Strategic analysis of the construction company PIK SibEcoDom. Analysis of the company's strategy on the example of LLC "Interprof" Modern strategic analysis on the example of the enterprise JSC
INTRODUCTION
1. Theoretical foundations of strategic analysis in the organization management system
1.2. Methods of strategic analysis
1.3. Modeling in the system of strategic analysis
2. Research of the strategic potential of LLC " Construction Department"
2.1. Financial and economic organization's activities
2.2. Characteristics of the internal environment of the organization
2.3. Characteristic external environment organizations
3. Proposals for the implementation of TOOLS for strategic analysis in the management system of Construction Management LLC
3.1. STEP analysis of the organization
3.2. SWOT analysis of the organization
conclusion
List of references AND SOURCES
applications
INTRODUCTION
The new economic conditions generated by market transformations require an appropriate management paradigm. As a result of the rapid transformation of the Russian economy, all management functions that were previously performed by sectoral ministries and departments, including the functions of strategic management, were automatically transferred to the heads of enterprises. Neither the managers themselves, whose task had previously been only the implementation of operational functions to organize the fulfillment of tasks lowered from above, nor the internal organization of enterprises turned out to be ready for this.
The main difference between a market economy is that it does not work on tasks sent down from above, but on the demand of consumers and in accordance with the influence of the external and internal environment on the activities of enterprises. The ideology of strategic management differs significantly from the ideology of planned production. Strategic management solves more complex problems of choosing promising types of business in an informationally unclear future market environment and policies in relation to those types of businesses that are successful today, but which may lose their priorities in the future due to changes in social needs and consumer priorities. These changes tend to increase, and in recent years, many enterprises operate in the face of strategic surprises, loss of control over the external environment, slowing growth and limited resources.
The identified problem does not find an adequate solution in the scientific literature. Many researchers rely on the work of Western experts who are not adapted to the conditions of Russia, which is moving its own way towards a market economy. At the same time, in their works, strategic management is characterized either by a clear emphasis on operational and tactical departments, or attempts are made to reveal individual functions of strategic management and form tools for its implementation.
However, it is possible to avoid unsystematic management in the object of management only on the basis of a combination of operational, tactical and strategic management.
The current conditions in Russia require consideration of the problems of building an enterprise management methodology that would allow, on the one hand, to describe the functioning of organizations through the processes of strategic management; on the other hand, to show the internal nature of the mechanisms of strategic management and the factors that ensure the implementation of the chosen strategies, in the unity of the strategic, tactical and operational management.
The peculiarity of strategic management is that it has very few routine procedures and a lot of creativity, i.e. the role of art is very great. Therefore, the theory of strategic management is formed on the basis of a generalization of the practice of successfully solving the strategic tasks of managing a company and on the basis of highlighting individual management schemes and statements that indicate what can be used to achieve a successful result. In other words, the theory of strategic management says that in managing an organization can help it succeed in the market. Strategic management theory does not say "do it this way and you will succeed." She says that if you act in a certain way, you can succeed. At least before, this led to the success of the company. At the same time, the theory of strategic management rather describes what management will not be able to cope with its tasks without, rather than what guarantees their solution.
Strategic management for many Russian enterprises is still a new, unusual, but gaining momentum phenomenon. The core of strategic management is the system of market strategies, which includes a number of interrelated organizational, economic, legal and labor measures aimed at ensuring market advantages of economic entities over competitors.
The choice and implementation of a rational system of market strategies that ensure the achievement of the main goals of the enterprise is a key element in the activities of top management to ensure economic sustainability and competitiveness of the enterprise.
The degree of development of the topic. The works of well-known foreign scientists I. Ansoff, R. Ackoff, P.F. Drucker, M. Mescon, G. Mintzberg, M. Porter, A.J. Strickland, A.A. Thomson, M. Eddowes and others, as well as Russian researchers L.I. Abalkina, A.I. Anchishkina, M.I. Kruglova, N.F. Permicheva, S.S. Shatalina and others.
Their works deal with the concepts of various strategies, the functions of strategic management, and the choice of competitive strategies. However, such problems as the development and modeling of mechanisms for choosing strategies and their implementation are not touched upon, and if they are touched upon, then indirectly in connection with the research by the authors of other aspects. strategic management.
Recently, much attention has been paid to the problems of long-term planning and management of enterprises in the scientific developments of B.A. Anikina, M.I. Bukhalkova, V.A. Vinokurova, O.S. Vikhansky, I.B. Gurkova, G.B. Kleiner, E.S. Milner, M.M. Maksimtsova, E.A. Utkin.
However, in most of these works, the main emphasis in studying the enterprise management system is placed on operational and current management and the specifics of their use at the micro level.
The object of the study is the enterprise Construction Management LLC.
The subject of the study is the strategic analysis of the enterprise on the example of "Construction Management" LLC.
The purpose of the study is to consider the basic concepts and features of strategic management, as well as to conduct a strategic analysis of an enterprise using the example of Construction Management LLC.
Tasks solved in the course of work:
Determine the theoretical foundations of strategic management;
Analyze the stages of strategic management;
Reveal the essence of strategic planning;
Analyze strategic planning at the enterprise "Construction Management" LLC;
Suggest ways to improve strategic management on the example of "Construction Management" LLC.
The structure of the work: introduction, main part - three chapters, conclusion, list of references and applications.
To write the work, special literature was used on the organization and management of an enterprise, strategic planning and management, economics: textbooks, teaching aids, reference information.
Theoretical foundations of strategic analysis in the organization management system
1.1 The essence of the basic concepts of strategic analysis
The concept of "strategy" entered the management terms in the 50s, when the problem of responding to unexpected changes in the external environment became of great importance. At first, the meaning of this concept was not clear. Dictionaries didn't help. following military usage, they still defined strategy as "the science and art of deploying troops for combat."
Currently, there are many definitions of strategies. According to V.D. Markova and S.A. Kuznetsova, a "strategy" is a general program of actions that identifies the priorities of problems and resources to achieve the main goal. It formulates the main goals and the main ways to achieve them in such a way that the company receives a single direction of movement.
There are several distinguishing features of strategies:
1. The process of developing a strategy does not end with any immediate action.
2. The formulated strategy should be used to develop strategic projects using the search method.
3. The need for a strategy disappears as soon as the real course of development will bring the organization to the desired events.
4. In the course of formulating a strategy, it is impossible to foresee all the possibilities, so one has to use highly generalized, incomplete information about various alternatives.
5. As the search process uncovers specific alternatives, more accurate information emerges.
In other words, strategy is an elusive and somewhat abstract concept. Thus, the concept of "strategy" should be replaced by the systemic concept of "strategic management".
Strategic management is the process of making and implementing strategic decisions, the central link of which is a strategic choice based on a comparison of the enterprise's own resource potential with the opportunities and threats of the external environment in which it operates.
The term "strategic management" was introduced into use at the turn of the 60-70s. in order to indicate the difference between current management at the production level and management at the highest level. The need to fix this difference was caused primarily by changes in business conditions.
We can point to several constructive definitions that have been proposed by authoritative developers of the theory of strategic management. Schendel and Hatten considered it as "the process of defining and connecting an organization with its environment, consisting in the implementation of selected goals and in an attempt to achieve a desired state of relationship with the environment through the allocation of resources, allowing the organization and its units to operate effectively and efficiently."
