State standard of ferrous metals (download). Gost scrap of ferrous metals (download) Scrap for construction gost 1405 83
Approved
By the decree of the USSR State Construction Committee
STATE STANDARD OF THE UNION OF SSR
STEEL CONSTRUCTION SCRAP
TECHNICAL CONDITIONS
Pinch and wrecking steel bars. Specifications
GOST 1405-83
Group W 36
OKP 48 3320
Date of introduction
INFORMATION DATA
1. Developed and submitted by the Ministry of Construction, Road and Municipal Engineering.
Developers: V.V. Kulagin, N.I. Fedorov.
2. Approved and put into effect by the Decree of the USSR State Committee for Construction Affairs dated 02.21.1983 N 28.
3. Instead of GOST 1405-72.
4. Reference normative and technical documents
──────────────────────────────────────────────┬──────────────────
──────────────────────────────────────────────┼──────────────────
GOST 2.601-68│5.5
GOST 8.051-81│4.1
GOST 9.014-78│5.2
GOST 9.032-74│2.8
GOST 9.104-79│2.8
GOST 9.301-86│2.8
GOST 9.302-88│4.6
GOST 9.303-84│2.8
GOST 9.306-85│2.8
GOST 380-88│2.2
GOST 1050-88│2.2
GOST 2590-88│2.2
GOST 2879-88│2.2
GOST 3282-74│5.3
GOST 5631-79-2.8
GOST 7829-70│1.2
GOST 9013-59│4.4
GOST 15150-69│5.7
5. Reissue.
This standard applies to steel scrap used in construction in the production of construction and installation, rigging and other works.
1. TYPES AND MAIN DIMENSIONS
1.1. Scrap, depending on the purpose, should be made of the following types, indicated in table. one.
Table 1
─────┬─────────────────┬──────────────────────────────────────────
Type │Name│Appointment
─────┼─────────────────┼──────────────────────────────────────────
LG│Crowbar-nail clipper│ For pulling out nails during production
││ formwork and carpentry works
LM│ Assembly scrap For displacement and installation of elements, the assembly
Different building structures during installation
Buildings and structures and in production
││ rigging works
LOLom ordinary │ For loosening dense, frozen and rocky
││ primers, as well as in the production
││ rigging works
1.2. The main dimensions of the crowbars must correspond to those indicated in the drawing. 1 - 8 and in table. 2 - 4.
Crowbar-nailers type ЛГ
Standard sizes LG16, LG20, LG24
Crap. one
Note. Size (45 +/- 3) ° - reference.
Standard sizes LG15, LG19, LG22

Crap. 2
The rest of the dimensions - as hell. one.
Standard size LG16A

Crap. 3
Weight - no more than 0.8 kg.
Standard size LG15A

Crap. 4
Weight - no more than 0.78 kg.
The rest of the dimensions - as hell. 3.
Assembly crowbars, type LM
Standard sizes LM20, LM24, LM32

Crap. 5
Sizes LM19, LM22, LM30
Crap. 6
The rest of the dimensions - as hell. 5
Ordinary scrap type LO
Standard sizes LO24, LO28, LO32

Crap. 7
Standard sizes LO22, LO26, LO30
Crap. eight
The rest of the dimensions - as hell. 7.
table 2
Dimensions in mm
─────┬───┬───┬────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬───────┬─────┬─────┬──────
Like-│ D │ S │ L│Н│Н │а│а│b│l│R│ R│с│Mass,
times- │││││1 ││1 ││││1││kg, not
measure││││ +/- 5│ +/- 5│ +/- 3│ +/- 1│ +/- 2│ +/- 3│ +/- 0.5│ +/- 1│ +/- 1│more
LG16 │16 │-│320 │90│70│30│5│18│20│1.4│6│2.5│0.58
LG15 │-│15 │││││││││││0.57
─────┼───┼───┼────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼───────┼─────┼─────┼──────
LG20 │20 │-│600 │90│85│34│6│22│20│1.6│7.5│2.5│1.7
─────┼───┼───┤│││││ ││││├──────
LG19 │-│19 │││││││││││1.65
─────┼───┼───┼────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼───────┼─────┼─────┼──────
LG24 │24 │-│1000│110│100│45│8│28│30│2.1│9│3│3.9
─────┼───┼───┤│││││││││├──────
LG22 │-│22 │││││││││││3.7
Table 3
Dimensions in mm
─────┬───┬───┬────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬──────
Like-│ D │ S │ L│l│l│l│l│а│а │R│Mass,
times- │││││1 │2 │3 ││1 ││kg, not
measure││││ +/- 5│ +/- 5│ +/- 3│ +/- 3│ +/- 3│ +/- 1│ +/- 5│more
LM20 │20 │-│560 │30│80│15│70│32│6│20│1.35
─────┼───┼───┤│││││││├──────
LM19 │-│19 │││││││││1.35
─────┼───┼───┼────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼──────
LM24 │24 │-│1180│40│100│20│90│38│8│24│4.2
─────┼───┼───┤│││││││├──────
LM22 │-│22 │││││││││3.9
─────┼───┼───┼────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼──────
LM32 │32 │-│1320│50│110│20│100│45│10│32│8,4
─────┼───┼───┤│││││││├──────
LM30 │-│30 │││││││││8.2
Table 4
Dimensions in mm
──────┬──────┬──────┬──────┬──────┬──────┬──────┬──────┬──────────
Like- │D│S│L│l│ l │а│b│Mass, kg,
size│││││1│││not more
││││+/- 5 │+/- 5 │+/- 3 │+/- 3 │
LO24│24│-│1180│40│30│20│25│4.2
LO22│-│22││││││4.0
──────┼──────┼──────┼──────┼──────┼──────┼──────┼──────┼──────────
LO28│28│-│1400│55│40│25│30│6.8
──────┼──────┼──────┤││││├──────────
LO26│-│26││││││6.7
──────┼──────┼──────┼──────┼──────┼──────┼──────┼──────┼──────────
LO32│32│-│1400│70│53│30│35│9.4
──────┼──────┼──────┤││││├──────────
LO30│-│30││││││9.2
Limit deviations of the dimensions of the working part of the scrap that are not indicated in the drawings must comply with GOST 7829. The tolerance for the length of the scrap must not be more than +/- 1%.
1.3. Scrap symbols shall consist of the designation of the standard size of the scrap and this standard.
An example of a conventional designation of a scrap of standard size LG15:
LG15 GOST 1405-83
2. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
2.1. Scrap should be made in accordance with the requirements of this standard according to working drawings and standard samples, agreed with the base organization for standardization and approved in the prescribed manner.
2.2. Scrap should be made of steel grades 45 or 50 in accordance with GOST 1050.
The requirements for the range of steel must not be lower than the requirements established by GOST 2590 or GOST 2879.
It is allowed to make scrap from steel grades St6ps, St6sp in accordance with GOST 380 and from other grades, the mechanical properties of which are not lower than those of steel of the indicated grades.
2.3. Scrap should not have cracks, sunsets, hairs, captivity, inclusions.
Separate dents from scale are allowed on the surface of scrap processed by hot forging or stamping.
2.4. The ends of crowbars with a length of at least 150 mm must be heat-treated and have a hardness of 40 ... 47 (HRC 38 ... 46).
2.5. When pulling out the nails, the nail-pulling parts of scrap type ЛГ should not change the geometric shape and crumble. On their surfaces, after pulling out the nails, there should be no kinks, cracks and spalls.
2.6. The straightness tolerance of straight sections of scrap should not exceed 1% of their length.
2.7. Sharp edges of crowbars must be blunt.
2.8. Scrap must have a cover X im. Oaks. prm. according to GOST 9.306 or BT-577 coating according to GOST 5631. The oxide coating must comply with GOST 9.301, operating conditions - group 3 according to GOST 9.303.
The paintwork must correspond to class V in accordance with GOST 9.032, operating conditions - to group U1 in accordance with GOST 9.104.
It is allowed to use other coatings that provide anticorrosive protection of products.
3. RULES OF ACCEPTANCE
3.1. The scrap must be accepted by the technical control of the manufacturer.
3.2. Acceptance and delivery of scrap is carried out in batches.
The size of the lot is established by agreement of the parties.
A batch must consist of scrap of the same standard size, made of the same materials, processed according to the same technological process and simultaneously presented for acceptance according to one document.
3.3. When checking scrap for compliance with the requirements specified in paragraphs. 1.1, 1.2, 2.1 (in terms of compliance with working drawings), 2.4 - 2.6, two-stage control is used, for which scrap is taken from the batch in accordance with table. 5.
Table 5
────────────┬──────────┬──────────┬───────────┬─────────┬─────────
Size Steps Volume one- │Volume two │Receiving - │ Rejection -
batch control │ different choice- │ samples,
crowbars, pcs. ││ki, piece piece
51 - 90│Pervaya│8│16│0│2
│Second8││1│2
────────────┼──────────┼──────────┼───────────┼─────────┼─────────
91 - 150│First13│26│0│3
├──────────┼──────────┤├─────────┼─────────
│Second13││3│4
────────────┼──────────┼──────────┼───────────┼─────────┼─────────
151 - 280│First│20│40│1│4
│Second4│5
────────────┼──────────┼──────────┼───────────┼─────────┼─────────
281 - 500│First│32│64│2│5
├──────────┤│├─────────┼─────────
│Second6│7
────────────┼──────────┼──────────┼───────────┼─────────┼─────────
501 - 1200│First│50│100│3│7
├──────────┤│├─────────┼─────────
│Second8│9
3.4. A batch of scrap is accepted if the number of defective scrap in the first sample is less than or equal to the acceptance number, and rejected without assigning a second sample if the number of defective scrap is greater than or equal to the rejection number.
If the number of defective scrap in the first sample is more than the acceptance number, but less than the rejection number, a second sample is carried out.
A batch of scrap is accepted if the number of defective scrap in two samples is less than or equal to the acceptance number, and rejected if the number of defective scrap in two samples is greater than or equal to the rejection number.
3.5. Checking scrap for compliance with the requirements specified in paragraphs. 2.1 (in terms of compliance with reference samples), 2.3, 2.7, 2.8 should be carried out by the method of continuous control.
3.6. The consumer has the right to carry out a control check of the quality of scrap, applying the sampling procedure and test methods specified in this standard.
4. CONTROL METHODS
4.1. The dimensions of the scrap should be checked using measuring instruments, the measurement errors of which do not exceed:
The values specified in GOST 8.051 are for linear dimensions;
25% of the tolerance for the controlled size - for the deviation of the shape and location of surfaces.
4.2. The mass of scrap should be determined by weighing on a scale.
The limits of permissible error of mass measurements are +/- 0.02 kg.
4.3. Continuous scrap control is carried out visually - by comparing them with standard samples.
4.4. Determination of the hardness of heat-treated areas of scrap - in accordance with GOST 9013.
4.5. The strength of the claw part of the scrap (clause 2.5) is checked by alternately pulling out 5 nails with a diameter of 4 or 5 mm and a length of 120 to 150 mm, driven to a depth of 100 to 125 mm into birch or other wood of similar hardness.
4.6. Control of oxide coatings - in accordance with GOST 9.302.
5. MARKING, PACKAGING, TRANSPORTATION AND STORAGE
5.1. On the surface of each scrap should be applied:
Manufacturer's trademark;
Scrap type or size;
Price (when making a retail product).
Note. The method of applying these markings must ensure its safety during the entire service life of the scrap.
5.2. Oxide-coated scrap must be preserved in accordance with GOST 9.014. The term of protection of scrap without holding re-preservation must be at least one year old.
