
- administration and monitoring tools;
- development tools.
All business content is installed “on top” of the technology platform.
SAP ERP is an enterprise management system.
Main product of SAP for a long time was an enterprise management system. In its modern version, it was first released to the market on July 6, 1992 and was called SAP R/3, Where R- This "realtime"("real time"), A "3" is a three-tier architecture (client, application server, database). Over time, software versions have changed, and not all versions are released to the market. Main versions - 3.1, 4.0, 4.6B, 4.6C. In 2005, the name of the system was first changed to ECC 5.0 (Enterprise Core Component), then, in 2006 - to SAP ERP 6.0 (Enterprise Resource Planning, "enterprise resource planning").
The system itself is a “constructor” of interconnected modules, each of which is responsible for certain tasks of the enterprise. The names of the modules are abbreviations for the functionality: FI - finance (finance), LO - logistic (logistics), SD - sales and distribution (sales and distribution), HR - human resources (personnel), etc.
There is a standard picture depicting SAP R/3 as a construction set made from cubes - any official explanation of the architecture begins with it: 
Curious: the “human resources” module at some point changed its name to HCM (human capital management) - management human capital. Apparently, the company's marketing decided that calling people “capital” is more tolerant than “resource.”
All modules are based on "basis"— the technological core of the system, ensuring the operation of the entire system as a whole. The technical specialists responsible for the functioning of the basis of the system are usually called “ basic workers«.
It would seem that everything is clear and understandable: I bought and installed the system, launched it and started working. But no, that was not the case. If everything happened so simply, the market for SAP specialists (and, it must be said, the expensive market) simply would not exist. 🙂
The “trick” lies in the fact that the developers tried to provide for everything possible cases and application of the system. Because of this, SAP ERP is a set standard(and often from a German point of view) business processes and great amount settings, extensions, interfaces and other opportunities to change this process to suit your needs. Moreover, the system contains an internal programming language (ABAP) and development and debugging tools - that is, if desired, you can develop your own functionality within the system or significantly expand the existing one.
Often this opportunity is mistakenly perceived as permission to do whatever you want with the system. There are “specialists” on the market who have little understanding of standard SAP processes, but are excellent at writing “anything_for_your_money” in ABAP.
The consequences of such “work” are often difficult and expensive - difficulties with support, slow system operation, incomprehensible errors. The worst thing is if the system has not been fully tested and all problems are identified during productive operation. There is simple advice - where possible, use standard system capabilities.
In addition to the standard functionality, there are a large number of extensions for SAP ERP, also developed by SAP: industrial (SAP Industry Solution) (for example, for mechanical engineering, metallurgy, automotive industry), solutions for individual areas (for example, SAP Banking or SAP Retail solutions) and so on and so forth.
SAP Business Suite
SAP ERP is only one of a complete set of business products, the so-called SAP Business Suite. This set also includes:
- Customer Relationship Management(CRM) – a system for organizing work with clients;
- Product Lifecycle Management(PLM) – system for production;
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) – a product for working with resources, procurement, and supplies;
- Supplier Relationship Management(SRM) – organization of work with suppliers.
Data management.
SAP also develops various data management solutions. The main product is SAP Business Intelligence(in previous versions it was called SAP Business Warehouse), a solution for collecting, storing, processing data and generating reporting.
Deals with the basic data of the enterprise SAP Master Data Management(SAP MDM) is a long-suffering product. Initially developed in Germany, it was then frozen and a product from one of the acquired companies was released under the same brand. The main task of SAP MDM is the collection, storage and distribution of enterprise directories - all kinds of numbers, codes and other information that can be accessed by various services and systems of the enterprise. According to the latest information, SAP is preparing a surprise for its customers and is developing new version MDM practically from scratch - in order to get rid of the problems of previous versions and use new technologies.
SAP Identity Management— deals with the storage and distribution of basic user data.
New technologies.
IN last years SAP is actively investing in new technologies - clouds, mobile applications, in-memory computing.
HANA(High-Performance Analytic Appliance) is a high-performance database that runs entirely in RAM. SAP is actively adapting all its products to this technology.
SAP Mobility— platform for development, hosting, distribution and administration mobile applications. Appeared at SAP along with the acquisition of Sybase. Also briefcase mobile business applications was expanded by taking over the Syclo company.
The technology and infrastructure for providing cloud services was brought with it by the acquired company Ariba.
The most striking of the “cloud” solutions was purchased together with the SuccessFactors company - this is a solution for working with personnel.
