What are the composition and structure of the personnel of the enterprise. General composition and types of personnel documentation Issued when applying for a job
Classification, composition and structure of the personnel of the enterprise
Enterprise Personnel- these are constantly participating in the production, economic, commercial and financial activities workers who have undergone certain vocational training and have work experience. Or is it a collection of individuals who are with the firm as legal entity in relations regulated by the contract of employment.
According to the accepted classification frames businesses fall into two categories :
industrial production staff(PPP), which includes persons directly related to the production - economic activity;
non-industrial personnel employees not directly associated with production activities enterprises (employees of housing and communal services, cultural and community institutions listed on the balance sheet of the enterprise, etc.)
In turn, the PPP, depending on the functions performed, is divided into the following categories of employees:
1. workers- persons directly involved in the process of material production . Depending on the functions they perform, they are divided into:
on major directly involved in the manufacture of products (machine operators, operators of automatic lines, etc.);
auxiliary performing various maintenance functions production process(adjusters, repairmen, warehouse workers, etc.).
2. Leaders- persons performing the functions of organizing and managing production (director, his deputies, heads of departments, workshops, shifts, foremen, etc.).
3. Specialists- employees who have completed higher or secondary specialized education and perform the functions of technical preparation for production, research, design, etc. (technologists, designers, economists, lawyers, etc.)
4. Employees- persons performing various functions of production management - preparation and execution of documentation, accounting and control, economic and administrative services, etc. (clerks, cashiers, secretaries, etc.).
At individual enterprises, students and security guards can be assigned.
According to the nature and complexity of the work performed, all personnel for the purposes of planning the need for personnel are grouped according to professions, specialties and qualifications.
и Under profession understand a certain type of activity of a person who owns a complex of special knowledge and practical skills that allow him to perform a certain type of work.
è Speciality- a set of knowledge within the profession (toolmaker, assembly fitter, plumber)
è Qualification- the degree and level of training of the employee. It characterizes the degree of complexity of this particular type of work performed by him. For specialists and employees, the level of qualification is determined on the basis of the level of special education with subsequent adjustment based on the results of the assessments. For workers, the level of qualification is the tariff category assigned to each according to the results of the tests carried out.
Personnel structure is the share of the corresponding group of employees in the total number of employees. Composition study work force also involves obtaining the appropriate structural characteristics for a number of demographic characteristics: gender, age, level of general and special education, etc. These data are necessary for the enterprise to develop personnel policy and staffing prospects. The personnel structure is studied and analyzed both for the enterprise as a whole and for its individual divisions.
Personnel composition enterprises are characterized by the following indicators:
1. List and attendance number of employees
2. Average headcount for a certain period
3. Specific gravity workers certain categories in the total number of SPPs
4. The growth rate of the number of workers for a certain period
5. Average category of workers
6. Average work experience of managers and specialists
7. Staff turnover for hiring and firing
To account for the number of employees at the enterprise, indicators of the payroll, average payroll, attendance and the actual number of employees are used. IN payroll includes all employees hired for permanent, seasonal, or temporary work for a period of 1 day or more from the date they were hired. In this list, each calendar day is taken into account both actually working and absent for any reason. Average headcount for the reporting month is calculated by summing up the number of employees on the payroll for each calendar day of the reporting month, i.e. from 1 to 31, including holidays and weekends, and dividing the amount received by the number calendar days reporting month. When determining the average headcount, full-time employees, part-time employees with a coefficient of 0.5 and employees working under work contracts are included.
For small enterprises, a simplified definition of the average number of employees is allowed as half the sum of data on their availability at the beginning and end of each reporting month. Turnout number shows how many people on the list showed up for work. Number actually working- this is the number of personnel who came to work and actually started working. The difference between the turnout and the actual number allows you to determine the whole-day downtime. The change in the headcount is due to the hiring and dismissal of employees.