5.3. Scrap of the same size is placed in bundles and tied in at least two places with low-carbon steel wire in accordance with GOST 3282.
To avoid damage to the coating on the surface of the crowbars, thick paper should be placed under the wire. In bundled bundles, crowbars should not move.
5.4. By agreement with the consumer, other packaging of scrap is allowed, ensuring their safety from mechanical damage during transportation and storage.
5.5. Each pack must have a label in accordance with GOST 2.601.
5.6. Scrap can be transported by any type of transport.
5.7. Scrap storage - according to storage conditions group C in accordance with GOST 15150.
Notes:
1. The average chemical composition of waste two-layer steels is given in table. 7.
2. Scrap and waste of free-cutting steel shall be collected separately and supplied only for the smelting of this steel.
3. In the groups shown in table. 5, in which copper is not regulated, its residual content should not exceed 0.30%.
2.9. The chemical composition of charge ingots must meet the requirements of table. 5 and normative and technical documentation approved in the prescribed manner, according to table. 6.
2.10. Scrap and waste of high-alloy steel and alloys, which, in terms of chemical composition, cannot be assigned to the groups given in table. 5, must be surrendered and delivered blotted. The main brands are shown in table. 6.
Table 6
Standard designation |
||
38Х2МЮА (38ХМЮА) | GOST 4543-71 |
|
20X1M1F1TR (EP182) | GOST 20072-74 |
|
0ХН3В, 38ХН3В * | ||
4Х8В2 (ЭИ 160) ** | ||
GOST 5950-73 |
||
GOST 5950-73 |
||
GOST 19265-73 |
||
GOST 19265-73 |
||
R9K10 (EI920) | GOST 19265-73 |
|
R18F2K8M (EP379) * | ||
GOST 19265-73 |
||
GOST 19265-73 |
||
R6F2K8M5 (EP658) * | ||
R18K5F2 (R18K5F) | GOST 19265-73 |
|
06X20N11M3TB (EP89) | GOST 2246-70 |
|
03Х21Н21М4GB | GOST 5632-72 |
|
95X18 (9X18, EI229) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
10H14AG15 (DI-13) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
15KHSMFB (EP79) * | ||
03XN28MDT (000X23N28M3D3T, EP516), 06XN28MDT (0X23N28M3D3T, EI943, EP591) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
GOST 5950-73 |
||
15Х11МФ (1Х11МФ, EP369) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
25Х13Н2 (2Х14Н2, ЭИ474) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
09X16N4B (1X16N4B, EP56, 1X17N4B) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
Kh15N5D2T (EP225, VNS-2, EP410) * | ||
Neresist (Ж4НДХ 15-7-2) * | ||
80X20NS (EI992) * | ||
12X18N10E (X18N10E, EP47, EI452, EI453) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
0Х18Н12ТФ (ЭИ953) * | ||
GOST 5950-73 |
||
10X11N20T3R (X12H20T3R, EI696), X12N20T2R (EI696A), | GOST 5632-72 |
|
12X25N16G7AR (X25N16G7AR, EI835) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
36Х18Н25С2 (4Х18Н25С2) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
13Х14Н3В2ФР (ЭИ736) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
1X15N4AM3 (EP310, VNS-5) * | ||
Kh20N6MD2T (EP309) * | ||
31Х19Н9МВБТ (ЭИ 572) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
37H12N8G8MFB (4H12N8G8MFB, EI481) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
40X15N7G7F2MS (4X15N7G7F2MS, EI388) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
0X20N12ABF * | ||
10Х11Н23Т3МР (Х12Н22Т3МР, EP33) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
GOST 5632-72 |
||
KhN28VMAB (Kh21N28V5M3BAR, EP126, VZh 100) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
KhN30VMT (VK 102, EP437) * | ||
48AN1 (Kh18N22V2T2) * | ||
KhN35VT (EI 612) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
KhN35VTYu (EI 787) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
KhN38VT (EI 703) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
12Х12Н12Г6 (ЭИ 429, Н12ХГ) | GOST 9124-85 |
|
40N, 42N, (N42, EP 318), 45N | GOST 10994-74 |
|
50N, 52N (EI676) | GOST 10994-74 |
|
GOST 10994-74 |
||
GOST 10994-74 |
||
19NX, 20NG, 24NX | GOST 10994-74 |
|
GOST 10994-74 |
||
GOST 10994-74 |
||
77НМД (ЭП 233) | GOST 10994-74 |
|
GOST 10994-74 |
||
GOST 10994-74 |
||
49K2F (50KF, EP 207) | GOST 10994-74 |
|
TU 14-1-4487-88 |
||
EX9K15M2 (EX9K15M) | TU 14-1-4487-88 |
|
52K5F (52KF5) * | ||
52K7F (52KF7) * | ||
52K9F (52KF9) * | ||
52KF12 (52KFB) | GOST 10994-74 |
|
36N (N36, N36L) | GOST 10994-74 |
|
32NKD (EI 630A, N30K4D) | GOST 10994-74 |
|
GOST 10994-74 |
||
30NKD (N30K13D) | GOST 10994-74 |
|
33NK (N33K17, EP 139) | GOST 10994-74 |
|
47НХР (Н47ХР, Н47ХБ) | GOST 10994-74 |
|
GOST 10994-74 |
||
47NX (N47X, EI 677, EI563) | GOST 10994-74 |
|
42NA (Feni 42, EP333) | GOST 10994-74 |
|
40KHNM (K40HNM) | GOST 10994-74 |
|
36НХТЮ (ЭИ 702) | GOST 10994-74 |
|
36NKHTYu5M (36NKHTYuM5, EP51) | GOST 10994-74 |
|
36NKHTYu8M (36NKHTYuM8, EP52) | GOST 10994-74 |
|
42НХТЮ (Н41ХТ), 44НХТЮ (Н43ХТ) | GOST 10994-74 |
|
97 NL (EI 996) | GOST 10994-74 |
|
NIM025 (EI 639) * | ||
Kh20N46B (EP 350) * | ||
KhN60VT (EI868) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
KhN78T (EI 435) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
KhN60Yu (EI 559A) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
KhN70Yu (EI 652) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
KhN77TYUR (EI 437B, EI 437, EI437A) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
ХН80ТБЮ (ЭИ 607) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
KhN75TBYU (EI 869) * | ||
KhN67VMTYu (EP202) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
KhN70VMYUT (EI 765) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
KhN70VMTYu (EI 617) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
KhN70MVTYUB (EI598) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
KhN65VMTYu (EI893) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
KhN70VMTYu (EI826) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
KhN75MBTYu (EI602) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
KhN73MBTYu (EI698) * | ||
KhN56VMTYu (EP199) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
KhN55VMTKYU (EI929) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
KhN56VMKYU (EP109) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
ХН62МВКЮ (ЭИ867) | GOST 5632-72 |
|
GOST 10994-74 |
||
GOST 10994-74 |
||
VKS210 (EP637) * | ||
GOST 5950-73 |
||
40G18U3F (EP112) * | ||
4X2V2MFS (EP641, 45X2SV2MF) | GOST 5950-73 |
|
* According to the normative and technical documentation approved in accordance with the established procedure.
** According to the replaced GOST 5950-63.
*** According to table 7 of this standard.
Notes:
1. In charge ingots, the following deviations in terms of the minimum and maximum content of alloying elements from those indicated in table are allowed. 5 and in the standards given in table. 6:
± 0.2% - for chromium with its content up to 10%;
± 0.5% - for chromium when its content is over 10%;
± 0.15% - for nickel with its content up to 5%;
± 0.4% - for nickel with its content exceeding 5%;
± 0.1% - for tungsten with its content up to 2%;
± 0.25% - for tungsten when its content is over 2%;
± 0.05% - for molybdenum with its content up to 1%;
± 0.15% - for molybdenum when its content is over 1%.
2. In the designations of steel grades given in table. 5 and 6, the last letter A for high quality steel has been omitted. Steels of high quality grades are included in the same waste group as steels of these grades of normal quality.
Old designations of steel grades are indicated in brackets.
3. The designation of alloyed scrap and waste of a certain type and group consists of the type number and the designation of the group.
For instance:
steel scrap and waste No. 2 of B26 group will have the designation 2B26.
Alloyed scrap and waste of a certain type have a seven-character code, in which the code of the waste group or the code of the metal grade is added to the general code of the class, category and type.
For instance:
steel scrap and waste No. 2 of B26 group will have the code 1212026, steel scrap and waste No. 2 of grade X15N60-1212191.
2.11. Scrap and waste of two-layer steels, which are alloyed according to the average chemical composition, are distributed in accordance with the requirements of Table. 7.
Table 7
Designation of waste double layer steels | Main layer steel grade | Cladding steel grades | Average chemical composition of the mass of two-layer steel,% | Designation of the corresponding waste group |
VSt3, 10, 20K, 09G2, 09G2S (M), 16GS (3N) | 08Х13 (ЭИ 496, 0Х13) | Chromium - 1.3 - 1.5 | ||
VSt3, 20K, 10 | Chromium - 1.7 - 1.9 | |||
08Х13 (ЭИ 496, 0Х13) | Chrome - 1.5 - 2.5 | |||
Nickel - up to 0.30 Molybdenum - 0.3 - 0.6 |
||||
VSt3, 20K, 09G2T (M) | 08Х18Н10Т, 12Х18Н10Т | Chromium - 1.3 - 2.0 | ||
Nickel - 0.8 - 1.5 |
||||
Manganese - up to 1.3 |
||||
VSt3, 20K, 09G2S, 16GS | Chromium - 2.4 - 2.8 | |||
10HSND (SHL-4) | 08Х18Н10Т, 12Х18Н10Т | Chromium - 2.2 - 2.7 | ||
Nickel - 1.0 - 2.0 |
||||
Copper - 0.3 - 0.6 |
||||
08Х18Н10Т (0Х18Н10Т, ЭИ914) | Chromium 2.0 - 2.6 | Blotted |
||
Nickel - 0.8 - 1.2 |
||||
Molybdenum -> 0.3 - 0.6 |
||||
16GS (3N), 09G2S (M) 20K, 09G2S, VSt3 | 10Х17Н13М2Т, 10Х17Н13М3Т, 08Х17Н15М3Т | Chrome - 1.6 - 2.0 | ||
Nickel - 1.2 - 1.8 |
||||
Molybdenum - 0.2 - 0.4 |
||||
Chromium - 2.2 - 2.6 | Blotted |
|||
Nickel - 2.6 - 3.0 |
||||
Molybdenum - 0.2 - 0.4 |
||||
Copper - 0.2 - 0.4 |
||||
Chromium - 1.5 - 1.8 | Blotted |
|||
Nickel - 6.0 - 6.8 |
||||
Molybdenum - 1.4 - 1.8 |
||||
Tungsten - 0.2 - 0.5 |
||||
Nickel - 6.4 - 7.0 | Blotted |
|||
Chrome - no more than 0.2 |
||||
Molybdenum - 2.4 - 3.0 |
||||
Vanadium - 0.1 - 0.2 |
||||
Chromium - 1.8 - 2.4 | Blotted |
|||
Nickel - 7.0 - 7.6 |
||||
Monel: NMZhMts 28 - 2.5 - 1.5 | Nickel - 6.0 - 10.0 | Blotted |
||
Copper - 2.6 - 3.0 |
||||
Nickel - 10.0 | Blotted |
3. RULES OF ACCEPTANCE
3.1. Secondary ferrous metals are presented for acceptance in lots.
3.2. A batch is the amount of secondary ferrous metals of one type and one group or brand, shipped in one unit of vehicles and accompanied by one quality document.