Integration.
The SAP NW AS technology platform provides quite a lot of interface capabilities for interaction both between SAP products and with non-SAP systems.
There are also "connectors" for specific technologies - SAP .Net Connector, SAP Java Connector. These small independent products are used in cases where it is necessary to create an interface with the SAP system, but this cannot be done directly.
For more complex landscapes with multiple products, there is an integration platform SAP Process Integration- a product designed specifically for building, monitoring and administering all data exchange between all enterprise systems (both SAP and non-SAP).
It is also worth mentioning the system that allows you to centrally manage the entire “zoo” of SAP systems - this SAP Solution Manager.
Finally.
It is impossible to mention all SAP products in a short article - the portfolio is huge. There are also “small” products designed to solve specific problems within large systems, technical and technological products (for example, the TREX search engine or a monitor for Java - Wily Introscope). There is also a line of products for medium-sized (and, with some stretch, small) businesses.
Once colleagues told a story about SAP implementation R/3 for a company of.. 5 people. True, the company was engaged in purchase and resale, but in large volumes.
I declare with responsibility that it is impossible to know ALL SAP products. It is impossible in principle to know ALL SAP products in depth.
But this is why I recommend that when choosing a suitable product, you persistently ask whether there may be a “parallel” or complementary product that performs the functions you need and can make your life much easier.
That's all.
Thanks to everyone who was able to read this far. I hope it has become clearer to you what “SAP” is. 🙂
Sincerely,
Your Pitroff.
If we push SAP (and other major ERP system providers) to the end, we should note two features of the Russian market:
1. Until 2008 inclusive, the market for ERP systems for small and medium-sized businesses accounted for approximately 10% of the ERP market for enterpirse level. That is, it was more profitable for a system integrator to sell two large projects in a year than 20 medium or small ones.
2. Thanks to point 1, custom software development, a sort of “mini-ERP”, was done to automate small and medium-sized businesses. The most successful “mini-ERP” solutions were brought to the box and replicated. This is how universal ERP 1C: Enterprise, Compass, Parus, Bukhta, etc. appeared, as well as specialized subsystems developed for the oil and gas industry: production monitoring, control of diesel fuel consumption for drilling rigs, environmental monitoring, support for supervisors during field development.
Thus, to implement any ERP system you must go through next steps:
1. Understand what you ultimately want to get from ERP.
2. Determine the criteria for selecting an ERP system, including preliminary criteria for its acceptance.
3. Select a specific ERP solution (most likely it will be some kind of central solution plus, for example, a SCADA class subsystem - it depends on the specifics of your business).
4. Deploy and configure the solution, including integration work.
5. Improve/customize the functionality taking into account your enterprise.
Then there will be two ways:
1. The path of a large project. Choose one of the well-known ERP systems (for example SAP), contact one of its partners and conclude an implementation agreement with them. Next, a large project to implement the system will begin. Tatyana from TNK-BP can tell you how this epic is going in more detail. This famous story in the IT field. The path of a large project is quite expensive and resource-intensive, because at the initial stage it involves the automation of everything.
2. The path of a small project. This path has become popular now that financial resources are limited, and the ERP system is seen as a means of increasing the manageability of the enterprise - something on which one can survive. Here, when choosing a solution, the emphasis is not on the importance of the ERP brand, but on a clear elaboration of the final goals of the project (GOAL), identifying key technological business chains and their automation in the first place. Nobody says that if the project is small, then Microsoft brands or the same SAP will not be used there. Although most likely not. Whether the disadvantage of this path is that the solution is more heterogeneous than in the first case is doubtful. Practice shows that we get the same quality for less money.
Specific choice The ERP system solution depends on the specifics of your company. I started from oil and gas production.
Automation in industry has long become a common process. Smart controllers control technological processes on modern enterprises all industries, transmitting information to computers for human analysis and decision-making.
It is impossible to automate management decisions using a controller, so integrated systems such as SAP, which are a designer of interconnected modules for managing the production process, have been developed and are being successfully implemented around the world.
A little about the company and product
In 1972 in Germany, five former employees SAP was founded by IBM Corporation System Analysis and Software Development). Their goal was to develop standard software that integrates all business processes in an enterprise in real time.
Twenty-five years later, SAP has become the undisputed leader in the automation niche for enterprise resource planning (ERP). Today it is a corporation with branches and subsidiaries in all industrialized countries.