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Similar Documents
Characteristics of the SWOT analysis method, structure and graphical view of the matrix. Use of optimistic and pessimistic analysis combined with expert survey to determine the strengths and weaknesses of the organization (on the example of the Bank "Vozrozhdenie").
term paper, added 11/20/2010
Essence and principles of system analysis. SWOT analysis of external opportunities and threats, strengths and weaknesses of the enterprise. Identification of problems in the work of the organization using the Ishikawa diagram. Determining the significant qualities of a manager with a hierarchy analysis method.
control work, added 10/20/2013
SWOT and PEST analyzes of the firm's strengths and weaknesses, potential opportunities and threats. Definition of the strategic goal of the enterprise. SNW-analysis of the internal environment. Choice of enterprise development strategy. Prospects for investment management.
practice report, added 01/16/2015
The concept and main objectives of the strategic analysis of the external environment, resources and competitive opportunities of the company. The methodology for conducting a SWOT analysis is to determine the strengths and weaknesses of the enterprise, as well as the opportunities and threats emanating from the external environment.
presentation, added 01/24/2012
Consideration of the concept of the external environment of the organization. Features of using the SWOT matrix to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the enterprise and to assess the opportunities and threats to its development. Conducting an analysis of the external environment of a trading company on the example of DAVVA LLC.
thesis, added 10/20/2011
Methods of strategic management and their importance for the successful management of a company in market conditions. The sequence of actions for conducting a SWOT analysis and a comprehensive study of the internal and external environment of the organization. Technique of analysis of the macroenvironment.
test, added 08/06/2013
Studying the activities of LLC "Element-Trade". Analysis financial stability, business activity and profitability of the enterprise. Application of SWOT analysis to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the firm. Development management decisions; evaluation of their effectiveness.
term paper, added 10/14/2014
3. Technological, political and social factors give the enterprise moderate opportunities that it is able to realize if it correctly directs its strengths to it, and also if it manages to use these opportunities to strengthen its weaknesses.
Let us summarize the results obtained during the analysis of the external environment and summarize them in Table 11.
Table 11
Environment Profile Matrix
|
Importance for the industry X |
Impact on the organization |
Direction of influence |
Degree of importance |
||
|
Political and legal factors |
|||||
|
Economic forces |
|||||
|
Social factors |
|||||
|
Technological and technical factors |
|||||
|
Environmental factors |
|||||
|
Competitors |
|||||
|
Suppliers |
|||||
|
Buyers |
|||||
Taking into account the factors of the external environment of direct impact, it can also be concluded that the external environment of the organization is rather favorable.
An analysis of the external environment of the Rostec enterprise showed that economic factors pose the greatest threat to the company. Companies should first of all use their strengths in relation to these factors, which should help overcome existing threats.
The most favorable influence on the organization comes from buyers and suppliers from whom there are no significant threats. The same can be said about the political, social and technological factors of the external environment. Thus, it is precisely these opportunities, and, above all, from the side of buyers and suppliers, that the enterprise should use to overcome its weaknesses.
2. Analysis of the internal environment of the organization
2.1. functional analysis
OJSC Rostec cooperates with more than 150 manufacturers in Russia and the CIS countries, which allows it to have the widest range of products compared to other companies operating in this industry.
Complex delivery significantly saves the client's time in searching for the spare parts he needs, and is also very convenient.
Consulting and engineering services provided by the company's specialists allow customers to save time on getting acquainted with the features of the operation of the supplied products, replacing parts of the equipment used, etc.
Warranty service implies free repair or replacement of spare parts during the entire warranty period, which is practically not practiced by competitors.
Flexible payment system allows the client to choose the form of payment. The company is considering any proposals.
Delivery of products to the consumer is carried out by any type of transport at the request of the customer.
As of the end of 2006, the company's financial position is unstable. There is a low level of liquidity and solvency, and tendencies of their reduction prevail. An analysis of the creditworthiness indicators indicates a deterioration in the financial stability of the enterprise from the standpoint of the long-term perspective and an increase in the risk of lending to the enterprise. The balance structure should be recognized as harmonic. In 2006, negative changes took place in it: the volume of equity capital decreased, accounts payable and the amount of reserves increased.
The enterprise is characterized by high rates of turnover of funds in settlements and a low value of turnover of accounts payable and stocks. The company is characterized by a fairly high level of profitability. However, in 2006 there was a significant decline in all profitability indicators.
The head of the enterprise, as well as the heads of all departments have higher education. The high educational level of senior management ensures the high professionalism and competence of managers in any matters relating to the activities of JSC Rostec.
The General Director of the company has been at the head of the enterprise since its inception and has extensive experience in the field of management. It should be noted that it was the personality of the leader that played the most important role in the success of the company. By the time the Rostec company was opened in 1993, he already had experience working at large computer enterprises. At BMZ future general manager headed the department of cooperation, and then - commerce.
As for middle managers, each of them has at least 5 to 10 years of experience in the area entrusted to him.
Lower-level managers also have work experience sufficient for them to carry out operational management - about 2-3 years.
JSC Rostec has 5 levels of management. Because of this, most decisions are made at the top levels of the hierarchy. These include decisions on the direction of the enterprise, loans, investments, etc. At the same time, strict control over their implementation is carried out.
The commercial director oversees the activities of the enterprise related to the conclusion of contracts with suppliers and buyers of products, as well as the implementation of customer orders. The chief engineer deals with issues related to his own production at the enterprise. The director of Remtrans manages the activities of the company related to the provision of repair services. The director of "LDS-Trade" manages the foreign economic activity of the company. All of them report to the CEO.
In turn, the CEO is responsible for long-term planning, development of the company's policy, and is also responsible for coordinating and controlling the activities of all divisions that are part of Rostec OJSC.
At the lower levels of the hierarchy, decisions are made that relate only directly to the competence of a functional employee.
2.2. Value analysis
Today the staff of the company is about 250 people.
Average age and education:
supply department: 25-30 years old, higher;
sales: 23-28 years old, higher;
accounting: 30 years, higher;
leadership apparatus: 38-40 years old, higher;
production and repair: 35-40 years old, secondary technical, higher.
The company's staff is quite young. There is an opinion among the employees that getting a job at JSC Rostec is only half the battle: the main thing is to stay in the company, because employees here are required to give full dedication. Many of the employees have two higher educations, but continue to study: they master modern management, marketing and other subjects of a market economy in Bryansk and metropolitan universities.
The basis of the motivation system at the enterprise is the payment of bonuses. This provides for a one-time issuance of a certain amount of money to an employee in connection with his achievement of higher success in work compared to other employees.
As for the sales and supply departments, here the employees are paid a percentage of the volume of the transaction. Employees of other departments receive material rewards depending on the implementation of their plans.
Motivation (motivation to labor activity, stimulation of a certain behavior of an employee) is also due to the working conditions themselves, its organization, the level of enterprise management and other factors. These mechanisms at the enterprise are not limited to material incentives: their use provides for the creation of such an atmosphere, such a moral climate, in which the team is well aware of who works and how, and everyone is rewarded according to their merits. Such an approach requires ensuring that the conscientious work of an employee will always receive recognition and a positive assessment in the team, raise his authority and bring the well-deserved respect of colleagues. Therefore, the company has developed, in addition to material incentives, a system of moral incentives - a declaration of gratitude for the successful completion of the tasks assigned to the employee.
Due to the absence of the enterprise personnel service as such, the performance appraisal functions in the company are distributed among line managers. Based on corporate policy, they develop general principles for personnel assessment and control their implementation in practice.
The next certification at JSC Rostec is held annually and is mandatory for all employees. The basis of certification is a description of the work done and the results of the main activities.
Certification is preceded by preparatory work:
development of criteria and indicators for evaluation by category of positions;
preparation of the required number of forms for evaluation sheets of the employee's activities;
familiarization of the certified with the instructions for filling out the evaluation sheets;
· Approval of the certification schedule;
preparation of necessary materials for certified students;
· provision of organizational and methodological assistance to subdivisions for the performance appraisal of employees.
The organization of certification in divisions is assigned to their heads. The organization of certification of the heads of departments of JSC Rostec is assigned to its board (commercial director).
The manager (specialist) subject to certification independently fills out the appropriate section of the evaluation sheet, which contains all the information on certification, describes the main work done during the certification period: advanced training, the degree of implementation of proposals and comments of the previous certification, etc.