A lot of scrap and waste of high-alloy steel and special alloys is the amount of scrap and waste shipped in one packaging unit.
3.3. Acceptance of secondary ferrous metals should be carried out by metal weight. The weight discount for contamination with harmless impurities and oil should be made in accordance with the actual contamination determined during acceptance.
3.4. To check the compliance of secondary ferrous metals with the requirements of this standard in terms of their composition, purity, dimensions, weight, density, crumbling and limiting content of alloying elements, five bags or briquettes are taken from the batch, and for other types of scrap and waste, sampling is carried out by agreement of the parties.
3.5. Upon receipt of unsatisfactory test results for at least one of the indicators for it, repeated tests are carried out on a doubled number of samples or a doubled sample taken from the same batch. Retest results are final and apply to the entire batch.
4. TEST METHODS
4.1. The composition of the batch of secondary ferrous metals presented for acceptance is checked visually.
4.2. The contamination of secondary ferrous metals with harmless impurities and oil is determined by agreement between the consumer and the supplier by methods that ensure the correct determination of the amount of contamination.
The contamination is checked by weighing the taken samples.
4.3. The contamination of bags and briquettes with harmless impurities and oil is checked after destruction by breaking or cutting.
4.4. To determine the dimensions and mass of secondary ferrous metals, they are measured and weighed. The density of bags and briquettes is defined as the ratio of the mass of a bag or briquette to its volume.
4.5. To determine the crumbling of briquettes, they are thrown three times (by free fall) from a height of 1.5 m onto a metal or concrete slab, while they should not crumble by more than 10%. Out of five discarded briquettes, at least four briquettes must withstand the test. If the test results are unsatisfactory, eight briquettes should withstand the test from 10 re-dumped briquettes.
4.6. To determine the content of alloying elements and other elements limited in the relevant standards, samples are taken from at least five locations in the batch.
The permissible deviation in chemical composition in the content of an individual element in two samples should not exceed 15% of the lower or upper limits of the studied group indicated in table. 5.
The arithmetic mean of the results of all determinations, which should be within the study group, is taken as the result of the analysis.
Note. Sampling in bags and briquettes is carried out from the outer and inner parts after the cut.
4.7 The chemical composition of secondary ferrous metals is determined according to GOST 12344-88, GOST 12345-88, GOST 12346-78, GOST 12347-77, GOST 12348-78, GOST 12349-83, GOST 12350-78, GOST 12351-81, GOST 12352 -81, GOST 12353-78, GOST 12354-81, GOST 12355-78, GOST 12356-81, GOST 12357-84, GOST 12358-82, GOST 12359-81, GOST 12360-82, GOST 12361-82, GOST 12362 -79, GOST 12363-79, GOST 12364-84, GOST 12365-84 (for steel), GOST 28473-90 and GOST 2604.1-77, GOST 2604.2-86, GOST 2604.3-83, GOST 2604.4-87, GOST 2604.5 -84, GOST 2604.6-77, GOST 2604.7-84, GOST 2604.8-77, GOST 2604.9-83, GOST 2604.10-77, GOST 2604.11-85, GOST 2604.13-82, GOST 2604.14-82 (for cast iron) or by other methods, providing the required accuracy of determination.
4.8. If alloying elements not specified in this group are found in a sample or sample, the batch belongs to this group if the content of each of these elements does not exceed the upper limit provided for steel grades by the relevant standards or other regulatory and technical documentation.
5. MARKING, PACKAGING, TRANSPORTATION AND STORAGE
5.1. Each batch of secondary ferrous metals must be accompanied by a document certifying their compliance with the requirements of this standard and including:
a) the name of the shipping company;
c) date of dispatch;
d) car number;
A batch of secondary ferrous metals shipped from enterprises using radioactive substances in the production process must be accompanied by a decontamination document.
In the shipping documents, an inscription must be made: for alloyed scrap and waste - "Doped scrap for remelting" or "Doped scrap for processing", for carbon ones - "Carbon scrap for remelting" or "Carbon scrap for recycling".
(Modified edition, Amendment No. 3).
5.2. Scrap and waste of high-alloy steel and special alloys must be shipped packed in specialized containers in accordance with the normative and technical documentation. At the same time, in addition to the shipping and accompanying documents, a marking label is applied to the batch of scrap and waste, which indicates the mass, group of waste or metal grade.
Transport marking - in accordance with GOST 14192-77.
(Modified edition, Amendments No. 3, 4).
5.3. The supplied charge ingots must be marked individually with the indication of the heat number.
5.4. Secondary ferrous metals should be stored separately by types and groups or brands.
During storage, scrap metal and waste should not be mixed with non-metallic materials.
5.5. The oily shavings should be disposed of in dumps in the area of the site equipped with sedimentation tanks for oil, or in bins with an oil drain.
5.6. Secondary ferrous metals, including packages, are transported in bulk.
5.7. Secondary ferrous metals are transported by all types of transport in open vehicles in accordance with the rules for the carriage of goods in force for this type of transport.
Secondary ferrous metals are loaded into wagons and placed in them in accordance with the technical conditions for loading and securing goods approved by the USSR Ministry of Railways.
5.6, 5.7. (Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 4).
6. REQUIREMENTS FOR ENSURING EXPLOSION PROTECTION
6.1. Enterprises, organizations and farms that procure, hand over, process and remelt secondary ferrous metals, as well as unload or reload them in ports and other points, must check all secondary ferrous metals for explosion safety and remove from them all items containing explosive flammable and flammable substances.
Inspection of scrap metal delivered by schools, hospitals, etc. institutions should be produced by procurement organizations.
6.2. Deactivated explosive items must meet the following requirements.
6.2.1. Ammunition (shells, mines, warheads, aerial bombs, etc.) must not have explosive devices, must have an open goggle, an unscrewed bottom, and an empty chamber; their inner surface must be cleaned of explosives and special compounds; in shrapnel machines and jet mines, the inner baffle (diaphragm) must be removed.
6.2.2. The barrels of artillery and small arms must be with open through channels or deformed at the end of the barrel and breech (receiver) to a complex bend.
6.2.3. Store boxes of artillery and small arms must be open and empty or bruised (to the point of cracking).
6.2.4. Artillery and small arms cases must not have means of ignition (capsule sleeves, galvanic and galvanic shock tubes, etc.) and the remains of powder charges.
6.2.5. All types of military equipment handed over for scrap by military units must be written off in accordance with the established procedure of the USSR Ministry of Defense, rejected, disassembled and freed from combustible and lubricants, and the ammunition, solid fuels, initiators and other explosives contained in them must be removed ; the fluid from the cylinders of hydraulic, brake, anti-rollback and other devices must be drained.
6.2.6. Vessels of all types and sizes (cylinders, barrels, etc.) and all hollow objects (engine cylinders, etc.) must be cleaned of contents (and in winter - from ice and snow) and are accessible for inspection of the inner surface ; the necks of the cylinders must be open, and a second hole must be cut on their body; the bottoms of barrels and other containers must be opened.
6.2.7. Capacities of machine components (engines, gearboxes, etc.) must be free from residues of combustible and lubricants.
6.2.8. Beds, pallets, metal structures and other massive objects subjected to explosive crushing must not have unexploded charges or their remains.
6.3. If non-neutralized ammunition is found, further work with scrap metal should be suspended and measures should be taken to remove, neutralize or destroy them by representatives of the military unit.
6.4. Inspection of scrap and waste of ferrous metals for explosion safety and removal of explosive objects from them (except for those specified in clause 6.3) must be carried out under the guidance of a person * who has undergone special training and has an appropriate certificate.
6.5. For the removal and transportation of explosive objects, workers who have passed special equipment must be allocated, who, before starting work, must be instructed in the prescribed manner about the precautions for carrying out these works.
6.6. Cutting and shipment of scrap metal specified in paragraphs. 6.2.1 - 6.2.5, must be produced separately from other scrap.
6.7. Every vehicle with recycled ferrous metals must be accompanied by a document certifying their explosion safety.
The form of a certificate of explosion safety of scrap and waste of ferrous metals is given in the mandatory Appendix 3.
6.8. Unloading and inspection of the scrap and waste received at the enterprise for explosion safety in accordance with the requirements set out in clause 6.2 should be carried out under the supervision of a pyrotechnician. An entry must be made about the check in the book of records of the scrap received at the enterprise, indicating the name of the enterprise (organization) - the sender; consignment note numbers and explosion safety certificate, the name of the pyrotechnician with his signature. Explosion protection of packets is ensured by the sender.
6.9. Untested secondary ferrous metals should not be mixed with tested ones and cannot be accepted for processing or use as a metal charge.
6.10. All work related to the testing of secondary ferrous metals for explosion safety and their neutralization must be carried out with an illumination of at least 30 lux.
6.11. Explosive objects discovered during the inspection of secondary ferrous metals (except those specified in clause 6.3) must be removed and sent, accompanied by pyrotechnics, for temporary storage or disposal.
6.12. Upon detection of explosive objects, an act must be drawn up, the form of which is given in the mandatory Appendix 4.
6.13. The explosion safety of the supplied scrap metal is ensured by the sender, and the explosion safety of the received scrap (excluding packages) is ensured by the recipient.
6.14. Scrap metal to be processed by various methods (gas and scissor cutting, batching, crushing, etc.) must be checked for explosion safety in accordance with the requirements set out in clause 6.2.
6.15. Immediately before loading into troughs, scoops and buckets, scrap and waste must be checked for explosion safety in accordance with the requirements set out in clause 6.2. An entry must be made about the check in the metal charge book with the signature of the pyrotechnician who performed the check.
6.1 - 6.15.(Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 2).
6.16. The storage of explosive items (except for those specified in clause 6.3) is carried out in storage facilities built in accordance with the requirements of the "Unified Safety Rules for Blasting Operations" approved by the USSR Gosgortekhnadzor.
Storage facilities should be located at a distance of at least 30 m from buildings, structures and communication lines. Shelf life - no more than 15 days.
In storage facilities and at a distance of less than 30 m from them, it is prohibited to use open fire and perform gas-electric welding work.
The storehouses must be provided with lightning protection and fire-fighting equipment in accordance with the applicable rules and regulations.
(Modified edition, Amendments No. 2, 3).
6.17. Explosive objects that entered storage facilities must be placed in a stable position, excluding the possibility of their falling.
6.18. Neutralization or destruction of military explosive scrap metal and cylinders with unknown content must be carried out by the appropriate military units in the prescribed manner.
6.17, 6.18.
ANNEX 1
Reference
GROUPS AND BRANDS OF ALLOYED SCRAP AND WASTE INTENDED FOR PREPARATION OF SEPARATE TYPES OF SECONDARY FERROUS METALS
Type name | Group designation and brand |
Briquettes No. 1 and 2 from steel shavings | B3, B4, B5, B13, 38X2MYUA (38HMYUA) |
Packages No. 1 and scrap for packaging No. 1 | Any group or brand specified in this standard |
Steel ropes and wire | B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B8, B9, B10, B11, B12, B13, B15, B16, B18, B19, B21, B24, B25, B26, B32, B33, B34, B37, B42, B43, B53, B59, 38Kh2MYuA (38KhMYuA), Kh12M, EP589, 95Kh18 (9Kh18, EI229), EP609, 25Kh13N2 (2Kh14N2, EI474), 80Kh20NS (EI922), EP263, 0Kh18N12TF, EP128173 ), 40Kh15N7G7F2MS (4Kh15N7G7F2MS, EI388), 10Kh11N23T3MR (Kh12N22T3MR, EP33, 40N, 42N (N42, EP318), 45N, 36N (N36, N36L), 36KhNTU (EI702) N28KHTYu NIM025 (EI639), KhN78T (EI435), Kh15N60, N20N80 |
(Modified edition, Amendment No. 2).