In Russia, the company's history goes back 20 years. The first office of this international corporation was opened in Moscow back in 1992. Today, offices operate in St. Petersburg, Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Rostov-on-Don; Russian has become one of the main localization languages software products SAP company, more than 1000 Russian employees are involved in the implementation of basic software solutions.
What it is
SAP ERP – information corporate system, based on the ERP (enterprise resource planning) methodology and aimed at achieving optimal business processes.
For large state-owned industrial giants, stable execution of government orders within a strictly specified time frame is necessary, for private industrial enterprises What is more important is profit and payback on equipment.
Projects implemented using SAP help both public and private structures optimize costs and achieve their goals at every stage production cycle. At the same time, the basis for accepting management decisions individual methods and principles are laid down that are relevant only in a particular case.
The SAP ERP system allows the manager to see the production process in real time, while, without delving into the essence of the problems, correctly assess the dynamics of the processes in the enterprise.
video: SAP ERP - introduction
Main modules of the program
Accounting and control are necessary in any business, in business every percent of profit is accounted for, therefore the introduction of information systems that can reduce routine operations by more than 50%, show transparency of product manufacturing processes and provide easy access to any necessary information- this is the way to efficient work companies. The new generation SAP architecture allows you to effectively solve a variety of problems facing the enterprise.

All key areas of activity:
- operational production management;
- accounting areas (accounting, finance, warehouses, transport);
- planning and control;
- frames.
The system has not only broad functionality, but also complete integration between modules.
A set of standard modules designed to manage all areas of activity is given below.
- Module FI (Finance). One of the main ones, centralizes data accounting and financial management. Performs transactions with creditors and debtors, improves the quality and timing of reporting;
- Module AM (Fixed Assets). This includes all tasks for managing fixed assets: planning, control, repair, maintenance throughout the entire cycle of equipment operation;
- CO module (Controlling). Considers costs and profits. Forms a planned and actual cost, allows you to quickly respond to market changes, develops conditions for high-quality management decisions;
- PS (Projects). An application module that works with a specific object allows you to track the project using graphic elements: network diagrams, scheduling diagrams;
- Module MM (Material Flows). Resolves supply and inventory management issues by optimizing the purchase of materials and warehouse management. Tightly integrated with the FI financial module;
- SD (Sales). Organizes business processes for the shipment and sale of products with automatic issuance of invoiced reports.
- PM (Equipment Maintenance and Repair). Automates equipment repair processes, allows you to plan preventive maintenance with further control;
- QM (Quality Control and Management). Organizes planning and quality control in production and purchasing. Interacts with MM;
- HR (Human Resource Management). A system for working with personnel, from payroll to hiring new employees. This also includes training, retraining of personnel and organizational management;
- WF (Information Flows). Information is automated according to certain rules using special procedures. Email, document management system, integration with CAD - components of the module;
- IS (Industry Solutions). Special functionality is described that corresponds to a specific industry.

Additions to the package
The need for software updates is caused by life itself, the constant forward movement of human thought. What was good 10 years ago today requires improvement taking into account today's realities. That's why SPA has developed new strategy supply of software for their projects.
These are expansion packs that provide new functionality within a specific user group, without affecting the project architecture as a whole.

Today, the fourth update package has been released, providing additional capabilities in the areas of financial, purchasing, sales, personnel management, etc. It includes all previous updates, has additional features and services for working with WEB interface, it includes new industry solutions.
An example is the RCM module - this is electronic document management. It is otherwise called the enterprise content management module. A convenient element for working with documentation.
Implementation stages
Implementation of any information system The process is not easy, step-by-step, lengthy and expensive. But any phase of the project being implemented must have a final product with a description.

The process of launching an SAP ERP project can be divided into the following stages:
- creation of project management documentation (order, charter, schedule);
- inspection of the automation object;
- conceptual design. (creation of an enterprise management model);
- phased implementation;
- user support and training.
Benefits of the ERP package
What does the implementation of the system provide? In addition to the fact that this is a very expensive project, it also changes the management structure of the company. Therefore, it is impossible to evaluate how the project is working without analyzing and assessing the effectiveness of changes in the company’s work.