The assessment of the employee's activity is carried out by the immediate supervisor on the basis of a description of the work done during the attestation period, documents on advanced training and the degree of implementation of the proposals and comments of the previous attestation by the attested employee. These questions are discussed with him. It should be noted that it is the immediate superior who is assigned a decisive role in the evaluation of personnel, since he knows his subordinates better than others, is fully responsible for the results of their activities, the correct application of incentives and punishments, for their training and development. The ratings given by the manager generalize the ideas he received during constant communication with his subordinates. At the same time, the need to participate in the assessment encourages the manager to devote more time to subordinates, to weigh the strengths and weaknesses their vocational training, analyze business and personal qualities, more confidently control their work.
Materials on the attestation of an employee prepared by the person being attested and his immediate supervisor are considered by a higher manager. At the same time, he discusses the submitted materials with the immediate supervisor of the certified employee, and, if necessary, with the certified employee himself.
Certification is the basis for making a decision on the further stay of an employee in the company.
The company seriously cares about the level of education of its employees. Agreements are regularly concluded with higher educational institutions of Ulyanovsk and Moscow for the training of employees of the enterprise, and all this is aimed at obtaining a second higher education. All training is provided by the company. In addition, employees of the management staff of the enterprise are sent for training in presidential program on the basis of UlGTU.
Several times a year, executives are sent to thematic seminars in Moscow, organized by the Tandem-Forum company.
All these efforts are aimed at maximizing the qualifications of the employees of the enterprise, especially the management, in order to ensure the highest efficiency.
Let's summarize the data obtained and summarize them in a table:
2.3. Key points, competitive advantages and key capabilities of the organization's potential
Table 12
Enterprise potential analysis
|
Firm's areas of expertise |
||||||
|
Management |
||||||
|
Production |
||||||
|
Marketing |
||||||
The expanded matrix allows for a more detailed analysis of the potential of JSC Rostec.
Table 13
Structured analysis of enterprise potential
|
Potential components |
Strengths |
Weaknesses |
||
|
1. Marketing |
||||
|
Market share by main product |
||||
|
Phases of the life cycle of critical goods |
||||
|
Availability trademark |
||||
|
Range |
||||
|
Quality |
||||
|
Competitiveness |
||||
|
Order lead times |
||||
|
Availability of a sales network |
||||
|
Marketing Philosophy |
||||
|
Development of new products |
||||
|
Enterprise image |
||||
|
2. Scientific research |
||||
|
Availability of patents and inventions |
||||
|
Intensity and results |
||||
|
Use of new information technologies |
||||
|
3. Production |
||||
|
Equipment condition |
||||
|
Quality operational planning |
||||
|
Stability |
||||
|
Level of applied technologies |
||||
|
Production quality |
||||
|
Flexibility of production lines |
||||
|
4. Financial block |
||||
|
Sustainability |
||||
|
Liquidity |
||||
|
Profitability |
||||
|
Profitability |
||||
|
Sales Efficiency |
||||
|
Having a permanent client base |
||||
|
Sales organization |
||||
|
6. Supply |
||||
|
Reliability of suppliers |
||||
|
Fulfillment of delivery schedules |
||||
|
Supply quality |
||||
|
Age composition |
||||
|
Staff turnover |
||||
|
The level of education |
||||
|
8. Management |
||||
|
State of management |
||||
|
senior management |
||||
|
middle management |
||||
|
lower level |
||||
|
Strategic planning |
||||
|
tactical planning |
||||
|
The level of organization of the firm |
||||
|
Compliance with the structure of the company's strategy |
||||
|
Motivational policy |
||||
|
Organization of control |
||||
|
Entrepreneurial culture |
||||
Conclusion:
The analysis carried out shows that the internal potential of JSC Rostec is quite high. The position of the enterprise in sales, supply, personnel is strong, although the motivation of employees is insufficient, there is a turnover of personnel.
The level of management of the company is especially high.
At the moment, the company uses modern information technologies, all documentation and accounting are automated.
Despite the lack of a marketing service, Rostec's positions in this direction are also quite strong. However, the disadvantage is that research is not carried out, the pricing policy is weak, the marketing philosophy is very poorly developed. All this affects production. The weak side of the enterprise's activity, along with R&D, is finance.
3. Statement of problems
The most important stage in the development of an effective company strategy is a strategic analysis, which should give a real assessment of its own resources and capabilities in relation to the state (needs) of the external environment in which the company operates.
Strategic planning is a set of actions and decisions taken by management that lead to the development of specific strategies designed to help the organization achieve its goals.
The strategic planning process is a tool that helps in making managerial decisions. Its task is to provide innovations and changes in the organization to a sufficient extent. More precisely, the strategic planning process is the umbrella under which all managerial functions are hidden.
The word "strategy" comes from the Greek strategos, "the art of the general."
The strategy is a detailed comprehensive plan designed to ensure the implementation of the organization's mission and achievement of its goals. It should be developed from the perspective of the whole corporation, rather than a specific individual. It is rare that a company founder can afford to combine personal plans with organizational strategies. The strategy involves the development of reasonable measures and plans to achieve the intended goals, which should take into account the scientific and technical potential of the company and its production and marketing needs.
The strategic plan must be supported by extensive research and evidence. Therefore, it is necessary to constantly collect and analyze huge amount industry information National economy, market, competition, etc. In addition, the strategic plan gives the company a certainty, a personality that allows it to attract certain types of employees and help sell products or services.
Strategic plans must be designed in such a way that they not only remain coherent over the long term, but also remain flexible. The overall strategic plan should be seen as a program that guides the activities of the firm over an extended period of time, subject to constant adjustments due to the ever-changing business and social environment.
Strategic planning alone does not guarantee success, and an organization creating strategic plans may fail due to errors in organization, motivation, and control. However, formal planning can create a number of significant favorable factors for the organization of the enterprise. Knowing what an organization wants to achieve helps clarify the most appropriate course of action. By making informed and systematic planning decisions, management reduces the risk of making the wrong decision due to erroneous or unreliable information about the organization's capabilities or the external situation. In this way, planning helps to create a unity of common purpose within an organization.
Strategic planning functions:
The strategic plan sets the direction for the organization's activities and allows it to better understand the structure marketing research, the processes of consumer research, product planning, promotion, and marketing, as well as price planning.
The strategic plan provides each unit in the organization with clear goals that align with the overall objectives of the company.
The strategic plan stimulates the coordination of the efforts of various functional areas.
The strategic plan forces the organization to evaluate its strengths and weaknesses in terms of competitors, opportunities and threats in the environment.
This plan defines alternative actions or combinations of actions that an organization can take.
The strategic plan provides the basis for the allocation of resources.
The strategic plan demonstrates the importance of applying performance evaluation procedures.
The formation of a strategic plan is a thorough, systematic preparation for the future, carried out by top management:
1.) The choice of mission - the formation of goals (long-term, medium-term, short-term).
2.) Development of enabling plans - policy, strategy, procedures, rules, budgets.
Stages of drawing up a strategic plan
A. Chandler, the author of one of the pioneering works in the field of strategic planning, believes that strategy is “the definition of the main long-term goals and objectives of the enterprise and the approval of the course of action and the allocation of resources necessary to achieve these goals.” The definition of Chandler's strategy is supplemented by the requirement of economy for the courses of action taken: "The strategic alternative is determined by comparing the capabilities and resources of the corporation, taking into account an acceptable level of risk." Ultimately, the formation of an enterprise strategy should provide answers to three questions: What directions economic activity needs to be developed? What are the capital investment and available resource needs? What are the possible returns in the chosen areas?
A. Ansoff identifies several distinctive features of the strategy:
The strategizing process does not end with any immediate action. It usually ends with the establishment of general directions, the promotion of which will ensure the growth and strengthening of the company's position.
The formulated strategy should be used to develop strategic projects, search methods. The role of strategy in search is, firstly, to focus attention on certain areas or opportunities, and secondly, to discard all other possibilities as incompatible with the strategy.