Main reasons for dismissal workers are:
1. Causes of a physiological nature
2. Reasons provided by law (conscription into the army, admission to study, etc.)
3. Reasons related to the personality of the employee ( own wish, for absenteeism, in connection with a court decision, etc.)
To the main indicators characterizing personnel movement, relate:
1. Intensity factor receiving turnover:
where - the number of units of installed equipment;
Service rate characterizing the number of workers required to service a piece of equipment per shift;
Number of shifts;
Listing coefficient.
Human Resources Department is a structure in the organization that deals with personnel management.
The personnel department is not only a functional unit, it is also the face of the company, since it is in the personnel department that any applicant begins to get acquainted with the organization.
HR goal
The purpose of the personnel department is to contribute to the achievement of the goals of the enterprise (organization) by providing the enterprise with the necessary personnel and the effective use of the potential of employees.
The selection of employees is carried out with the help of specially developed strategies: submission of information about vacancies to the media and employment services, the use of selection methods, testing, procedures for the adaptation of specialists and subsequent advanced training.
Tasks of the personnel department
The main task of the personnel department is to correctly take into account the work of employees, determine the number of working, weekends and sick days for calculating salaries, vacations and submitting information to the accounting department of the organization.
The main tasks of the Human Resources Department are:
organizing the selection, recruitment and hiring of personnel with the necessary qualifications and in the required volume. The selection of employees is carried out using specially developed strategies: from submitting information about vacancies to the media and employment services to the application of selection, testing, adaptation procedures for specialists and subsequent advanced training;
creation effective system staff members;
development of career plans for employees;
development of personnel technologies.
In addition, the personnel department must submit information about employees to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, insurance companies, the Tax and Migration Services.
Functions of the Human Resources Department
The main function of the personnel department in the enterprise is the selection of personnel.
The main functions of the personnel department in the enterprise include:
determination of the needs of the organization in personnel and selection of personnel together with the heads of departments;
analysis of staff turnover, search for methods to deal with a high level of turnover;
introduction of labor motivation systems;
preparation staffing enterprises;
registration of personal files of employees, issuance of certificates and copies of documents at the request of employees;
carrying out operations with work books (receiving, issuing, filling out and storing documents);
keeping records of vacations, scheduling and processing vacations in accordance with the current labor law;
organization of employee attestation;
preparation of staff development plans.
HR structure
The structure of the personnel department of the enterprise and its number is determined by the director of each company, depending on total personnel and activities.
In small companies (up to 100 employees), one or two HR employees are sufficient.
At the same time, in small enterprises there may not be an individual employee, and then such work is performed by the chief accountant or general director.
In medium-sized organizations (from 100 employees to 500 people), it is advisable to create a personnel department of personnel from three to four personnel specialists
On the large enterprises where 500 or more people work, the personnel department may have from 7 to 10 employees.
Relationship between HR and other departments
To effectively perform their functions personnel service It is necessary to constantly and closely interact with other departments of the enterprise:
Interaction with the accounting department of the organization
The personnel department interacts with the organization's accounting department to resolve issues related to remuneration.
So, the personnel department submits documents and copies of orders for dismissal, employment, business trips, vacations, incentives or penalties for employees to the accounting department of the organization.
Liaison with the legal department
The Legal Department provides Human Resources staff with information about recent changes in the current legislation, provides comprehensive legal support.
Interaction with other divisions of the company
By personnel matters the personnel department constantly interacts with all structural divisions of the company.
Still have questions about accounting and taxes? Ask them on the forum "Salary and personnel".
Human resources department: details for the accountant
- The employee changed his mind about working in a new place? How to cancel an employment contract and employment relationship
00 minutes. We, the undersigned Head of the Human Resources Department Volkova O.N., Chief Accountant... 06.2019 No. 24-k. Send a notification to the specialist of the personnel department Gordeeva M.V. ... to assign this order to the head of the personnel department Volkova O.N. Reasons: ... Memorandum of the head of the personnel department Volkova O.N. dated 24 ... Ilyin Head of Human Resources Volkova, O. N. Volkova 26 ... need to get work book in the personnel department of MKU "Gorvodokanal". You also...