And yet...The introduction of programs of this class allows you to remove the most painful points in the work of enterprises. These include “transparency” of production and inefficiency. To understand “where it hurts”, the head of the company needs to study the “symptoms”. This is what such a system helps to do.
It also eliminates the problem of inefficiency by automating a huge number of functions. human factor. Where a person spent more than a day preparing a report, the system generates data in a few minutes.
Description of SAP R3
On Russian market gains the greatest popularity SAP program R3. What it is? This is a package of business applications that, in the latest 4.0 version, supports full Internet access, accessible to small and medium-sized businesses based on price characteristics. The package allows standardization of internal business processes and increases the efficiency of the enterprise.

Photo: production management based on SAP R3
All important areas of planning, production, control are included in the system. Built on client/server principles, it has become accessible to medium-sized businesses.

The introduction of such systems since 1995 allows us to state that today they operate in more than 40 countries. In Russia it is very widely used for generating orders and making deliveries.
More and more representatives of medium and small businesses are realizing the need for integrated automation of their enterprises, this is facilitated by innovations from SAP, which develops projects that are affordable and timely for implementation for this market niche, for example, SAP “Financing”.
According to statistical surveys, already 76% of companies vote that IT is their assistant in business. The process of competition forces managers to come to the right decision: engage in the implementation of SAP projects.
With the development of technology, accounting processes become largely automated and this happens thanks to the introduction of new software, but if many have heard about C1, then much fewer people know what the SAP program is.
In turn, this program is very popular and relevant, because it allows you to perform a huge number of actions related to managing the resources of the selected company.
However, SAP is the program is far from simple, as usual to everyone office workers And .
It requires special knowledge and it’s great when the company has a person who understands this or has experience, but It is not always possible to have a specialist of this kind at hand. And then to learn you have to start using instructions and other resources to try to figure everything out.
A little about where it came from
The creator of this system is German company, engaged in software development for its further corporate use.
Initially referred to as SAP AG, the software appeared on the CIS market in 2003 and immediately gained a foothold due to its reliability and versatility.
The creator company, in turn, only developed the product, constantly absorbing competing firms.
In 2006, a scheme was established to train clients in all the intricacies of working with SAP, because the system is considered far from easy to use.
By 2014, this approach changed slightly and teachers took over the role.
They have now begun to turn to them for help, because people in this profession have extensive experience in working with such programs and can tell and show everything through .
It is worth noting that so far it is found only in big companies who can afford and pay for its installation and staff training. Smaller enterprises continue to use the C1 system, which is organized and implemented much simpler.
What kind of program is this?
The software of German origin includes a wide range of capabilities, including: trade and warehouse operations, personnel and financial accounting.
It even involves working with logistics, which is why it is valued so highly. The system processes completely different data, which explains its complex structure.

Important! DownloadSAPon the Internet and even more so It's not free. The program is distributed by purchasing it and then implementing it into the company's system. Free versions on the network are unlikely to be installed without putting your PC at risk.
It is worth considering that before installing software that must keep everything in exceptional order, the company’s system itself must be clearly structured.
SAP definitely will help speed up the processes carried out on data, but is not designed to correct errors and shortcomings in the very structure of the company.

Positive and negative sides
The program has, according to experts, a number of advantages that allow it to differ dramatically from other similar products:
Positive:
- an easy process of setting up both simple parameters - choosing a language or currency, as well as more complex ones - the formation of cultural characteristics, etc.;
- requires almost no updates;
- works with data in real time;
- has a positive effect on staff performance;
- minimizes the possibility of errors;
- has a simple mechanism interface with other office programs;
- covers a huge scope of permissible work, which, as a rule, covers the needs of even the largest companies;
- full interface customization, which allows you to work out the structure of the product down to the smallest detail;
- focuses on the results and indicators of leading companies in order to always be an up-to-date product.
Negative:
- the program, after the company has concluded a contract with one of the vendors, until the line expires according to the documents, does not allow you to switch to another vendor. In general, this can be done, but such a step will result in losses for the company;
- failure to adapt. SAP may be slightly different from the company’s activities and you will have to pay money to debug it;
- the program is not the cheapest and its purchase can take quite a long time to pay off;
- its presence and use is far from a guarantee that the project being developed will be successful.

Most of the shortcomings depend directly on who and how will work behind the established software . If a person has experience or has completed a full-fledged training course, this will certainly affect the rate of payback and the success of the implementation of the planned project.
The company's most popular products
SAP software contains a lot of different developments and it is not known in advance which one to choose.
It all depends on the capabilities of the program and the characteristics of the company, but most often users still make their choice on SAP ERP, also known as R/3.
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is system for planning external and internal resources of an enterprise.