The need for this strategy disappears as soon as the real course of events will lead the organization to the desired development.
While formulating strategies, it is not possible to foresee all the possibilities that will open up when drafting specific activities. Therefore, one has to use highly generalized, incomplete and inaccurate information about various alternatives.
As more accurate information becomes available, the validity of the original strategy may be questioned. Therefore, feedback is needed to ensure timely reformulation of the strategy.
The strategy implementation process can be divided into two major stages:
a) the process of strategic planning - the development of a set of strategies, ranging from the basic strategy of the enterprise and ending with functional strategies and individual projects;
b) the process of strategic management - the implementation of a certain strategy in time, the reformulation of the strategy in the light of new circumstances.
Strategic planning is a systematic and logical process based on rational thinking. At the same time, it is the art of forecasting, researching, calculating and choosing alternatives.
Enterprise strategies should be built on a hierarchical basis. At the same time, the levels of strategies, their complexity, their integration are very different depending on the type and size of the enterprise. So, a simple organization can have one strategy, and a complex one can have several at different levels of action.
The conceptual model of the strategic plan allows you to define the following stages of drawing up a strategic plan for an enterprise (see Appendix):
Environmental analysis:
a) the environment
b) internal capabilities.
Determination of the enterprise policy (goal setting).
Formulation of strategy and selection of alternatives:
a) marketing strategy
b) financial strategy,
c) R&D strategy
d) production strategy,
e) social strategy,
f) organizational change strategy,
g) environmental strategy.
The result of the activity according to the above scheme for drawing up a strategic plan for an enterprise is a document called the “Strategic Plan of an Enterprise” and usually has the following sections:
Goals and objectives of the enterprise
Current activity of the enterprise and long-term tasks.
Enterprise strategy (basic strategy, main strategic alternatives).
functional strategies.
The most significant projects
Description of external operations.
Capital investment and resource allocation.
Planning for the unexpected.
Attachments: Calculations, references, other business documentation, including:
a) The volume of annual sales by product groups,
b) Annual profit and loss by division,
c) Annual exports and its relation to the volume of sales by
departments.
d) Changes in product mix and market share.
e) Annual Capital Expenditure Program.
f) Annual cash flows.
g) Balance at the end of the last year of the plan.
h) Policy of takeovers and acquisitions.
An analysis of the literature on strategic planning in Western companies has shown that both the number and content of the stages of drawing up a strategic plan, as well as its very form, can vary significantly and depend on many factors, among which the main ones are:
Form of ownership of the enterprise.
Type of enterprise (specialized or diversified)
Industry affiliation of the enterprise.
Enterprise size (large, medium or small).
Likewise, there is no single strategic planning horizon. In Europe, long-term, 10-year plans are common, Americans use 5-year plans, and the Japanese generally use 3-year plans.
Organization goals
One of the most significant decisions in planning is the choice of the purpose of the organization. The main overall goal of the organization is designated as a mission, and all other goals are developed for its implementation. The significance of the mission cannot be overstated. The developed goals serve as criteria for the entire subsequent process of making managerial decisions. If leaders do not know the organization's primary purpose, then they will not have a logical starting point for choosing the best alternative. Only the individual values of the leader could serve as a basis, which would lead to a dispersion of efforts and vagueness of goals. The mission details the status of the firm and provides direction and benchmarks for setting goals and strategies at various levels of development. Mission formation includes:
finding out which entrepreneurial activity the firm is engaged;
determination of the working principles of the company under the pressure of the external environment;
revealing the culture of the company.
The mission of the firm also includes the task of identifying the basic needs of consumers and effectively satisfying them in order to create a clientele that will support the firm in the future.
Table 14
Value Orientations
|
Types of Preferred Goals |
|||
|
Theoretical |
True. Knowledge. Rational thinking. |
Long-term research and development |
|
|
Economic |
Practicality. Utility. |
Growth. Profitability. Results. Wealth accumulation. |
|
|
Political |
Power. Confession. |
Total capital, sales, number of employees. |
|
|
Social |
Good human relations. Attachment. No conflict. |
Social responsibility regarding profitability. indirect competition. |
|
|
aesthetic |
Artistic harmony. Compound. Shape and symmetry. |
Product design. Quality. Attractiveness. |
|
|
religious |
Agreement with the universe. |
Ethics. Moral issues. |
|
General corporate goals are formed and set on the basis of the overall mission of the organization and certain values and goals that top management is guided by.
Specific and measurable goals (this allows you to create a clear base of reference for subsequent decisions and evaluation of progress).
Orientation of goals in time (here it is necessary to understand not only what the company wants to achieve, but also when the result should be achieved).
Achievement of the goal (serves to increase the efficiency of the organization); setting a goal that is difficult to achieve can lead to disastrous results.
Mutually supporting goals (actions and decisions necessary to achieve one goal should not interfere with the achievement of other goals).
Objectives will only be a meaningful part of the strategic management process if they are properly formulated, effectively institutionalized, communicated and driven by top management throughout the organization.
Conduct a primary strategic analysis by compiling a SWOT matrix. The SWOT analysis methodology involves first identifying strengths and weaknesses, as well as threats and opportunities.
Table 15
SWOT - analysis of the activities of OJSC Rostec
|
Strengths 2. Wide market 4. Flexible system of discounts 6. Multiple payment for the delivery of goods 7. Attentive attitude to the customer and long-term cooperation |
Opportunities 1. Political stability 4. The customer's need for complex deliveries 5. Decrease customs duties 6. Big market work force highly qualified 7. Large selection of suppliers 8. The emergence of modern production technologies and high-performance equipment |
|
|
Weaknesses 2. High prices 4. High staff turnover 10. Overstocking warehouses 11. Significant wear and tear of equipment |
1. Unstable financial situation of customers 2. Increasing requirements for product quality and low prices 3. Growth in the number of competitors 4. Seasonality of orders 5. Preference of the customer to have a supplier in close proximity 6. Volatility in supplier prices 7. Instability of supply from suppliers 8. Risk of using modern technologies by competitors 9. Increasing energy prices 10. Increase in prices for transportation 11. High taxes 12. Critical state of production infrastructure |
|
We will evaluate the quantitatively identified strengths and weaknesses, as well as opportunities and threats.
Table 16
Quantitative SWOT Analysis
|
Importance (X) |
Influence (Y) |
Result |
||
|
Strengths |
||||
|
1. Wide range of products 2. Wide market 3. Comprehensive supply of spare parts 4. Flexible system of discounts 5. Convenient conditions for the delivery of goods to the client 6. Multiple payment for the delivery of goods Attentive attitude to the customer and 7. long term cooperation 8. Provision of consulting and engineering services 9. Extensive experience in carrying out all types of repair of equipment for which the company supplies spare parts 11. Development of own production 12. Flexible the production cycle 13. Young, promising staff 14. Opportunity for staff training 15. High educational level of staff 16. Efficient system employee motivation 17. Business and professional specialization 18. The ability of employees to work in a team 19. Development of plans for complex service enterprises 20. Active participation in the public life of Ulyanovsk and the region |
||||
|
Total Average |
||||
|
Weaknesses |
||||
|
1. Lack of market research 2. High prices 3. Lack of knowledge about competitors 4. High staff turnover 5. Low level of flexibility in employee relations 6. Deteriorating financial situation 7. Decrease in profitability of activities due to outstripping growth of costs 8. Inefficient use of resources 9. Lending to an enterprise is associated with risk 10. Overstocking warehouses 11. Significant equipment wear 12. Lack of skilled workers |
||||
|
Total Average |
||||
|
Opportunities |
||||
|
1. Political stability 2. Decreasing the refinancing rate 3. The growth of the purchasing power of the ruble 4. Creation in the near future e........... |
Pages: | | | |
ECONOMIC PROBLEMS OF REGIONS AND INDUSTRY COMPLEXES
STRATEGIC COMPETITIVE ANALYSIS IN THE CONSTRUCTION INDUSTRY
S.V. Romanova,
Associate Professor of the Department of Accounting, South-Russian State University of Economics and Service (Shakhty),
PhD in Economics [email protected]
In the work, using econometric methods, strategic aspects are analyzed construction activities. It is concluded that an important step in the analysis is to identify alternative strategies that can be implemented by competitors, and planning a response to such potential threats.