APPENDIX 2
Reference
TYPES OF SECONDARY FERROUS METALS INTENDED FOR USE AS METAL CHARGE IN VARIOUS MELTING UNITS
Melting units | Types of secondary ferrous metals | Symbol |
|
1. Converters | Steel scrap and waste No. 3 | ||
Packages No. 1 | |||
Packages No. 2 without shavings | |||
Packages No. 3 | |||
Steel scrap and waste No. 3 | |||
Packages No. 1 | |||
Packages No. 2 | |||
Packages No. 3 | |||
Briquettes No. 1 from steel shavings | |||
Steel shavings No. 2 | |||
Steel ropes and wire | |||
3. Electric arc furnaces: | |||
a) with a capacity of up to 20 tons | Steel scrap and waste No. 2 | 2A, 2B Packages No. 2 Sizes no more | |
Packages No. 3 600 "600" 800 mm, | |||
Steel ropes and wire | |||
4. Electric induction furnaces: | |||
e) for steel smelting | Steel scrap and waste No. 1 | ||
Steel scrap and waste No. 4 | |||
Briquettes No. 1 from steel shavings | |||
b) for smelting pig iron | Steel scrap and waste No. 1 | ||
Steel scrap and waste No. 2 | |||
Steel scrap and waste No. 4 | |||
Briquettes No. 1 from steel shavings | |||
Briquettes No. 2 from steel shavings | |||
Steel shavings No. 1 | |||
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 1 | |||
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 2 | |||
Cast iron briquettes | |||
Cast iron shavings | |||
5. Cupola ovens | Pig iron scrap and waste No. 1 | ||
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 2 | |||
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 3 | |||
Steel scrap and waste No. 1 | |||
Briquettes No. 1 from steel shavings | |||
Briquettes No. 2 from steel shavings | |||
Cast iron briquettes | |||
6. Blast furnaces | Blast furnace | ||
Rolling and forging mill scale | |||
Welding slag | |||
7. Ferroalloy furnaces | Steel shavings No. 1 |
APPENDIX 3
Mandatory
(ministry, department) ___________________________________________________________________________ Drawn up in duplicate. One copy with the invoice is sent to the recipient, and the second remains with the sender. CERTIFICATE No. _________ on explosion safety of scrap and waste of ferrous metals "_______" _______________________ 19 ______ Recipient of scrap and waste ___________________________________________________ Mass __________________ tons Wagon (car) No. ____________ consignment note No. _______________ The specified scrap and waste meet the requirements of GOST 2787-75, are explosion-proof and can be approved for processing and use as a metal charge. Responsible representative supplier _________________ _____________________ (signature, seal) (initials and surname) |
APPENDIX 4
Mandatory
___________________________________________________________________________ (ministry, department) ___________________________________________________________________________ (name of the delivery company) Drawn up in triplicate. Sent: one copy - to the sender with copies of his invoice and explosion safety certificate, the second - to the technical labor inspector of the sender, and the third - remains at the enterprise. "APPROVED" Chief Engineer ________________________ "___" ____________ 19___ ACT No. ________ on the detection of explosive objects when checking scrap and waste of ferrous metals "___" ____________ 19___ Shipper of scrap and waste __________________________________________________ Name of scrap and waste _________________________________________________ Mass ______________________ tons Wagon (car) No. _______________________________________________________ Invoice No. ________ date of arrival "____" 19____ g Explosion protection certificate No. ______ dated "____" 19_____ ___________________________________________________________________________ Verification established: ______________________________________________________ (describe in detail each explosive item) Administration representative recipient enterprise _________________ _____________________ Pyrotechnic ______________________ _____________________ (signature) (initials and surname) |
Appendices 3, 4 (Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 2).
INTERSTATE STANDARD
METALS BLACK SECONDARY
GENERAL TECHNICAL CONDITIONS
Official edition
IPK PUBLISHING STANDARDS Moscow
UDC 669.1.002.68:006.354 Group B17
STATE STANDARD OF THE UNION OF SSR
METALS BLACK SECONDARY
General specifications
Ferrous secondary metal.
General technical requirements
GOST 2787-63
By the decree of the State Committee of Standards of the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated December 26, 1975 No. 4035, the date of introduction is established
The limitation of the validity period was lifted according to the protocol of the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (IUS 2-93)
This standard applies to secondary ferrous metals intended for use as a metal charge in metallurgical furnaces in the smelting of steel and iron, in the manufacture of steel and iron castings and in the production of ferroalloys, as well as for processing for subsequent use in metallurgical furnaces.
1. CLASSIFICATION
1.1. Secondary ferrous metals are subdivided:
b) by the presence of alloying elements - into two categories: A - carbon, B - alloyed;
Official edition Reprinting prohibited
* Reprinted (February 2002) with amendments No. 1, 2, 3, 4, approved in July 1979 August 1979, June 1981 v December 1982
(IUS9-79, 10-79, 9-81, 4-83)
© Publishing house of standards, 1975 © IPK Publishing house of standards, 2002
c) in terms of quality indicators - for 28 types;
d) by the content of alloying elements - by 67 groups.
1.2. The distribution of secondary ferrous metals by classes, categories and types, their designation and code should be made in accordance with table. 1 and 2.
Table 1
|
designation |
||||
|
Steel scrap and waste No. 1 | ||||
|
Steel scrap and waste No. 2 | ||||
|
Steel scrap and waste No. 3 | ||||
|
Steel scrap and waste No. 4 | ||||
|
Oversized steel scrap and waste (for recycling) | ||||
|
Packages No. 1 | ||||
|
Packages No. 2 | ||||
|
Packages No. 3 | ||||
|
Scrap for packaging No. 1 | ||||
|
Scrap for packaging No. 2 | ||||
|
Steel ropes and wire | ||||
|
Steel shavings Nq 1 | ||||
|
Steel shavings No. 2 | ||||
|
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 1 | ||||
|
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 2 | ||||
|
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 3 | ||||
|
No. 1 (for processing) | ||||
|
Cast iron briquettes | ||||
|
Cast iron shavings | ||||
|
Blast-furnace garden | ||||
|
Oversized blast-furnace garden (for processing) | ||||
|
Welding slag |
Note. Groups and grades of alloyed scrap and waste intended for the preparation of certain types of secondary ferrous metals are given in reference annex 1.
table 2
|
General cipher |
||||
|
Steel scrap and waste No. 1 | ||||
|
Steel scrap and waste No. 2 | ||||
|
Steel scrap and waste No. 3 | ||||
|
Steel scrap and waste No. 4 | ||||
|
Oversized steel scrap and waste | ||||
|
(for processing) | ||||
|
Briquettes No. 1 from steel shavings | ||||
|
Briquettes No. 2 from steel shavings | ||||
|
Packages No. 1 | ||||
|
Packages No. 2 | ||||
|
Packages No. 3 | ||||
|
Scrap for packaging No. 1 | ||||
|
Scrap for packaging No. 2 | ||||
|
Steel ropes and wire | ||||
|
Steel shavings Nq 1 | ||||
|
Steel shavings No. 2 | ||||
|
Loose steel shavings (for | ||||
|
processing) | ||||
|
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 1 | ||||
|
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 2 | ||||
|
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 3 | ||||
|
Oversized pig iron scrap and waste | ||||
|
No. 1 (for processing) | ||||
|
Oversized pig iron scrap and waste | ||||
|
No. 2 (for processing) | ||||
|
Oversized pig iron scrap and waste | ||||
|
No. 3 (for processing) | ||||
|
Cast iron briquettes | ||||
|
Cast iron shavings | ||||
|
Blast furnace | ||||
|
Oversized blast furnace additive (for | ||||
|
processing) | ||||
|
Rolling and blacksmithing mill scale | ||||
|
production | ||||
|
Welding slag |
1.3. The distribution of alloyed scrap and waste of category B into groups and their designation and code should be made in accordance with table. 3.
Table 3
|
Designation |
Group name |
|
|
Scrap and waste of ball bearing and tool chromium steels |
||
|
Scrap and waste of structural steels alloyed with chromium, nickel, tungsten and molybdenum (in which one part of molybdenum replaces three parts of tungsten) |
||
|
Scrap and waste of structural steels alloyed with chromium, nickel, with a high content of tungsten and molybdenum (in which one part of molybdenum replaces three parts of tungsten) |
||
|
Scrap and waste of heat-resistant steels alloyed with chromium and chrome in combination with titanium |
||
|
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant chromium steels |
Continuation of table. 3
|
Designation |
Group name |
|
|
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant steels alloyed with chromium, nickel, molybdenum and their combinations, with titanium, aluminum and other elements, except tungsten and boron |
||
|
Scrap and waste of tool steels alloyed with tungsten, chromium and their combinations with silicon, vanadium and other elements except nickel |
||
|
Designation |
Group name |
|
|
Scrap and waste of high-speed chromium-tungsten-cobalt-vanadium steels with cobalt content up to 6% |
||
|
Scrap and waste of structural and tool steels alloyed with chromium, nickel, and tungsten |
||
|
Scrap and waste of tool steels alloyed with tungsten, chromium and their combinations with silicon and other elements other than nickel |
||
|
Scrap and waste of hard magnetic chromium-tungsten steels |
||
|
Scrap and waste of nickel-free structural and tool steels alloyed with chromium, tungsten and molybdenum and their combinations with silicon and vanadium |
||
|
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant steels, chromium-nickel-molybdenum-niobium steels |
||
|
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant steels alloyed with chromium, nickel, and titanium |
||
|
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant chromium-nickel-niobium steels |
||
|
Scrap and waste of heat-resistant chromium-nickel volt-niobium steels with boron (in which one part of molybdenum replaces two parts of tungsten) |
||
|
Scrap and waste of steels alloyed with chromium, nickel, molybdenum, vanadium and copper |
||
Continuation of table. 3
|
Designation |
Group name |
|
|
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant steels alloyed with chromium, nickel and molybdenum and their combination with titanium and other elements, except tungsten and boron |
||
|
Scrap and waste of low-phosphorous structural steels alloyed with chromium, nickel, molybdenum, tungsten, silicon and vanadium |
||
|
Scrap and waste of chromium-nickel cast iron |
||
2. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
2.1. Secondary ferrous metals must be handed over and supplied sorted by types, groups or grades in accordance with
the requirements of this standard. It is not allowed to deliver and deliver unassembled units and machines that have been scrapped.
2.2. Carbon steel scrap and waste (including scrap and waste of low-alloy manganese and silicon steel, not included in the classification of this standard as alloyed) should not contain alloyed steel scrap and waste and scrap and waste of cast iron, non-ferrous metals and alloys; alloyed scrap and waste should not contain carbon scrap and waste and scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals and alloys.
2.3. Groups of alloyed scrap and waste should not contain grades that do not belong to this group in terms of chemical composition.
2.4. Delivery to the consumer of oversized secondary ferrous metals mixed with oversized ones is not allowed. A list of the types of secondary ferrous metals used as metal charge in various smelters is given in reference annex 2.
2.5. Secondary ferrous metals must be handed over and delivered in a condition that is safe for transportation, processing, remelting; must be made harmless from explosive and radioactive materials. Scrap and waste generated at enterprises using radioactive substances in the production process must be rendered harmless by them from these substances in accordance with the established procedure. Scrap and waste coming from chemical plants must be cleared of chemicals.