- Dismissal for absenteeism: controversial points
Colleagues) did not give a result. Head of the Human Resources Department Ivanova S. N. Reliability ... L. The following people are familiar with the order: - Head of the Human Resources Department Ivanova S. N.; - head of therapeutic ... absence. We ask you to provide an explanatory note to the head of the personnel department, Ivanova S.N. If written ... conduct an internal audit. Compiled by: the head of the personnel department, Ivanova S.N., in the presence of ... the employee also refused him. Head of the Human Resources Department Ivanova S. N. Reliability...
- Bypass sheet: application practice
He will not submit a signed bypass sheet to the accounting department (human resources department). As far as this ... he will not submit a signed bypass sheet to the accounting department (human resources department). How much given ... debts on undelivered books; in the personnel department on the delivery of the VHI policy; in ... include departments such as accounting, personnel department, warehouse, etc. As a rule ... applications for the dismissal of a civil servant, the personnel department issues a bypass sheet to the dismissed person (application ...
- What to do if an employee goes missing?
2019 We, the undersigned: Human Resources Inspector Petrova Elena Dmitrievna, Secretary Mishina... . Signatures of the persons who drew up the act: Inspector of the personnel department Petrova E. D. Petrova Secretary ...
- How to make a part-time worker the main employee?
Job According to the information available in the personnel department, you quit your main job ... Code No. 20 of the Russian Federation. Human Resources Specialist Koneva Limited Liability Company... Code No. 20 of the Russian Federation. Human Resources Specialist Koneva Limited Liability Company... Code No. 20 of the Russian Federation. HR Specialist Koneva Limited Liability Company...
- We appoint and register for the position of a contract manager correctly
12.12.2019 No. 55. Prepare for the HR specialist additional agreement to the labor ... of this order to assign to the head of the personnel department Mashkova S.S. Head Dmitriev ... . Dmitriev Acquainted with the order: Head of the Personnel Department Mashkova, S. S. Mashkova 10 ...
On 09/06/2018, submit to the personnel department a certificate from a medical institution confirming the fact ... the execution of the order is assigned to the head of the personnel department Egorova V. D. Reason: personal ... .) (signature) (full name) Head of the personnel department Egorova V.D. __________ /________________________ ... to donate blood and turned to the personnel department with a question about what ...
The growth of labor productivity largely depends on personnel, their level of qualification and attitude to work.
Industry Personnel include permanent employees in the field industrial production workers who have received appropriate professional training and have practical experience and work skills. They are divided into employees of industrial enterprises, industry management apparatus, employees of research, design, technological institutes and organizations.
The personnel of the enterprise (personnel, labor collective) is a set of employees included in its payroll.
Personnel of the enterprise consists of industrial and non-industrial personnel.
Determination of the need for personnel, their planning and accounting is carried out for the following categories of employees:
1. Workers (main and auxiliary).
2. Engineering and technical workers (managers and specialists).
3. Employees (technical performers).
4. Junior service personnel.
5. Security and students.
workers occupy the largest share in the total number of employees (3/4 of the part). The level of professional and qualification readiness of workers in conditions of tense balance labor resources is of particular importance, since it directly affects labor productivity.
Management, technical, economic and organizational management of the enterprise is carried out engineering and technical workers (ITR). Improvement of technology and organization of production and labor, introduction new technology involve the participation of architects, design engineers, technologists, mechanics, power engineers, specialists in automation, electronics, etc. Critical role belongs to linear engineers - foremen, foremen, etc.
Managers - employees holding the positions of heads of enterprises and their structural divisions(functional services), as well as their deputies.
Specialists - employees performing engineering, economic and other functions. These include engineers, economists, accountants, sociologists, legal advisers, raters, technicians, etc.
Category employees includes employees associated with accounting, finance, supply, storage of material assets, housekeeping, etc. These include clerks, clerk-typists, timekeepers, draftsmen, copyists, archivists, agents, etc.