Key words: competitive analysis, competition, price, market, strategy, value chains, external environment, economic security.
BBK U053.9(2)29.0
Strategic competitive analysis is an effective tool for identifying competitive advantages, developing, implementing and changing the competitive strategy of a construction organization aimed at ensuring its dynamic development and sustainable economic growth. It involves an analysis of environmental factors and an analysis of the resources and competitive capabilities of the construction company itself. This will improve the effectiveness of the current strategy, identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of the company, competitiveness in terms of prices and costs, stability of the position compared to competitors. All this has become more important in recent years.
Competitive advantage is expressed in the identification of the market, market niche or "warm place" that the company has in terms of prices, costs or scale of investment and construction activities. Competitive advantage is expressed in the fact that the company has a greater market share in a certain segment, and confirmation of this fact requires the development and implementation of an appropriate conceptual approach to strategic competitive analysis in the construction industry.
The methodology for the formation of competitive strategies is based on the models of competitive strategies by M. Porter and S.S. Ma-tour. According to M. Porter, obtaining an advantage in competition is based on: A) low costs; B) differentiation (Fig. 1).
superior advantage advantage on
Relative position by differentiation-based differentiation
differentiation "Stuck Advantage on
in the middle" based on low
Lagging cost
Lagging Superior
Relative cost position
Rice. 1. Get a competitive edge
A value chain system is a method of classifying this value chain (from feedstock to final consumers) into strategically important economic activities in order to understand cost behavior and sources of differentiation. An organization can survive competition either by keeping costs low or by offering products that outperform those of competitors.
M. Porter identifies these sources of competitive advantage with the ability to work in a wide or narrow segment (Table 1).
In accordance with his concept, the state of competition in the industry is determined by five main forces that determine the attractiveness of the industry and the position of the company in the competition: the emergence of new competitors; the threat of replacing this product with new products; the strength of the supplier's position; the strength of the position of buyers; competition among manufacturers within the industry itself.
The analysis of existing and potential competitors should be carried out in the context of the presented competitive forces,
Table 1
Competitive strategies according to Porter
Area of competition Source of competitive advantage
Cost Leadership Differentiation
Wide Wide competition for cost leadership Wide differentiation
Narrow Cost leadership with a focus on a narrow segment Differentiation with a focus on a narrow segment
which will make it possible to identify areas for creating competitive advantages in their industry in a competitive environment (Fig. 2).
Strategic competitive analysis involves not only an analysis of the factors of the external environment in which a construction organization operates (characteristics of the construction industry, forms and intensity of competition in the industry, reasons for changes in the structure of competition and the external environment, strong and weak competitors, possible actions of competitors, key success factors in competition, the overall attractiveness of the industry and the prospects for profitability), but also an analysis of the resources and competitive capabilities of the company itself (the effectiveness of the current strategy, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of the company, strategic problems of the company, competitiveness in terms of prices and costs, stability of the position compared to competitors).
Rice. 2. Basic strategies for competition and competitive advantage
Today, practice is still dominated by the current competitive analysis, which is reduced to the study of only real competitors, and most often the analysis is limited (due to lack of budget, time or personnel) only to the analysis of priority competitors. Such an approach is fraught with an irretrievably lost competitive advantage in its own market if a foreign competitor quickly breaks into it, which at one time fell out of sight of management, marketers and competitive intelligence specialists.
Classification of competitive strategies S.S. Matura involves differentiation of the offer of goods and services with the corresponding support offered to the client (Table 2).
table 2
Matura Competitive Strategies
Product Differentiated "System" "Product"
Undifferentiated "Service" "Simplicity"
Differentiated Undifferentiated
Support
G. Hamel noted that "future competitiveness is not determined by current rules", which determines the need to organize and conduct a strategic competitive analysis in the construction industry in the following areas:
Analysis of potential competitors;
Forecasting the situation taking into account the change competitive strategy;
Adjustment of the strategy as a result of the predicted change in the competitive situation and market conditions;
Predictive analysis of the results of changing the competitive strategy;
Evaluation of the effectiveness of the competitive strategy;
Strategic monitoring of competitors.
A sign that testifies to the strength of competitive
the position of the company is the competitiveness of its prices and costs in comparison with competitors in the industry. Cost and value chain analysis is a necessary tool for comparing the prices and costs of a firm and its competitors in determining the effectiveness of certain activities of the company and in identifying those areas of activity that require more thorough research.
Thus, the analysis of competitors' prices is an extremely important stage in the pricing mechanism in construction (Fig. 3).
Fig.3. Stages of pricing
Given these provisions, a conceptual approach to strategic competitive analysis in construction is presented in fig. 4.
This approach focuses users on the model of strategic development of a construction organization, strategic initiatives, assessment of market attractiveness: size
(capacity) and growth rate of the market, market quality, competitive situation, the influence of environmental factors, etc. when developing a competitive strategy for a construction organization.
The development of the competitive strategy of the organization is carried out within the framework of the general model of its strategic development, focused on the dynamic increase in the ownership of the construction organization in the form of indicators of net assets and net liabilities.
The main directions of strategic analysis of competitors are carried out according to the following classification criteria:
Types of investment and construction activities: construction, contracting, design, reconstruction, technical re-equipment, repair, installation, development, trust management, subcontracting, investment, real estate, intermediary, leasing, engineering, consulting, venture, engineering surveys, feasibility studies, etc. ;
Scale of activity: local, regional, national, international, global;
Ways of organizing construction activities: contracting activities, subcontracting activities, economic method, development activities, mixed method, trust management;
Resource support for construction: property, availability of the necessary capacities in the construction organization, specialization, provision with an industrial construction base, availability and condition of communications, characteristics of the raw material base for production building materials, availability of necessary energy resources, etc.;
Forms of construction products (product range): certain types works (construction and installation works, non-capital works), stages of work (completed stages, incomplete stages), construction objects (buildings, structures), construction sites (a set of buildings, a set of structures), goods-objects (multi-complex objects under construction, single-complex objects under construction) , turnkey facilities (single-profile, multi-profile);
The level of cost of construction products relative to the established cost (high, medium, low): participants in the price formation mechanism, the nature of buildings and structures under construction, local construction conditions, etc.;
Quality and special properties of products according to priority evaluation criteria;
Pricing policy: price maximization, price minimization, price maintenance at a certain level;
Development of R&D: own R&D, acquisition of ready-made new achievements of scientific and technical progress, lack of R&D;
Strategic intentions: leadership, position holding, survival;
Type of strategy: aggressive, moderately aggressive, moderate, conservative, defensive;
Competitive strategies: cost leadership, product differentiation, concentration (specialization);
Goals to achieve market share: aggressive expansion, expansion, retention of existing market share, reduction of market share;
Taxation system: general taxation system, simplified taxation system;
Contractual policy with suppliers and clients (customers): a system of contracts, contractual terms - permanent economic relations based on long-term contracts, permanent economic relations based on short-term contracts, permanent relationships without contracts (on request), casual relationships;
Settlement terms: the procedure and terms for acceptance of completed works and settlements for them during the construction process, terms for the contractor to eliminate comments received from the customer on the quality of work performed, terms for final settlements upon completion of construction, settlements for structural elements for the performance of individual works and services, settlements for stages, settlements after the completion of all work under the contract.