2.6. If the consumer submits increased requirements, the supply of secondary ferrous metals is carried out by Vtorchermet according to the normative and technical documentation approved in the prescribed manner.
2.7. The quality indicators of secondary metals in terms of their composition, purity, dimensions and weight must comply with the requirements of table. 4.
Table 4
Lumpy scrap and waste, convenient for loading smelting units. Wire and wire products are not allowed
Lumpy scrap and waste, as well as charge ingots, convenient for loading smelting units. Wire and wire products are not allowed
Steel scrap and waste no.
The presence of scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals is not allowed. Carbonaceous scrap and waste should not be mixed with alloyed ones. The metal should not be burnt, corroded by acids and corroded (rust deposits are allowed).
Contamination with harmless impurities should not exceed 2% by weight
Steel scrap and waste no.
The presence of scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals is not allowed. Alloyed scrap and waste should not be mixed with carbon and should be of only one group or grade. The metal should not be burnt, corroded by acids and corroded (rust deposits are allowed). Contamination with harmless impurities should not exceed 1% by weight
The dimensions of the piece should be no more than 300 200 150 mm. The thickness of the metal must be at least 6 mm. Piece weight must be at least 0.5 kg, but not more than 40 kg
Piece dimensions should be no more than 600 350 250 mm. By agreement of the parties, rejected ingots, blooms, billets, structural shapes, as well as alloyed charge ingots may have increased dimensions. The thickness of the metal must be at least 8 mm. The length of the protrusions of rectangular pieces should not exceed 100 mm. The pipes must have an outer diameter of not more than 150 mm and a wall thickness of at least 8 mm. Large diameter pipes must be flattened or cut along the generatrix. Piece weight must be at least 2 kg
* Waste steel grades 08kp, 08, 05kp, 08Yu, 08ps and 08Fkp with a chromium content of not more than 0.1% by weight are supplied separately from other carbon steel waste.
** At the request of the customer, steel scrap and waste must contain sulfur and phosphorus no more than 0.05% each.
Lumpy scrap and waste and steel scrap, convenient for loading smelting units. Wire and wire products are not allowed
Small lumpy wastes of hardware and other industries, scrap of hardware products (crutches, bolts, nuts, etc.), convenient for loading melting units.
Steel scrap and waste No. 3 * **
The presence of scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals is not allowed. Alloyed scrap and waste should not be mixed with carbon and should be of only one group or grade. The metal should not be burnt, corroded by acids and corroded (rust deposits are allowed). Contamination with harmless impurities should not exceed 1.5% by weight
Steel scrap and waste No. 4 **
The presence of scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals is not allowed. Alloyed scrap and waste should not be mixed with carbon and should be of only one group or grade. The metal must not be burnt, corroded by acids and corroded (rust
Piece sizes must be no more than 800 500
500 mm. For rolls of sheet metal, increased dimensions are allowed by agreement of the parties, but not more than 1000 mm. The thickness of the metal must be at least 6 mm. Channels and I-beams with a wall thickness of at least 4 mm in an amount of not more than 20% of the batch weight are allowed. The pipes must have an outer diameter of not more than 150 mm and a wall thickness of at least 6 mm. Large diameter pipes must be flattened or cut along the generatrix. The length of the protrusions of straight pieces should not exceed 100 mm. The deflection arrow of bent pieces should not exceed 250 mm. The mass of the piece must be at least 1 kg.
Piece sizes should be no more than 200 * 150 *
100 mm. The thickness of the metal must be at least 6 mm. Piece weight must be at least 0.025 kg, but not more than 20 kg
* Scrap with a contamination of no more than 5% during shipment must not be mixed with other waste and scrap.
** For vacuum induction furnaces, scrap and waste must be supplied with dimensions of at least 30 * 30 * 30 mm.
Wire and wire products are not allowed
allowed). Contamination with harmless impurities should not exceed 0.5% by weight
Oversized steel scrap and waste * (for recycling)
Lumpy scrap and waste and steel scrap. Wire and wire products are not allowed
Presence is not allowed. The thickness of the metal of the dolly and non-ferrous metal waste should be at least 6 mm. Alloyed scrap and waste should not be mixed with carbon and should be of only one group or grade. The metal should not be burnt, corroded by acids and corroded (rust deposits are allowed). Contamination with non-metallic impurities should not exceed 3% by weight
Briquettes No. 1 from steel shavings
Steel shavings briquettes
Briquettes should be pressed from steel shavings, not mixed with cast iron shavings and non-ferrous metal shavings. Briquetted carbon chips should not be mixed with alloyed chips, and alloyed chips during briquetting should be of only one group or grade. Briquetting of rusted (rusty deposits is allowed), burnt and acid-corroded shavings is not allowed. The total content of harmless impurities and oil in briquettes should not exceed 1% by weight
Dimensions are not regulated. The mass of briquettes should be at least 2 kg and not more than 50 kg with a density of at least 5000 kg / m 3. The amount of shavings crumbled from briquettes during transportation and unloading at the consumer should not exceed 3% of the batch weight
* Scrap with a contamination of no more than 5% during shipment must not be mixed with other waste and scrap. Scrap with a contamination of more than 5% is supplied by agreement of the parties.
Steel shavings briquettes
Pure lightweight steel waste bags
Briquettes No. 2 from steel shavings
Briquettes should be pressed from steel shavings, not mixed with cast iron shavings and non-ferrous metal shavings. Briquetted carbon chips should not be mixed with alloyed chips, and alloyed chips during briquetting should be of only one group or grade. Briquetting of rusty (rusty deposits is allowed), burnt chips corroded by acids is not allowed. The total content of harmless impurities and oil in briquettes should not exceed 3% by weight
Packages No. 1
Packages should be compressed from clean sheet, strip and high-quality metal on waste and pipe production waste that does not contain scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals. Carbon shavings are not allowed. Alloyed shavings are allowed in bags of alloyed metal waste. The pressed carbon steel should not be mixed with the alloyed steel, and the alloyed steel during pressing should be of only one group or grade. Pressing of tinned, enameled, galvanized, coated with other non-ferrous metals, corroded by acids, corroded (rusty deposits is allowed) and burnt metal is not allowed. The content of harmless impurities in bags should not exceed 1% by weight
Dimensions are not regulated. The mass of briquettes should be at least 2 kg and not more than 50 kg with a density of at least 4500 kg / m 3. The amount of shavings crumbled from briquettes during transportation and unloading from the consumer should not exceed 5% of the batch weight
Packages should be no more than 2000 *
1050 750 mm and density not less than 2000 kg / m 3. At the request of the consumer, packages should be no more than 500
* 500 * 600 mm or not more than 600 600 800 mm. The weight of the bags must be at least 40 kg
Packages No. 2 *
High density bags of lightweight steel waste and scrap
Packages should be compressed from lightweight waste and scrap that does not contain scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals. Chips are allowed. Compressed carbon steel should not be mixed with alloy steel. Pressing of tinned, enameled, galvanized, coated with other non-ferrous metals, corroded by acids, corroded (rusty deposits is allowed) and burnt metal is not allowed. The content of harmless impurities in bags should not exceed 2% by weight
Packages No. 3 *
Bag sizes should not exceed 2000 * 1050 750 mm. The weight of the bags must be at least 40 kg with a density of at least 1800 kg / m 3
Low density bags made from lightweight steel waste and scrap
Packages should be compressed from lightweight waste and scrap that does not contain scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals. Chips are allowed. Compressed carbon steel should not be mixed with alloy steel. Pressing of tinned, enameled, galvanized, coated with other non-ferrous metals, corrosive acids, corroded (rusty deposits is allowed) and burnt metal is not allowed. The content of harmless impurities in bags should not exceed 2% by weight
Bag sizes should not exceed 2000 * 1050 750 mm. The weight of the bags must be at least 40 kg with a density of at least 1200 kg / m 3
Scrap for packaging No. 1
Pure steel sheet, strip, section waste and pipe production waste
The presence of scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals is not allowed. Carbon steel should not be mixed with alloy steel, and alloy steel should only be
The thickness of the metal must be less than 6 mm. The maximum linear dimensions should not exceed 3500 2500 * 1000 mm.
At the request of the consumer, packages should not contain shavings.
one group or brand. The metal should not be tinned, enameled, galvanized, coated with other non-ferrous metals, burnt, corroded by acids and corroded (rust is allowed).
Contamination with harmless impurities should not exceed 1% by weight
Steel, sheet, strip and high-quality waste, roofing, light industrial and household scrap, wire and wire products, metal structures, pipes. Steel ropes are not allowed
Steel ropes and wire, rolled into coils, tied with steel wire in at least five places around the circumference of the coil. Steel ropes cut into dimensional pieces
Scrap for packaging No. 2
The presence of scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals is not allowed. Carbon steel should not be mixed with alloy steel. The metal should not be tinned, enameled, galvanized, coated with other non-ferrous metals, burnt, corroded by acids and corroded (rust is allowed). Contamination with harmless impurities should not exceed 2% by weight
The thickness of the metal must be less than 6 mm. The maximum linear dimensions should not exceed 3500 * 2500 * 1000 mm.
Steel ropes and wire
The presence of scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals is not allowed. Contamination with non-metallic impurities should not exceed 6% by weight
The diameter of the coil should be no more than 1000 mm, and the length should not be more than 500 mm. The weight of the coil must be at least 20 kg. Pieces of ropes with a diameter of at least 20 mm and a length of no more than 800 mm.