Non-industrial personnel include employees employed in the non-industrial sphere of the enterprise: in housing and communal services, medical, educational, children's institutions, etc.
Depending on the nature labor activity the personnel of the enterprise are divided into professions, specialties and skill levels.
Profession- a certain type of activity (occupation) of a person, due to the totality of knowledge and labor skills acquired as a result of special training.
Speciality- a type of activity within a particular profession, which has specific features and requires additional special knowledge and skills from employees. For example: an economist-planner, an economist-personnel manager, an economist-financier. Or: fitter, fitter, plumber.
Qualification- degree and type vocational training employee, his knowledge, skills and abilities necessary to perform work or functions of a certain complexity, which is displayed in the qualification (tariff) categories and categories.
The quantitative characteristics of personnel is measured primarily by such indicators as payroll, attendance and average headcount workers.
payroll- this is the number of employees on the payroll on a certain date, taking into account the employees hired and left for that day.
Turnout number includes employees who report to work.
Average headcount employees per month is defined as the quotient of dividing the sum of all list data for each day by the calendar number of days in the month. However, on weekends and holidays the list number of employees on the previous date is shown.
In the conditions of continuous movement of personnel, which is caused by numerous reasons of an economic, social and demographic nature, the enterprise constantly has an additional need for employees and the stability of personnel can only be ensured by constantly replenishing those leaving.
The most important task is to retain personnel at the enterprise, since one of the reasons for the additional need for personnel is their turnover, i.e. withdrawal from the enterprise, which causes significant material and financial losses, adversely affects the volume and quality of products.
Consequently, reducing staff turnover and eliminating, on this basis, the loss of working time is tantamount to reducing the need for additional staff.
2. Labor productivity: the essence and methods of measurement.
The efficiency of the use of labor resources of an enterprise characterizes labor productivity, which is determined by the quantity of products produced per unit of working time, or labor costs per unit of output or work performed . IN market conditions labor productivity is the subject of negotiations and contracts between the administration of the enterprise and its labor collective under a special or collective agreement.
The main indicators of labor productivity at the enterprise level are indicators of production (B) and labor intensity (Tr) of products, which can be calculated using the formulas:
where: q - the volume of manufactured products or work performed in natural or conditionally natural units of measurement;
H cn - the average number of working people;
T is the time spent on the production of all products, standard hours.
Product development - This is the most common and universal indicator of labor productivity in industrial enterprises depending on the unit of measurement of production volume (q), there are three methods for determining output:
1. natural;
2. cost;
3. normalized working hours.
It is most clearly possible to characterize labor productivity by the indicator of output in in kind, measured in tons, meters, etc. If an enterprise produces several types of homogeneous products, then the output can be expressed in conditionally natural units.
But if the enterprise produces heterogeneous products, then the output indicator can be calculated only in value terms. .
In value terms, the output at the enterprise can be determined by the indicators of gross, marketable, net output, depending on the scope of this indicator. If the output cannot be measured either in physical units or in cost units, then the output indicator is determined in standard hours. Production can be:
1. hourly (per one worked man-hour);
2. day (worked man-day);
3. annual, quarterly or monthly (per one average
employee per year, quarter, month).
Labor intensity represents the cost of working time for the production of a unit of output in physical terms for the entire range of products and services . The labor intensity indicator has some advantages over the output indicator:
1. Firstly, it reflects a direct relationship between the volume of production and labor costs;
2. secondly, its application makes it possible to link the problem of measuring labor productivity with the factors and reserves of its growth;
3. thirdly, it allows you to compare labor costs for the same products in different shops and sections of the enterprise.
Depending on the composition of the costs included in the labor intensity of products, technological, production and total labor intensity, labor intensity of production maintenance and labor intensity of production management are distinguished.
Technological complexity reflects all the labor costs of the main pieceworkers and time workers.
Production labor intensity includes all labor costs of the main and auxiliary workers.