In order to structure and focus the comparative analysis of competitors, it is necessary to analyze the existing and potential competition. Should be evaluated
Strategic
construction
organizations i am
Strategic initiatives
Attractiveness rating
market to her and
Assessing Barriers to Entry and He About
leaving the industry >I
Estimation of the current market I UZ 1=3
OE situations
Score change I'm about
competition in the market 4- He n o
Grouping competitors by C * I
the nature of their impact and
areas of analysis
Analysis of competitor strategies
competitive position at
Adopted competitive oh
strategy & me
Pressure from existing competitors New competitors in the market Market power of suppliers Market power of customers (customers) Alternative products
Conducted from the point of view of competitors' pressure on the implementation of the strategic development model of a construction organization
Analysis of existing and potential competitors
Strategic analysis of competitors in the construction industry
to n n o I to
G Un D He s
.°3 L- "3 n to
Directions of competitor analysis
Analysis of the effectiveness of competitive strategy in terms of the model of strategic development of a construction organization
Methods and models of analysis
k £ § v-p-5 i o
N her O He § & 5 o
* £ § § i 9" i b
£*5 5 ga n o, &1 i i
Engineering Analysis Toolkit
“ I o Yo 8. & _ and © s s
2 2 § £ & h o o
o 2 „ ^ a i £ ha o
Analysis algorithm
Adopted competitive strategy of the organization;
Adjustment results;
Resources and sources;
Making decisions
Indicators
strategic
to "oh oh oh and
jonomics
security
(active,
passive,
neutral"
security:
active,
passive,
normative
2 I am about. but I
"I ha i o © o i
Section 5 | § He O O He
Rice. 4. Conceptual approach to strategic competitive analysis in the construction industry
ECONOMIC PROBLEMS OF REGIONS AND INDUSTRY COMPLEXES
possible alternative strategies of each of the competitors, their commitment to a specific product or market based on the compilation and use of market derivative balances of a situational and forecast nature.
The conceptual approach to strategic competitive analysis is focused on the option of integrating methods for analyzing market attractiveness, competitive position in the market, and competitive strategy with the presented analytical tools of derivative balances, which makes it possible to predict the situation of changes in competitive strategy based on the results of a strategic analysis of competitors, to evaluate the effectiveness of a competitive strategy based on the calculation of indicators ownership and the definition of economic zones and margins of safety.
Calculation and analytical procedures are based on the use of the information base of a strategic structured chart of accounts, which acts as the initial operator and allows you to create a system of indicators to assess the effectiveness of the competitive strategy implemented by the organization, which determines the degree of aggregation of the calculated indicators.
As Professor K. Ward rightly points out, the analysis, which consists in evaluating the company's effectiveness in comparison with direct and currently obvious competitors, may turn out to be too simplistic, which requires forecasting the situation of the emergence of new competitors and the organization's appropriate response to this based on analytical engineering tools.
The algorithm of the process of strategic competitive analysis in the construction industry with the assessment of the results of predicting the situation, taking into account the emergence of new competitors and the results of changing the competitive strategy based on the results of the analysis, is as follows:
Adoption of a competitive strategy for a construction organization;
Adjustment of the strategy in connection with a change in the competitive position of the organization and market conditions;
Adjustment results;
Resources and sources;
Making decisions to optimize the competitive strategy of the organization and strengthen its position in the market.
Forecasting the situation, taking into account changes in the strategy in relation to competitors and the behavior of the organization in the market based on the results of the analysis, is carried out in terms of the impact of these changes on the value of the construction organization.
An important stage of the analysis is the identification of alternative strategies that can be implemented by competitors, and planning their response to such potential threats, for which it is proposed to use alternative, situational and predictive derivative balances.
Calculation and analytical procedures involve the use of aggregated records for reflection:
The adopted competitive strategy and the value of the organization, taking into account the adopted strategy with the relevant resources and their sources and the calculation of the net asset indicator in the market assessment;
Changes in competitive strategy as a response to a potential threat from competitors and the results of such a change with the balance of resources and sources and the definition of adjusted net assets in a market assessment;
Hypothetical processes of conditional sale of assets and satisfaction of liabilities with obtaining an indicator of net liabilities in a fair assessment and analysis of the price component in the competitive strategy of the organization.
The composition of resources and sources is determined in accordance with the economic aggregates of the strategic structured chart of accounts adopted for calculation. Analysis of the effectiveness of the competitive strategy, which is carried out from the perspective of a model of strategic development of a construction organization with the allocation of the following system of indicators:
Indicators of strategic success in the form of aggregated indicators of net assets in balance sheet and market assessment and disaggregated indicators of net liabilities in a fair assessment;
Economic security zones;
margin of safety.
The aggregate state of ownership is analyzed taking into account the organization's adopted competitive strategy, taking into account its expected or actual change, taking into account price changes.
Based on the data obtained, the economic security zone is determined, which characterizes the effectiveness of the competitive strategy of the construction organization:
Active zone: an active competitive strategy leading to an influx of resources and sources (profit);
Passive zone: passive strategy with an outflow of resources and sources (losses);
Neutral zone: neutral strategy with relative equality of indicators.
The economic safety zone can be determined by one of two methods:
According to the initial (permanent) base by direct comparison of net assets and net liabilities with the base potential;
By the method of chain substitutions by sequential comparison of net assets and net liabilities according to the obtained derivative balance.
The safety margin is determined by comparing the indicators of strategic success (net assets and net liabilities) with the strategic standard - the standard of competitive strategy, the standard of resources, the limit value (active margin of safety - excess of resources over the established standard; passive margin of safety - lack of resources in comparison with the standard; standard margin of safety - relative compliance with the standard).
The conceptual approach to strategic competitive analysis in construction is implemented within the framework of the following aggregates: the competitive strategy of a construction organization, analysis of existing and potential competitors, areas of competitor analysis, methods and models of analysis, engineering tools for analysis, analysis algorithm, analysis of the effectiveness of a competitive strategy from the perspective of a strategic development model construction organization, analysis providing the organization and conducting a strategic analysis of competitors based on the integration of methods and models of analysis and analytical engineering tools. This allows you to evaluate the change in the cost of a construction organization, taking into account the developed and adopted competitive strategy, the results of its implementation and changes, and make informed tactical and strategic decisions.
Literature
1. Strategic competitive analysis in the transitive economy of Russia / A.M. Ilyshev, N.N. Ilysheva, T.S. Selevich. - M.: Finance and statistics; INFRA-M, 2010.
2. Lapin A.N. Strategic management modern organization. - M .: LLC "Journal" Personnel Management ", 2004.
3. Economic forecasting: tutorial/ Yu.N. Lapygin, V.E. Krylov, A.P. Chernyavsky. - M.: Eksmo, 2009.
4. Ward K. Strategic management accounting / Per. from English. - M.: CJSC "Olimp-Business", 2002.
5. Shank J.K., Govindarajan V. Strategic cost management / Per. from English. - St. Petersburg: Business Macro, 1999.
annotation. The article is devoted to demonstrating the process and analyzing the results of evaluating the strategy implemented by the company in the market. The experience of implementing the model of five competitive forces by M. Porter, PEST-analysis and VCG-matrix is shown to clarify the existing positions of the company in the developing market.
Keywords: analysis, strategy, consumers, firm position
An analysis of the strategy implemented by the company in the market is an important step in diagnosing the correctness of the market efforts being applied and can make it possible to formulate the necessary corrective measures to improve work efficiency. Leading Russian marketing scientists note the importance of strategy in planning a company's marketing activities. In order to analyze the effectiveness of the existing strategy and propose measures to improve market sustainability, various marketing analysis tools of the market environment can be used, for example, SWOT analysis or M. Porter's analysis of competitive forces.
This article demonstrates the analysis of the company's strategy on the example of Interprof LLC (Temryuk). Interprof LLC is a publishing house that prints advertisements for the purchase and sale of various goods, the provision of services, the performance of work, job search, etc. One of the organization's most successful projects is the VSE newspaper, which is also the company's brand. By placing a bet on the classified (advertisings, divided into thematic categories), the company has acquired a leading position in the market.