Small steel shavings as well as die-cutting. Lump waste and scrap are not allowed
Fine steel shavings without tangles of loach-shaped shavings and die-cutting. Lump waste and scrap are not allowed
Steel shavings No. 1
Carbon steel shavings should not be mixed with cast iron and non-ferrous and alloy metal shavings. The shavings must not be burnt or corroded (rust deposits are allowed). The content of non-metallic impurities (including oil) should not exceed 3% by weight
Steel shavings No. 2
The length of the turn of shavings and nibbling should be no more than 50 mm. Coils up to 100 mm in length are allowed in an amount of not more than 3% by weight. Die-cut weight should be no more than 0.025 kg
The length of the turn of shavings and nibbling should be no more than 100 mm. Coils up to 200 mm in length are allowed in an amount of not more than 3% by weight. Die-cut weight should be no more than 0.05 kg
Loamy steel shavings (for processing)
Loose steel shavings. Lump waste and scrap are not allowed
Steel shavings should not be mixed with cast iron and non-ferrous metal shavings. Carbon shavings should not be mixed with alloy chips. Alloy chips should only be of one group or grade. The shavings must not be burnt or corroded (rust deposits are allowed). The total content of harmless impurities and oil should not exceed 3% by weight
Not regulated
Pieces of machine iron castings, as well as ingots of secondary foundry iron
Pieces of cast iron molds and pallets
Pieces of iron castings with a high and high phosphorus content (furnace, dishware, artistic). Ductile iron lumps, cast iron pipes
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 1
The presence of scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals is not allowed. Carbonaceous scrap and waste should not be mixed with alloyed ones. The metal should not be burnt, corroded by acids and corroded (rust deposits are allowed). Contamination with harmless impurities should not exceed 2% by weight. Allowed impurity of hard-to-separate steel is not more than 5% by weight
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 2
The presence of scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals is not allowed. Carbonaceous scrap and waste should not be mixed with alloyed ones. The metal must not be corroded (rust deposits are allowed). Contamination with harmless impurities should not exceed 2% by weight. Allowed impurity of hard-to-separate steel is not more than 5% by weight
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 3
The presence of scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals is not allowed. The metal should not be burnt, corroded by acids and corroded (rust deposits are allowed). Contamination with harmless impurities should not exceed 2% by weight. Allowed impurity of hard-to-separate steel is not more than 5% by weight
The maximum size of a piece should be no more than 300 mm, and the other dimensions should correspond to the size of a piece weighing no more than 40 kg, but not less than 0.5 kg. At the request of the consumer, it is allowed to supply pieces of increased dimensions and weight. Pieces weighing less than 0.5 kg are allowed in an amount of not more than 2% of the batch weight
The maximum size of a piece should be no more than 300 mm, and the other dimensions should correspond to the size of a piece weighing not more than 20 kg, but not less than 0.5 kg. Pieces weighing less than 0.5 kg are allowed in an amount of not more than 2% of the batch weight
Machine-made castings - The presence of gunny castings of scrap and nonferrous metal waste
fishing. Carbonaceous scrap and waste should not be mixed with alloyed ones. The metal should not be burnt, corroded by acids and corroded (rust deposits are allowed). Contamination with non-metallic impurities should not exceed 3% by weight. Allowed impurity of hard-to-separate steel is not more than 5% by weight
Not regulated
Oversized pig iron scrap and waste No. 2 (for processing)
Cast iron outlines - It is not allowed to have a bed and pallets of scrap and non-ferrous metal waste
fishing. Carbonaceous scrap and waste should not be mixed with alloyed ones. The metal must not be corroded (rust deposits are allowed). Contamination with non-metallic impurities should not exceed 3% by weight. Allowed impurity of hard-to-separate steel is not more than 5% by weight
Not regulated
Oversized pig iron scrap and waste No. 3 (for processing)
Iron castings with high and high phosphorus content (furnace, dishware, artistic). Ductile iron castings, cast iron pipes
The presence of scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals is not allowed. The metal should not be burnt, corroded by acids and corroded (rust deposits are allowed). Contamination with non-metallic impurities should not exceed 3% by weight. Allowed impurity of hard-to-separate steel is not more than 5% by weight
Not regulated
Cast iron briquettes
Pig iron shavings without lump waste and scrap
Corroded, exposed to prolonged temperature or acid exposure, enameled and galvanized lump scrap and waste; cast iron crochet; shot or granules; rusty and sintered steel and cast iron shavings; slagged scrap
Cast iron briquettes
Briquettes should be pressed from cast iron shavings, not mixed with steel shavings and non-ferrous metal shavings. Briquetting of rusted (rusty deposits is allowed) and burnt shavings is not allowed. The total content of harmless impurities and oil in briquettes should not exceed 2% by weight
Cast iron shavings
Cast iron shavings should not be mixed with steel and non-ferrous metal shavings. Alloyed cast iron shavings must not mix with carbon. The shavings must not be rusted (rust deposits are allowed). The total content of harmless impurities and oil should not exceed 2% by weight
Blast with hell
The presence of scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals is not allowed,. Scrap metal, mined from slag dumps with a contamination of more than 5% by weight, is supplied by agreement of the parties
Dimensions are not regulated, The mass of briquettes must be at least 2 kg, but not more than 20 kg with a density of at least 5000 kg / m 3. The amount of shavings crumbled during transportation and unloading from the consumer should not exceed 5% of the batch weight
Not regulated
Piece dimensions should be no more than 250 * 250 * 250 mm. The length of the turn of the steel shavings should be no more than 100 mm. Coils up to 200 mm in length are allowed in an amount of not more than 3% of the mass of chips in a batch. Weight is not regulated
Oversized blast furnace additive (for processing)
Corroded, exposed to prolonged temperature or acid exposure, enameled and galvanized lump scrap and waste; slagged scrap
The presence of scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals is not allowed
Not regulated
Rolling and forging mill scale
Rolling and forging mill scale. Pieces of sawn-off and
Contamination with non-metallic impurities should not exceed 5% by weight
Not regulated
Note. Alloyed scale is supplied according to special specifications.
Welding slag
Slag from reheating furnaces
Contamination with non-metallic impurities should not exceed 5% by weight
Not regulated
Notes:
1. Harmless impurities are impurities, the presence of which in a limited amount does not adversely affect the quality of the metal being smelted. Harmless impurities include moisture, wood, earth, rags, sand and other similar impurities.
2. A metal is considered to be corroded if there is a layer of rust on its surface that flakes off when subjected to impact.
3. Deviations from the maximum permissible linear dimensions of secondary ferrous metals should not exceed 10% upward.
4. For enterprises of the USSR Ministry of Ferrous Metals, it is allowed in the types "Steel scrap and waste No. 3" and "Oversized steel scrap and waste (for processing)", the thickness of the metal is not less than 4 mm, and in the types "Scrap for packaging No. 1 and No. 2" less than 4 mm.
(Modified edition, Amendments No. 1, 4).
2.8. The chemical composition of alloyed scrap and waste of category B must comply with the requirements of table. 5.
Table 5
|
Group name | |||
|
Scrap and waste of low-alloy structural and tool steels alloyed with chromium and combinations of chromium with elements other than nickel, molybdenum and tungsten |
From 11X to 50X, from 45X1 to 48X1, 9X1, from 4XC to 40XC, from 18XG to 50XG, 35XG2, HGS, from 5HGS to 38HGS, from 7HF to 75HF, from 25HGF to 35HGF, from 15HR to 40HR, from 20 HGR to 40HGR, from 15HGT to 30HGT, 40HGTR, 45HTs, 20HG2Ts, ShH15SG, ShH20SG, 50X05, DS1, DS2 |
Chromium - 0.4-1.8 Nickel - no more than 0.4 Silicon - no more than 1.6 Manganese - 02-1.9 Vanadium - no more than 0.3 Titanium - no more than 0.12 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of structural and tool chromium steels |
45X3, 46X3, 7X3, 8X3, EXZ, DS5 |
Chromium - 2.4-3.8 Nickel - no more than 0.35 Manganese - no more than 0.6 Silicon - no more than 0.4 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of ball screws and tool chromium steels |
ШХ15, ШХ9, X, EX, 9X |
Carbon - no less than 0.8 Chromium - 0.9-1.7 Nickel - no more than 0.3 Manganese - no more than 0.5 Silicon - no more than 0.4 Copper - no more than 0.25 Phosphorus - no more than 0.030 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of structural nickel steels |
06NZ to 25NZ, 13N5 to 21N5 |
Nickel 2.7-5.0 Chromium - no more than 0.3 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of structural chromium-nickel steels |
From 12ХНЗ to 37XH3, 12Х2Н4, 20Х2Н4, 20ХН4, 20ХН4Ф |
Nickel - 2.7-4.2 Chromium - 0.6-1.8 Vanadium - no more than 0.3 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of structural steels alloyed with chromium, nickel, tungsten and molybdenum (in which one part of |
38Х2Н2М (38Х2Н2В), 40Х2Н2М (40Х2Н2В), 30ХН2МФ (30ХН2ВФ), 30ХН2М (30ХН2В), 38XH3M (30XH3B) |
Nickel - 1.2-3.3 Chromium - 0.6-1.7 Vanadium - no more than 0.20 |
libdenum replaces three parts of tungsten) *
Scrap and waste of structural steels alloyed with chromium, nickel with a high content of tungsten and molybdenum (in which one part of molybdenum replaces three parts of tungsten) **
18Х2Н4М (18Х2Н4В), 25Х2Н4М (25Х2Н4В)
Nickel - 4.0-4.5 Chromium - 1.3-1.7
Scrap and waste of structural steels alloyed with nickel and molybdenum and their combinations with chromium, silicon, manganese and other elements, except tungsten