Full labor intensity reflects the labor costs of all categories of industrial and production personnel of the enterprise.
The labor intensity of production maintenance reflects the labor costs of auxiliary workers.
Labor intensity of production management- employee labor costs.
The personnel service (CS) of an organization is a structural association that performs the duties of controlling personnel. The initial task is to optimize the labor process.
The level of competence of the Constitutional Court and the limits of authority are divided as follows:
- Full subordination to the administrative manager (all coordinating schemes are in a single subsystem).
- Direct reporting to the director of the enterprise.
- It has the status of the second step in the vertical after the head.
- The CS is included in the management of the enterprise.
The organizational chart of the service depends on:
- activities;
- the number of employees by state;
- level of managerial potential of the CS.
Organizational structure of the personnel department
- Quick response to changes, additions.
- Optimization of the functions of employees with the transfer of direct control to the lower management level.
- Distribution, consolidation of appointments within the organization.
- Regulation of a rational number of employees subordinate to the manager.
- Compliance with the rights and obligations of employees.
- Clear distribution of organizational powers.
- Minimization of expenses of the management structure.
This is an incomplete list. The following groups of factors influence the scheme of work:
- Features of the device organization.
- Technologies, type of production.
- Style of corporate ethics.
- Developing or following effective existing patterns.
One or more factors can influence the design of a service organization. For the initial data, indicators are taken:
- The number of levels of leadership.
- State.
- Control type.
The structure of the personnel department combines two levels - functional and linear. The first type of management reflects the division between the management of the enterprise and other links. For its construction, fixing technological sequence production for each manager (or authorized person) apply the principle of the matrix.
Responsibilities of personnel officers
Job Responsibilities of these specialists are formulated in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The main attention is paid good governance regular resources:
- Building relationships.
- Evaluation of the suitability of the applicant for the position.
- Development of training programs and social projects for company employees.
These functions require regular internal innovations, training of specialists for the service, development of programs, and trainings.
Actions are due to the need for high-quality performance of a number of functional tasks:
- Establishing a qualification level in accordance with current economic requirements.
- Controlling the increase in workflow costs.
- Formation of corporate policy, taking into account the established multinational mix of employees.
- The HR Department deals with the settlement of working relations with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- Implementation of remote access to organization resources.
Conventionally, there are two functional areas of the CS:
- Control of relations in the team.
- Documentation of the employment contract.
 The first paragraph means:
The first paragraph means:
- State planning.
- Staffing of the enterprise.
- position held.
- Education, career workers.
- The system of encouragement in the social sphere.
- Compliance with safe working conditions.
The terms of the employment agreement must be recorded in the documents of the personnel department:
- Instructions, orders.
- Filling in established accounting information forms.
- Preparation and maintenance of labor documentation.
- Formation.
- Consulting services.
- Calculation of the schedule of working hours.
- Issuance of documents for payments (benefits, allowances).
The functional range of the CS requires a high-quality selection of its employees.
Organization of the work of the personnel department
 The number of specialists for the CS is justified by rational delimitation and stabilization labor process everyone a separate enterprise. To do this, use the "Qualification Handbook", which indicates the positions:
The number of specialists for the CS is justified by rational delimitation and stabilization labor process everyone a separate enterprise. To do this, use the "Qualification Handbook", which indicates the positions:
- management staff;
- specialists;
- technical performers.
For each there is a characteristic, including prescriptions:
- range of duties;
- special knowledge;
- qualification requirements.
The organization of work takes place in accordance with the level of complexity and volume of tasks. Each employee must have the knowledge and skills to:
- Full possession of information about the specifics of the enterprise.
- Management and leadership qualities.
- Learnability.
- Possession of the basics of financial formation.
- Diplomatic skills.
 CS organizations provide the following vacancies:
CS organizations provide the following vacancies:
- Head of Human Resources Department.
- Manager:
- for personnel work;
- social benefits;
- compensation;
- Specialist:
- on work with applicants;
- learning;
- employment;
- personnel management.