The organization provides services for placing ads. The topics of announcements are presented in Table 1.
Table 1 - Subjects of the announcements of the publication of LLC "Interprof"
|
Ad Subject |
Characteristic |
Number of ads |
|
Auto and moto |
Sale and purchase of passenger cars, trucks, motorcycles, auto parts, boats, snowmobiles |
|
|
The property |
Sale and purchase of apartments, new buildings, rental of apartments and rooms, commercial real estate, garages |
|
|
Electronics and home appliances |
Audio, video, home appliances |
|
|
Computer technology |
Computers and components, laptops, PDAs and smartphones, peripherals and office equipment |
|
|
Phones and communications |
Mobile and DECT phones, faxes |
|
|
The photo. Optics. Photo services |
Digital and film cameras, lenses, accessories, photo services |
|
|
Construction and repair |
Construction materials, repair and decoration, design, windows, plumbing, cleaning |
|
|
Equipment |
Commercial and industrial equipment, machine tools, security systems, washing equipment |
|
|
Products for children |
Children's clothing, shoes, strollers, car seats, toys, baby products |
|
|
Business and partnership |
Selling and buying a business, investment, consulting, accounting services, audit |
|
|
Furniture, interior, household |
Furniture for home and office, lighting equipment, interior items |
|
|
Clothes, shoes, accessories |
Men's, women's clothing, shoes, watches, jewelry, bijouterie |
|
|
Books, textbooks, magazines |
Artistic and educational literature, periodicals |
|
|
Music, art, collections |
Musical instruments, artwork, collectibles |
|
|
Sports, tourism, recreation |
Sports goods, hiking equipment, bicycles |
|
|
Services and activities |
Transport services, lawyers, translators, organization of events, photography and video filming |
|
|
Work and education |
Search for work and employees: vacancies, resumes, courses, trainings |
|
|
Health and beauty |
Cosmetics and perfumes, medical equipment, correction, weight loss, medical services |
|
|
Dating and communication |
Contacts by interests, dating to create a family, search for new friends |
|
|
Animals and plants |
Dogs, cats, fish, birds, plants, exotic animals, veterinary services |
|
|
I'll give it away |
Priceless things in good hands |
|
The company has a large number of readers and an extensive circulation. The existence of a company is possible only if its products are consumed by someone. The success of the company depends on how consumers behave: the more consumers, the more profit.
Figure 1 shows some of the characteristics of the readers of the VSE publication.
 |
Rice. 1 Characteristics of the readers of the newspaper "VSE"
a) reader demographics
b) the social status of the reader
From Figure 1, we can conclude that regular readers of the VSE newspaper are men and women, aged 25 to 40 years (the most active phase of life), with higher and secondary specialized education, social status - employees-specialists with an income of
9,000 to 30,000 rubles About 8 percent of the readership is in leadership positions.
About 30 percent of regular readers are car owners (19.1 percent own a foreign-made car), 25 percent plan to buy a car in the near future. 71 percent of the newspaper's readership actively use the Internet, 63 percent have Personal Computer Houses.
In the near future, readers of the VSE newspaper are planning to purchase a car, furniture, building materials and household appliances, and about 5 percent of readers are also going to improve their living conditions.
The profit of the organization is influenced by customers who place ads.
The clients of the organization are not only individuals, but also various organizations, placing their ads on the provision of services, the sale of goods and the performance of work. The task of the organization is to attract as many customers as possible.
Competitors also have a direct impact on the performance of LLC Interprof. Let's analyze the Five Forces of Competition by M. Porter's method.
In accordance with the model of M. Porter, to determine the significance of each of the five forces of competition, factors were identified (Table 2) that affect the degree of its manifestation.
Let us consider the forces of competition presented in the table in relation to Interprof LLC and its VSE brand.
table2 - Factors of competition according to the model of M. Porter
|
The power of competition |
|
|
Intra-industry competition |
|
|
Degree of market saturation and concentration (number and market share of large banks competing in the market) |
|
|
Influence from potential competitors (threat of the emergence of a new player) |
Market entry barriers (including: need for investment, market knowledge, experience and knowledge of technology, reputation in this market) |
|
Impact of substitute products |
|
|
Buyer Influence |
Number of audience |
|
Influence of suppliers |
Product quality |
Intra-industry competition. At the moment, there are four major players in the city market:
- "Vse" (LLC "Interprof");
- "Orbit";
- "23 Region";
- "Even freer than Temryuk."
However, each of the publications has its own characteristics and emphasizes its difference from the others.
The difference between “VSE” and its competitors is a loyal audience, as this newspaper has been on the market for a long period of time, and the reader gets used to the specifics of presenting information. Also, first of all, a newspaper is a source of reliable information, so the emphasis in ads is on the accuracy and efficiency of data. Each of the newspapers, despite the fact that they are in the same market, has its own characteristics and its own audience, trying to lure readers and customers with the help of marketing ploys underlying the marketing strategy.
Influence of buyers. The audience of "VSE" is numerous due to the thematic focus. Its core is very diverse. These are people who expect accurate and complete information and have an active lifestyle. The reader is looking for quality information and a convenient form of its presentation.
Threats from substitute products. The VSE newspaper is a product for which it is difficult to find a similar product, but specialized radio and television programs and the Internet can serve as sources of information, on the one hand, but they are not perfect substitutes, as they have a completely different format, and the quality of information can seriously differ from what is required, on the other hand, the opposite is true. Therefore, the threat from substitute products can be considered significant.
Influence of suppliers. One of the distinguishing features of the VSE newspaper is the paper used to make the newspaper. The company buys it from a single manufacturer, therefore, without compromising the recognition of its brand, the newspaper cannot change the supplier. In addition, "Vse" also depends on distributors: a small number of local chains of newsstands are affected. Therefore, the company is forced to agree to conditions that are inconvenient for it.
The threat of a new player. Here, such advantages of the company as a strong brand, reputation and access to reliable sources of information are important. Moreover, existing companies are ready to resist, for example, given that the main source of income in the industry is advertising, newspapers already present in the market are able to reduce the price of this service. On the other hand, the market is quite attractive, and VSE managed to gain a foothold on it several years ago.
Each of the considered factors for each of the five forces of competition is assessed on a point scale (range of estimates from 1 to 3 points): "1" point corresponded to the absence of the factor manifestation; "2" points corresponded to a weak manifestation of this factor; "3" points corresponded to a significant manifestation of this factor.
Based on the results, the average score for each factor and each competition strength was calculated (Table 3).
Table 3 -Evaluation and average score of each competition strength(points)
|
Forces |
Expert 1 |
Expert 2 |
Expert 3 |
Average score |
|
|
Intra-industry competition |
Attractiveness of the market for competing organizations operating on it |
||||
|
The degree of saturation and concentration of the market |
|||||
|
Variety of related services offered by competitors to the market |
|||||
|
Average score for strength |
|||||
|
Influence from potential competitors |
Barriers to market entry (including: need for investment, knowledge |
||||
|
market, experience and knowledge of technologies, reputation in this market) |
|||||
|
Average score for strength |
|||||
|
Impact of substitute products |
Transition to new ways of presenting information |
||||
|
Average score for strength |
|||||
|
Buyer Influence |
Number of audience |
||||
|
Average score for strength |
|||||
|
Influence of producers |
Product quality |
||||
|
Average score for strength |
|||||
In accordance with the applied methodology for calculating and analyzing the influence of competition forces, the level of influence of each of the forces was assessed based on the average score obtained (Figure 2).
As follows from Figure 2, at the moment the level of power of influence of substitute goods and the influence of buyers is very high and amounts to 2.67 points.
Thus, these are the main competitive forces of the industry that affect the activities of Interprof LLC and its VSE brand. All other forces have either a reduced or moderate effect.