15N2M (15NM), 20N2M (20NM), 20GNM, from 20KHGSNM to 30KHGSNM, TVM, 14KHGSN2M (ETT176), 18KHGSN2M (DI-4), 20KHN2M (20KHNM), 40KHN2M (40KHN2F), 45 ОХНМФ, 0ХН1М, 0ХН2М, 34ХН1М, 06ХН2М (EI582), 42Х2ГСНМ (VKS-1), 36Х2Н2МФ (36ХН1МФ), DS8, 25ХГСНМР, 25ХГНМ, 5ХГНМ, 40Х2Н2М,
Nickel - 0.4-2.3 Chromium - no more than 2.0 Molybdenum - 0.1-0.6 Silicon - no more than 1.5 Manganese - no more than 1.5 Vanadium - no more than 0.3
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant steels alloyed with chromium and chromium in combination with elements other than nickel, molybdenum, tungsten, boron
15X5 (X5), X8, 40X5T, 9X5F, 12X5F,
15Х6СЮ (ЭИ428,
Х6СЮ), 40Х9С2 (4Х9С2, Х9С2)
Chrome - 4.0-10.0 Nickel - no more than 0.6 Silicon - no more than 3.0 Titanium - no more than 1.0 Aluminum - no more than 1.1
Vanadium - no more than 0.3
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant chromium steels
12X17 (0X17), 08X17T (EI645, 0X17T)
Chrome - 16.0-18.0 Titanium - no more than 0.8 Nickel - no more than 0.6 Phosphorus - no more than 0.035
Scrap and waste of structural steels alloyed with molybdenum in combination with chromium, vanadium, silicon and other elements, except nickel and tungsten
16M, 55CM, or 0XM to 38XM, 12XM, 5HGM,
25HGM, 12HSM, from 35HMF to 40HMF, 35H2GSM, 55SMZF, 55SM5F,
12Х1МФ (12ХМФ),
25X1MF (25X2MF, EI10), 60X2M, 28X2M, DSZ
Chromium - no more than 2.5 Nickel - no more than 0.3 Molybdenum - 0.1-0.6 Vanadium - no more than 0.4 Silicon - no more than 1.0
Scrap and waste of heat-resistant steels, and alloyed with chromium and chromium in combination with titanium
15X25T (X25T, EI439), 15X28 (X28, EI349)
Chrome - 24.0-30.0 Nickel - no more than 0.6 Titanium - no more than 0.8 Phosphorus - no more than 0.035
Scrap and waste of structural steels alloyed with nickel and chromium and their combinations with elements other than molybdenum and tungsten
From 12XN to 60XH, 60X2H, from 12XH2 to 17XH2, from 14XGN to 38XGN, 30X2GN2, from 5XNT to 20XNT, 15XGN2T
(15ХГНТ), from 50ХНФ to 60ХНФ, 0ХН2Ф, from 20ХНР to 40ХНР (ЭИ753), from 15ХГНР to 40ХГНР, 18ХСНР (ЭИ609), 20ХГСН, 30ХГСН2 (30ХГСН),
25H2GNT, 15H2GN2T, 15H2GN2TR, 20HGNTR, 25HNTTS, DS4, 36GSN, 16HSN, 25HGSNT
Nickel - 0.4-2.3 Chromium - 0.4-2.0 Titanium - not more than 0.15 Vanadium - not more than 0.3 Boron - not more than 0.005
Scrap and waste of structural steels alloyed with chromium, nickel and molybdenum
From 17ХНЗМ to 50ХНЗМ, 0XH3M, 14Х2НЗМ (18Х2НЗМ), 18ХН2М, 0ХН4М, ХНЗМ, 38XCH3M, 35ХН2М
Nickel - 1.7-3.8 Chromium - 0.6-2.7 Molybdenum - 0.2-0.5
Continuation of table. 5
|
Group name |
List of the main brands included in the group | ||
|
Scrap and waste alloys of high ohmic resistance, alloyed with chromium and aluminum |
0Х23Ю5 (ЭИ595), 0Х27Ю5 (ЭИ626) |
Chrome - 21.0-28.0 Nickel - no more than 0.6 Aluminum - 4.5-5.8 Silicon - no more than 0.6 Phosphorus - no more than 0.025 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of heat-resistant steels, alloys of high ohmic resistance, alloyed with chromium, aluminum, silicon |
10Х13СЮ (1Х12СЮ, ЭИ404), 15Х18СЮ (Х18СЮ, ЭИ484) |
Chrome - 12.0-20.0 Nickel - no more than 0.6 Aluminum - 0.7-5.5 Silicon - no more than 2.0 Phosphorus - no more than 0.035 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of tool steel |
4X4VMFS (DI-22), 5HZVZMFS (DI-23) |
Chromium - 2.5-3.8 Nickel - 0.1-0.6 Tungsten - 0.8-3.6 Vanadium - 0.6-1.8 Molybdenum - 1.1-1.6 Silicon - 0.5 -1.0 Niobium - no more than 0.15 Phosphorus - no more than 0.025 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant chromium steels |
08X13 (0X13, EI496), 12X13, (1X13), 20X13 (2X13), 30X13 (3X13), 40X13 (4X13), 08X13L, 20X1ZL |
Chrome - 12.0-14.0 Nickel - no more than 0.6 Phosphorus - no more than 0.035 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of heat-resistant chromium-nickel steels |
0Х20Н13 (2Х21Н13, ЭИ997), 08Х20Н14С2, (0Х20Н14С2, ЭИ732), 20Х20Н14С2 (Х20Н14С2, ЭИ211), EP75, EP87, 20Х23Н13 (Х23Н13, ЭИ319), 30Х24Н12С |
Nickel - 11.0-15.0 Chromium - 19.0-27.0 Titanium - no more than 1.0 Silicon - no more than 3.0 Phosphorus - no more than 0.035 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of heat-resistant chromium-molybdenum steels |
Х6СМ (ЭСХ6М), 25Х5М |
Chrome - 4.0-6.5 Nickel - no more than 0.5 Molybdenum - 0.4-0.6 Silicon - no more than 2.0 |
|
Group name |
List of the main brands included in the group | ||
|
Scrap and waste of tool and structural steels alloyed with tungsten in combination with chromium, silicon, manganese, vanadium, except nickel |
HVG, 6HVG, 9HVG, OHV, HVSG, V1, HV1G, 65S2V, 55SVF |
Tungsten - 0.5-1.6 Chromium - no more than 1.2 Nickel - no more than 0.35 Vanadium - no more than 0.30 Manganese - no more than 1.2 Silicon - no more than 2.0 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of wear-resistant manganese steels with a high manganese content |
85G13 (EI700), G13 (EI256), G13L |
Chromium - no more than 0.5 Nickel - no more than 0.6 Manganese - 11.0-14.0 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of structural and tool steels alloyed with chromium, molybdenum and vanadium and their combinations with elements other than nickel and tungsten |
25X2M1F (EI723), 15X1M1F, 12X2MFSR, 25X1M1F (P2), 4XSMF |
Chromium - 0.9-2.6 Nickel - no more than 0.4 Molybdenum - 0.5-1.2 Vanadium - 0.2-1.0 Titanium - no more than 0.4 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of heat-resistant and heat-resistant steels alloyed with chromium, molybdenum and silicon |
1X13M, 40X10S2M (4X10S2M, EI107, X10S2M) |
Nickel - no more than 0.6 Chromium - 9.0-14.0 Molybdenum - 0.2-0.9 Silicon - no more than 2.6 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant steels alloyed with chromium, nickel and manganese |
10X14G14NZ (DI-6), 10X14G14N4T (X14G14NZT, EI711), 20X13N4G9 (2X13N4G9, EI100) |
Nickel - 2.5-5.0 Chromium - 12.0-15.0 Manganese - 8.0-15.0 Titanium - no more than 0.6 Phosphorus - no more than 0.035 |
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant steels alloyed with chromium and nickel and their combinations with silicon, manganese and titanium, except for molybdenum, tungsten, niobium and boron
12Х18Н9 (Х18Н9),
17Х18Н9 (2Х18Н9, ЭЯ2), 12Х18Н9Т (Х18Н9Т),
08Х18Н10Т (0Х18Н10Т, ЭИ914, ЭИ825),
08X18H10 (0X18H10),
04X18H10 (00X18H10, EI842, EP550),
12X18N YuT (Kh18N10T), 06X18N11 (0Kh18N11, EI684), 12Kh18N12T (Kh18N12T), 08Kh18N12T (0Kh18N12T), 2Kh18N8S2 (EI95), OZKh18N11, 03Kh18N12, 15Kh18N12794TYu
Nickel - 8.0-13.0 Chromium - 17.0-20.0 Manganese - no more than 2.0 Silicon - no more than 4.0 Phosphorus - no more than 0.035 Titanium - no more than 1.2 Tungsten - no more than 0, 2 Molybdenum - no more than 0.3
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant steels alloyed with chromium and nickel and their combinations with silicon, manganese, titanium, aluminum and other elements, except for molybdenum, tungsten, niobium and boron
30Х13Н7С2 (3X13H7C2, EI72), Х17Н7Ю (ЭИ973), 09Х17Н7Ю (0Х17Н7Ю), 09Х17Н7Ю1 (0Х17Н7Ю1), 09Х15Н8Ю (Х15Н9Ю, СН2,
ЭИ904), 07Х16Н6 (ЭП288), 0Х17Н7ГТ (ЭИ814)
Nickel - 5.0-9.5 Chrome - 12.0-18.0 Titanium - no more than 1.2 Silicon - no more than 3.0 Aluminum - no more than 1.4
Scrap and waste of heat-resistant and heat-resistant chromium-nickel steels with a high content of chromium and nickel
20Х23Н18 (Х23Н18, ЭИ417),
10Х23Н18 (0Х23Н18), Х25Н20,
20Х25Н20С2 (Х25Н20С2, ЭИ288)
Nickel - 17.0-21.0 Chromium - 22.0-27.0 Phosphorus - no more than 0.035
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant steels alloyed with chromium, nickel, molybdenum and their co-
08X21N6M2T (0X21N6M2T, EP54) 45X22N4MZ (EP48), 10X17N5M2 (X17N5M2, EP405),
Nickel - 4.0-8.5 Molybdenum - 1.6-3.5 Aluminum - no more than 1.8
|
Group name |
List of the main brands included in the group | ||
|
throwing with titanium, aluminum and other elements, except tungsten and boron |
08Х17Н5МЗ (ЭИ925, СН-3), 0X16N7M2Yu (EP294), Kh15N7YuM2 (SN-4, EP35) |
Titanium - no more than 0.4 Chromium - 14.0-23.0 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant chromium-nickel steels with boron |
00X17N15R1 (EP166), 00X17N15R2 (EP167), 00X17N15RZ (EP168a), 00X18N15R4 (EP168), 00X19N15R6 (EP169) |
Chromium - 15.0-20.0 Nickel - 14.0-16.0 Boron - 0.08-0.65 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of tool steels alloyed with tungsten, chromium and their combinations with silicon, vanadium and other elements, except nickel |
8ХВ2Ф (ЭИ190), from 4ХВ2С to 6ХВ2С |
Tungsten - 2.0-2.7 Chromium - 1.0-1.4 Nickel - no more than 0.3 Vanadium - no more than 0.3 Silicon - no more than 0.9 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant chromium-nickel steels with low nickel content |
Х17Н, 0Х17Н, 2Х17Н1 (EP209, EP406), 14Х17Н2 (1Х17Н2, ЭИ268), 20X17H2 (2X17H2, EP210, EP407) |
Nickel - 1.0-2.8 Chromium - 16.0-18.0 Phosphorus - no more than 0.035 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of steels with special physical properties alloyed with manganese and aluminum |
45G17YUZ (EI839), 15G19YUZ, 15G20YUZ, 80G20YU4 (EP28), EP42 |
Chrome - no more than 0.5 Nickel - no more than 0.6 Manganese - 16.0-21.0 Aluminum - 2.4-5.8 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of high-speed chromium-tungsten-vanadium steels |
R9, R9F (EI347) |
Chromium - 3.8-4.6 Nickel - no more than 0.4 Tungsten - 8.5-10.0 Molybdenum - no more than 1.0 Vanadium - 1.2-2.6 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of high-speed chromium-tungsten-vanadium steels with a high tungsten content |
R12, R12FZ (EI597) |
Chromium - 3.1-4.1 Tungsten - 12.0-13.5 Vanadium - 1.5-3.0 Molybdenum - no more than 1.0 |
Continuation of table. 5
|
Group name |
List of the main brands included in the group | ||
|
Scrap and waste of high-speed chromium-tungsten-cobalt-vanadium steels with cobalt content up to 6.0% |
R9K5, R10K5F5 (EI931), R12F4K5 |
Chromium - 3.5-4.6 Nickel - no more than 0.4 Tungsten - 9.0-14.0 Cobalt - 5.0-6.0 Vanadium - 2.0-5.1 Molybdenum - no more than 1.0 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of high-tungsten high-speed chromium-tungsten-vanadium steels |
R18, R18F2 (EI916), R18F2M (EI917) |
Chromium - 3.6-4.4 Nickel - not more than 0.4 Tungsten - 17.0-19.0 Molybdenum - not more than 1.0 Vanadium - 1.0-2.4 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of structural steels alloyed with chromium, nickel, molybdenum and vanadium |
From 15Х2Н2МФ to 20Х2Н2МФ, 18ХН2МФ, 38ХНЗМФ, ОХНЗМФ, 30ХН2МФ, 12ХНЗМФ |
Nickel - 1.9-3.5 Chromium - 0.6-2.0 Molybdenum - 0.2-0.5 Vanadium - 0.1-0.3 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of structural and tool steels alloyed with chromium, nickel and tungsten |