A system of this kind creates a common field for work within the company, becoming the only control center for all key tasks.
Its peculiarity is that all operations are performed in real time. The processed information is immediately sent to the updated server.
SAP ERP contains three fundamentally different sections, each of which contains submodules.

Section "Accounting and reporting" globally includes accounting, counting of funds and is generally responsible for all financial transactions carried out. All of the above in more detail contained in the FI module, and as for monitoring funds and drawing up final reports on profit and loss - this is the CO module.
Section "Logistics" includes four modules: MM– full control over the procurement process, search for a supplier, selection of the most profitable one; RR– drawing up a production plan and its further implementation; RM– equipment care, inspections, testing and repairs; SD– selling products, justifying prices, sending and creating receipts for payment.
Section "Personnel" consists of only one HR module, which is responsible for organizing the HR department, searching and recruiting new personnel, as well as calculating earnings for each employee.
No less famous and popular is the program SAP SRM (Supplier Relationship Management), which is focused exclusively on establishing relationships between the company and suppliers.
It is included in the application package Business Suite and fully automates the process of selecting, purchasing and paying for various goods or resources.
Its main goal– this is to reduce costs for services for enterprises of any size. The program uses methods for ranking suppliers, assigning appropriate ratings to each of them, and also has the ability to build a strategy for the future, which significantly saves time and effort.

Software Add-ons
After the implementation of the main software package, management often has need for addition.
The range of tasks is very wide, but each enterprise has many of its own specific features that were provided for by the creators; they are not included in the main software package.
As a rule, the problem with an add-on is solved by SAP BW, which includes the following possibilities:
SAP BW takes full advantage of everything available functions ERP, but is not limited to them.

Implementation of software into the enterprise operating system
Regardless of which software package management chooses, the process of its implementation will always follow four key stages that have been developed, described in detail and tested by the German manufacturer.
| Stage one | On the first step all necessary documentation is prepared, an implementation plan is created, risks are calculated, and the company's charter is described. |
|---|---|
| Stage two | Further consultations are held with employees, during which the interviewer checks how well the company's employees know their business and are familiar with the ideology of the place in which they work. Questions are indirectly asked about knowledge about SAP programs. |
| Stage three | After completing the collection of information and preparation of documentation, move on to conceptual design. The company's business processes are completely built and its configuration is recreated piece by piece. |
| Stage four | At the final stage the project is being implemented. It is most often carried out in a test version and according to several scenarios at once in order to identify as many shortcomings as possible at the very beginning, and not during the launch of the system into the working process. If all the goals have been achieved, then the implementation can be considered successful. |
In percentage terms, such success is equal to 90% of further stable and reliable operation of the system.
But even if in all scenarios everything went smoothly and successfully, this does not cancel out the 10% of unforeseen failures that may occur later in the work, since the software structure is complex and depends on many parameters and criteria.

Bottom line
SAP software is very multifaceted and contains many nuances and various individual applications aimed at solving local problems.
For each of the programs, a lot of data can be collected and displayed, but It’s very difficult to fit everything into one article. Also, the structure of the system depends on the enterprise and for each it is configured in its own way, which is also illuminated in a different light.
The only thing you should know about software of this kind is that it is very expensive, but at the same time reliable and worth the money.
Built on the principles of openness and with the goal of solving any problems and issues, it deservedly takes a leading place, leaving other accounting and logistics applications out of competition.
 Plan and purpose of the trip: examples Purpose of the trip in the travel certificate examples
Plan and purpose of the trip: examples Purpose of the trip in the travel certificate examples What payments are due upon voluntary dismissal?
What payments are due upon voluntary dismissal? Job description of an inspector of the HR department, job responsibilities of an inspector of the HR department, sample job description of an inspector of the HR department HR specialist
Job description of an inspector of the HR department, job responsibilities of an inspector of the HR department, sample job description of an inspector of the HR department HR specialist Sample decision of the founders on the appointment of a director of an LLC
Sample decision of the founders on the appointment of a director of an LLC What is narrative text
What is narrative text Sergei Bogdan about air combat, aerobatics and the main thing for a pilot
Sergei Bogdan about air combat, aerobatics and the main thing for a pilot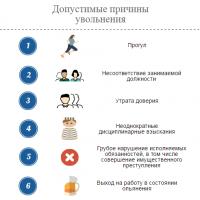 What to do if you are forced to write a statement “of your own free will”?
What to do if you are forced to write a statement “of your own free will”?