The availability of positions is determined by the specifics of the enterprise and the functional tasks of the personnel service.
To carry out the production process, three factors or economic resources are necessary:
- means of labor (OPF);
- objects of labor (OS);
- labor resources.
Human resources is a broad concept. This is the population of working age, not employed in manufacturing or non-manufacturing sphere. Persons of working age involved in production are called production personnel.
The quality of products, the costs of their production and, ultimately, the efficiency of production depend on the composition of personnel, their structure, qualifications, and attitudes towards work.
All workers in production are divided into 2 groups:
1) industrial and production personnel (these are people directly involved in production);
2) non-industrial personnel. This group includes workers serving non-industrial facilities and enterprise organizations (ZhKO, children's institutions, vocational schools, clubs, medical units, subsidiary farms etc.).
Depending on the functions performed, the PPP is divided into the following categories:
- workers;
- managers and specialists;
- employees;
- security, students.
Depending on the participation in production, workers are divided into Main AND Auxiliary.
Essential Workers Directly carry out technological processes manufacturing products, that is, they affect the object of labor and control production equipment.
Auxiliary workers Carry out repair of equipment, instrumentation, control over the course of the process, the quality of raw materials and products, transportation, movement of raw materials, materials and finished products, that is, they perform the functions of maintenance and production support.
Managers and specialists They perform the functions of management, planning, technical and organizational management of production: these are shop managers, technologists, mechanics, power engineers, economists, employees of functional services and departments. In the number of SPPs, they account for approximately 14% ( chemical industry), 11% (PSM).
Employees. This category includes workers performing accounting, clerical and economic work (accountants, typists, employees of the AHO). They account for approximately 3% of the total number of PPPs.
MOS- these are workers engaged in consumer services for workers (cloakroom attendants, cleaners of industrial premises, janitors, etc.).
VOKhR and students- employees of guard and fire protection, apprentices - persons, regardless of age, undergoing individual or team production training directly at the enterprise. The share in the number of SPPs of the last two groups is approximately 3%.
The main and auxiliary workers differ in profession, specialty and qualifications.
Profession is a type of work activity that requires special training for work in this industry.
The profession includes Specialties. For example, the profession of a locksmith includes specialties: assembler, repairman, toolmaker, plumber, etc.
Qualification Means a set of knowledge, skills and abilities to perform certain work. It is characterized by a tariff category.
A modern worker deals with a large flow of information, therefore, he must have not only general and professional knowledge, but also the ability to correctly perceive and interpret information, and quickly respond to its changes.
In modern conditions, the requirements for specialists with higher education. They must be able to think economically, master new methods of management, study system analysis and issues of production management in market conditions, to acquire knowledge in the field of sociology, psychology, law, financing, foreign economic activity.
Periodic certification of specialists, the system of training and retraining of personnel are aimed at solving these problems.
The personnel structure is understood as the percentage ratio of the number of each of the listed categories to the total number of PPPs. The structure of personnel is changing as a result of the scientific and technical progress (the share of engineering and technical workers is increased, the share of auxiliary workers and the share of workers engaged in heavy unskilled labor in the number of workers is reduced).
Analysis of the structure of personnel allows you to determine the need for them, plan their training.
 About freaks and people: indecent pictures of Diane Arbus
About freaks and people: indecent pictures of Diane Arbus How to take amazing photos
How to take amazing photos How to photograph waterfalls How to photograph a fountain with a DSLR
How to photograph waterfalls How to photograph a fountain with a DSLR About Steve McCurry and his photos
About Steve McCurry and his photos How I became a photographer (and what it takes)
How I became a photographer (and what it takes) How to take pictures with an external flash
How to take pictures with an external flash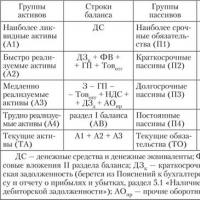 The essence and significance of the liquidity and solvency of the enterprise
The essence and significance of the liquidity and solvency of the enterprise