The main competitors of Interprof LLC in the city and district are:
LLC "23 REGION" ("23 Region");
 Rice.2.
Assessment of the degree of influence of the identified forces of competition
Rice.2.
Assessment of the degree of influence of the identified forces of competition
Table 4 - Characteristics of the VSE publication (Interprof LLC) and competing publications
|
Criterion name |
LLC "Newspaper association "Prichernomorie"" ("Orbita") |
LLC "23 REGION" ("23 Region") |
OOO "Temryuk Publishing House" ("Even Free Temryuk") |
"All" |
|
Location of publication |
Temryuk |
Temryuk |
Temryuk |
Temryuk |
|
Market Presence |
21 years (since 1994) |
22 years (since 1993) |
10 years (since 2005) |
23 years (since 1992) |
|
Total circulation, copies |
||||
|
Periodicity |
1 time per week |
2 times per week |
1 time per week |
2 times per week |
|
Number format |
||||
|
Volume of the issue (number of lanes) |
||||
|
Chroma |
full color |
full color |
full color |
full color |
|
Own delivery service |
Present |
Missing |
Present |
Present |
|
Distribution terms |
Paid Edition |
Paid Edition |
Paid Edition |
Paid Edition |
|
Present |
Present |
Present |
Present |
|
|
Present |
Present |
Present |
Present |
|
|
Application deadline |
||||
|
The cost of one ad, rubles |
||||
|
Web site |
||||
On the basis of the table, we will single out the competitive positions of Interprof LLC in relation to the VSE publication and evaluate them in comparison with other publications. As such, we single out: staff qualifications, brand, range of services, location, cost of services. Let's evaluate the advantages on a ten-point system (we proceed from the fact that 10 points is a strong advantage, 1 point is a low advantage). The evaluation results are presented in Table 5.
Table 5 - Assessment of competitive strength (points)
|
Competitive forces |
VSE (Interprof LLC) |
OOO "Temryuk Publishing House" ("Even Free Temryuk") |
LLC "Newspaper association "Prichernomorie"" ("Orbita") |
LLC "23 REGION" ("23 Region") |
|
Range of services |
||||
|
Cost of services |
||||
|
Location |
||||
|
Personnel qualification |
Figure 3 shows the competitive profile of Interprof LLC and its VSE brand. 
Rice. 3 Competitive profile of Interprof LLC and its VSE brand
An analysis of the data in Table 5 and Figure 3 shows that in most of the highlighted advantages, "VSE" outperforms its competitors, and in some it lags behind them. So, for example, the Brand position (10 out of 10 points), the range of services - 9 out of 10 points, gets a good rating, while these positions are lower for competitors. This gives excellent advantages in the market and allows you to implement almost unhindered any projects of the organization.
According to the rating company "Reklama on-line" for 2014 in the subject "Newspapers with ads" places between publications are distributed as follows: "Vse" (LLC "Interprof") - 1st place; "23 Region" (LLC "23 REGION") - 2nd place; "Orbita" (LLC "Newspaper association "Prichernomorye"") - 3rd place; "More Free Temryuk" (LLC "Temryuk Publishing House") - 4th place.
All this suggests that the strategy of Interprof LLC is currently optimal in the selected segment, since the company has a constant client base, a good reputation among customers, large volumes of orders for delivery, but at the same time, there are also shortcomings in the implemented strategy.
Let's do a STEP analysis. To begin with, we highlight the environmental factors that affect the activities of the organization.
political factors. Of the political factors of the external environment, the following are important: the stability of the government regime; change in legislation; other government influence. Any fluctuations in the political regime can affect the activities of the organization as a whole. The same consequences may arise with changes in legislation.
Economic forces. Here, first of all, any changes in the economic situation (for example, a crisis) can cause the loss of consumers and customers. Inflation also affects the press to some extent, as commodity prices rise and the consumer's real income falls.
The main economic factors are: the economic situation and trends; effective demand; investment climate.
sociocultural factors. The basis of the VSE audience is made up of people with an average income, mainly people who need this kind of information and have a certain social status. Thus, social mobility and stratification will also affect demand. The change in social values is also important, since it is they that affect the subjective importance of information. Thus, a change in societal values can also cause a change in demand.
Technological factors. For this industry, the influence of technological factors on the emergence of new and change in the old ways of disseminating information is important. For example, the development of the Internet has led to the fact that the Internet resources of such newspapers can no longer remain just copies of printed publications, but have become separate projects important for maintaining the brand, and further development of the network and an increase in the number of users requires organizations to pay more attention to their Internet resources. .
Social, technological and economic factors of the external environment are of the greatest importance. Therefore, when developing an organization's strategy, it is necessary to pay special attention to them. Also, one should not forget about the political factors of the external environment, which are important today, but can also play their role in the development of the organization.
Let's build a BCG matrix for Interprof LLC. To do this, we use the information presented in Table 6.
Table 6 - Data for building the BCG matrix
|
Strategic business unit |
Sales volume, thousand rubles |
Market share |
market growth rate, |
Based on these data, we will build the BCG matrix (Figure 4).

Rice. 4 BCG matrix for LLC Interprof
Analyzing the matrix, we can draw the following conclusions:
Cash Cows (“Ads and Advertisements Placement in a Printed Publication”, “Ads and Advertisement Placement on an Internet Site”) - source stable income, which, however, does not have great prospects. The main strategy for these business units is to maintain the current level.
Based on the analysis of the external and internal environment, as well as the strategy of Interprof LLC, it is possible to identify the strengths, weaknesses and neutral aspects of the organization.
Strengths of the organization: full competence in key issues; a good impression of the company among customers and consumers; the ability to avoid (at least to some extent) strong pressure from competitors; Extensive experience in this market segment.
Neutral sides: adequate financial resources, a well-researched functional strategy.
Weaknesses: weak corporate culture, limited number of regular customers, high costs.
Summing up the presented analysis of the strategy implemented by the company, it can be noted that, in our opinion, the current strategic position of Interprof LLC and its VSE brand as a whole can be assessed as stable.
Under these conditions, the most preferred strategic option for the newspaper at the moment may be activities aimed at strengthening the brand and increasing the audience. The implementation of such a strategy seems to be the most promising, since it covers the most important market opportunities, new means of providing information, and at the same time relies on one of the main competitive advantages of the publication - an already existing strong brand.
- Golubkov E.P. On the concept of "strategy", its role and place in marketing planning // Marketing in Russia and abroad. - 2014. - No. 5. - S. 3-20.
- Bondarenko V. A., Voronova R. S. Substantiation of a number of measures to improve market sustainability for enterprises (on the example of Cargill LLC) // Concept. - 2015. - Special issue No. 16. - ART 75220..htm. - ISSN 2304-120X.
- Bondarenko V. A., Voronova R. S. Conducting a SWOT analysis in the market activity of a company on the example of Cargill LLC // Concept. - 2015. - Special issue No. 24. - ART 75295..htm. - ISSN 2304-120X.
- Fundamentals of Marketing. Kotler, Philip. Short Course. : Per. from English. - M.: Williams Publishing House, 2009. - 656p.
 Where can I place free advertising on the Internet?
Where can I place free advertising on the Internet?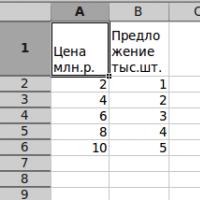 Proposal: supply factors, law The law of supply in brief
Proposal: supply factors, law The law of supply in brief "soft" corruption How to determine if there is nepotism in the administration
"soft" corruption How to determine if there is nepotism in the administration The SEVCO WMS computer system is a powerful and flexible warehouse management tool
The SEVCO WMS computer system is a powerful and flexible warehouse management tool How to open a nightclub from scratch: a business plan to help a beginner
How to open a nightclub from scratch: a business plan to help a beginner Different structure and density
Different structure and density Best-selling goods in Russia: statistics
Best-selling goods in Russia: statistics