From ZOKHNV to 45KHNV, 30KH2NV (30KH2N2VF), 5KHNV, 5KHNSV, 0ХН1В, 45ХНВФ, from 12Х2НВФ to 30Х2НВФ, 0ХН2В, 40ХН2СВ (ЭИ643), 40Х1НВ, 38Х2Н2В, 40Х2Н2В, 30ХН2ВФ, 30ХН2В |
Nickel - 0.8-2.4 Chromium - 0.5-2.4 Tungsten - 0.4-1.6 Manganese - 0.3-0.8 Vanadium - no more than 0.3 Silicon - no more than 0.9 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of low-phosphorous structural steels alloyed with chromium, nickel, tungsten and their combinations with silicon and vanadium |
From 25HSNVF to 30HSNVF (VP25-VP30) |
Nickel - 0.9-1.2 Chromium - 0.9-1.2 Tungsten - 0.5-1.0 Vanadium - 0.05-0.15 Manganese - 0.5-0.8 Phosphorus - no more than 0.015 Silicon - 0.9-1.1 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of tungsten, chromium alloyed tool steels |
4X5V2FS (EI958), 9X5VF (EP24), Х6ВФ, 15Х5ВФ (Х5ВФ), 12Х8ВФ (Х8ВФ) |
Tungsten - 0.4-2.4 Chromium - 4.5-8.5 Nickel - no more than 0.4 Vanadium - 0.2-1.2 |
|
Group name |
List of the main brands included in the group | ||
|
and their combinations with silicon and other elements other than nickel |
Silicon - no more than 1.2 |
||
|
Scrap and waste of tool and magnetically hard chromium-tungsten steels |
XB4 (XB5), EB6 (E7B6) |
Tungsten - 4.5-6.2 Chromium - 0.4-0.7 Nickel - no more than 0.25 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of nickel-free structural steels alloyed with chromium, molybdenum and tungsten |
18HZMV (EI578, N8), 20HZMVF (EI415, EI579, NYU) |
Tungsten - 0.3-0.6 Chromium - 2.0-3.5 Nickel - no more than 0.25 Molybdenum - 0.3-0.6 Vanadium - no more than 0.6 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of nickel-free structural and tool steels alloyed with chromium, tungsten and their combinations with silicon and vanadium |
4X5V4FSM (EI956), 4X2V5FM (EI959), 4X5V4FZM, 5X4SV4MF |
Tungsten - 3.5-5.5 Chromium - 2.0-5.0 Nickel - no more than 0.35 Molybdenum - 0.4-0.6 Vanadium - 0.3-1.2 Silicon - no more than 1.0 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of structural steels alloyed with chromium, nickel, molybdenum, tungsten and their combinations with manganese, silicon and vanadium |
30Kh2N2VFM, 30Kh2GSNVFM, 18KhGSN2VFM (DI-2), 30Kh2GSN2VM, 12Kh2NVFM, 30Kh2GSNVM (VL-1D), 5Kh2NVMF (DI-32), 27Kh2N2VFM, 38KhNZMV |
Nickel - 1.0-3.0 Chromium - 1.2-2.4 Tungsten - 0.2-1.4 Molybdenum - 0.2-0.6 Vanadium - no more than 0.5 Silicon - no more than 1.2 Manganese - no more than 1.3 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant chromium-nickel molybdenum steels |
08X16N13M2B (1X16N13M2B, EI680), X17N16M2B (EI403), 0X17N16MZB |
Chromium - 15.0-19.0 Nickel - 12.0-17.0 Molybdenum - 2.0-3.0 Niobium - 0.2-1.3 |
Continuation of table. 5
|
Group name |
List of the main brands included in the group | ||
|
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant steels alloyed with chromium, nickel and titanium |
08X22N6T (0X22N5T, EP53, 12X21N5T (1X21N5T, EI811) EI810 |
Nickel - 4.8-6.3 Chromium - 18.0-22.0 Titanium - no more than 0.6 Phosphorus - no more than 0.035 Silicon - no more than 3.0 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant chromium-nickel-niobium steels |
08X18N12B (0X18N12B, EI402), 09X14N16B (EI694), 1X14N16BR (EI694R), 1X15N9SZB (EI302), 0X18N10B, 08X19N10B |
Chromium - 13.0-20.0 Nickel - 8.0-17.0 Niobium - 0.7-1.2 Boron - no more than 0.005 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of heat-resistant chromium-nickel wave-niobium steels with boron (in which one part of molybdenum replaces two parts of tungsten) * |
1X14N18V2B (EI695), 09X14N19V2BR (1X14N18V2BR, 09X14H19V2BR1 (1X14H18V2BR1, EI726), Kh16N14V2BR (EP17) |
Chromium - 13.0-18.0 Nickel - 13.0-20.0 Niobium - 0.9-1.3 Boron - no more than 0.025 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant steel with nitrogen, alloyed with chromium, nickel and manganese |
55Х20Г9АН4 (EP303), 0Х20Н4АГ10 (НН-3), 12Х17Г9АН4 (Х17Г9АН4, EI878), Х18Г14АН4 (EP197), 0Х18Н4АГ10 (НН-2) |
Chromium - 16.0-22.0 Nickel - 3.5-4.5 Manganese - 8.0-14.0 Nitrogen - 0.15-0.50 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant steel with nitrogen, alloyed with chromium, nickel, manganese, vanadium and niobium |
0X18N4G11AF (NN-ZF), 0X18N5G11BAF (NN-ZBF), 0X20N4G10B (NN-ZB) |
Chromium - 17.0-20.0 Nickel - 4.0-5.5 Manganese - 10.0-13.5 Nitrogen - 0.4-0.5 Niobium - no more than 0.4 Vanadium - 0.8-1 , 2 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of steels alloyed with chromium, nickel |
15H2NZMDF, |
Copper - 0.6-1.5 Chromium - 0.6-2.0 Nickel - 2.0-5.0 |
lem, molybdenum vanadium and copper
Molybdenum - 0.2-0.7 Vanadium - no more than 0
Scrap and waste of low alloy steels containing copper
10HSND (SKHL-4), 15HSND (SKHL, NL-2), 10HGSN1D (SKHL-45), 10GND
Copper - 0.2-0.8 Chromium - no more than 0.9 Nickel - 0.3-1.3
Scrap and waste of steels alloyed with nickel and copper and their combinations with manganese and vanadium, as well as two-layer steels in which the average content of alloying elements meets the established limits
12ND2FL, 08GDNFL, DS6
Copper - 0.3-0.6 Chromium - 1.8-2.7 Nickel - 0.7-2.0 Manganese - no more than 1.3
Scrap and waste of corrosion-resistant steels alloyed with chromium, nickel and molybdenum and their combinations with titanium and other elements, except tungsten and boron
08H17N13M2T (0H17N13M2T) 10X17H13M2T (H17N13M2T, EI448) H17N13M (EI400), X16H13M3 (EI592), 10X17H13M3T (X17H13M3T, EI432), 03X16H15M3 (00H16N15MZ, EI844) 0H16N16MZ, 08H17N15MZT (0H17N16MZT, EI580) 03H17N13M2, H18N12MZT, 04H19N11MZ
Nickel - 11.0-17.0 Chromium - 14.0-19.0 Molybdenum - 1.8-4.0 Titanium - no more than 0.8 Phosphorus - no more than 0.035
Scrap and waste of low-phosphorous structural steels, alloyed
From 28HZSNMVF to 45HZSNMVF (SP28-45)
Manganese - 0.5-0.8 Nickel - 0.9-1.2 Chromium - 2.8-3.2 Tungsten - 0.8-1.2
Continuation of table. 5
|
Group name |
List of the main brands included in the group | ||
|
chromium, nickel, molybdenum, tungsten, silicon and vanadium |
Molybdenum - 0.3-0.5 Copper - no more than 0.15 Vanadium - no more than 0.15 Silicon - 0.9-1.2 Phosphorus - no more than 0.015 |
||
|
Scrap and waste of heat-resistant steels alloyed with chromium, nickel, molybdenum, tungsten and vanadium |
15H12VNMF (1H12VNMF, EI802) 20H12VNMF (2H12VNMF, EP428), 2H13NVMF, 1H12N2VMF (EI961) 2H12NVMF (VPS-6, EP311), 2H13N2VMF (EP65) 11X11N2V2MF (H12N2VMF, EI962), EP428, 16X11N2V2MF (2H12N2VMF, EI962A ) |
Nickel - 0.4-2.6 Tungsten - 0.7-2.2 Chromium - 10.5-15.5 Molybdenum - 0.3-0.7 Vanadium - 0.1-0.7 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of high-speed steels alloyed with chromium, tungsten, molybdenum, cobalt and vanadium with a cobalt content of up to 10.5% |
R12F2K8MZ (EP657), R10FZK10M4 |
Chromium - 3.7-4.4 Nickel - no more than 0.4 Tungsten - 10.0-13.0 Cobalt - 7.5-10.5 Molybdenum - 2.8-4.2 Vanadium - 1.8-3 ,eight |
|
|
Scrap and waste of heat-resistant steels alloyed with chromium, nickel, molybdenum, tungsten and their combinations with silicon |
1Х14Н14В2М (ЭИ257), 45Х14Н14В2М (4Х14Н14В2М, ЭИ69), Х14Н14СВ2М (ЭИ240) |
Nickel - 12.0-16.0 Chromium - 13.0-16.0 Tungsten - 1.7-2.8 Molybdenum - 0.2-0.6 Silicon - no more than 3.25 Phosphorus - no more than 0.035 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of nickel-free tool steels alloyed with chromium, molybdenum, vanadium and silicon |
4Х5МФС, 4Х5МФ1С |
Chromium - 4.5-5.5 Molybdenum - 1.2-1.5 Vanadium - 0.3-1.0 Silicon - 0.8-1.2 |
|
Group name |
List of the main brands included in the group | ||
|
Scrap and waste of nickel-free tool steels alloyed with chromium, tungsten, molybdenum, vanadium and manganese |
4HZVMF, 7HG2VM |
Chromium - 1.5-3.6 Nickel - no more than 0.40 Tungsten - 0.6-1.3 Molybdenum - 0.5-0.8 Vanadium - 0.1-0.9 Manganese - no more than 2.3 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of dynamo and transformer steels |
E11-E13, E21, E22, E31, E32, E41-E48, E310-E380, |
Carbon - no more than 0.05 Silicon - 0.8-4.8 Phosphorus - no more than 0.015 Copper - no more than 0.15 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of free-cutting steels alloyed with chromium, nickel and lead |
АС19ХГН, АС14ХГН, АС12ХН |
Nickel - 0.5-1.2 Chromium - 0.4-1.2 Manganese - 0.3-1.2 Lead - 0.15-0.30 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of free-cutting steels alloyed with chromium, molybdenum and lead and their combinations with nickel and manganese |
AS20HGNM, ASZOKHM, AS40HGNM, AS38HGM |
Nickel - up to 1.0 Chromium - 0.4-1.2 Manganese - 0.3-0.9 Molybdenum - 0.15-0.25 Lead - 0.15-0.30 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of chromium-nickel chu-gun |
KhND, KhNK, LHCH (1-6), SCHSCH-1 |
Chrome - 0.6-3.8 Nickel - 0.5-1.4 |
|
|
Scrap and waste of chromium-molybdenum cast irons |
Chromium - 0.8-1.2 Nickel - not more than 0.3 Molybdenum - not less than 0.15 |
||
|
Charge ingots of low-phosphorous soft iron containing nickel |
Nickel - 0.8-2.5 Chromium - no more than 0.3 Carbon - no more than 0.08 Phosphorus - no more than 0.008 Copper - no more than 0.2 |
Notes:
1. The average chemical composition of waste two-layer steels is given in table. 7.
2. Scrap and waste of free-cutting steel shall be collected separately and supplied only for the smelting of this steel.
3. In the groups shown in table. 5, in which copper is not regulated, its residual content should not exceed 0.30%.
2.9. The chemical composition of charge ingots must meet the requirements of table. 5 and normative and technical documentation approved in the prescribed manner, according to table. 6.
2.10. Scrap and waste of high-alloy steel and alloys, which, in terms of chemical composition, cannot be assigned to the groups given in table. 5, must be surrendered and delivered blotted. The main brands are shown in table. 6.
Table 6
|
Standard designation |
||
|
38Х2МЮА (38ХМЮА) |
GOST 4543-71 |
|
|
20X1M1F1TR (EP182) |
GOST 20072-74 |
|
|
4Х8В2 (ЭИ160) ** | ||
|
GOST 5950-73 |
||
|
GOST 5950-73 |
||
|
GOST 19265-73 |
||
|
GOST 19265-73 |
||
|
GOST 19265-73 |
||
|
R18F2K8M (EP379) * | ||
|
GOST 19265-73 |
||
|
GOST 19265-73 |
||
|
R6F2K8M5 (EP658) * | ||
|
R18K5F2 (R18K5F) |
GOST 19265-73 |
|
|
06X20N11MZTB (EP89) |
GOST 2246-70 |
|
|
03X21H21M4GB |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
95X18 (9X18, EI229) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
10H14AG15 (DI-13) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
15KHSMFB (EP79) * | ||
|
GOST 5632-72 |
||
|
(000Х23Н28МЗДЗТ, | ||
|
(0Х23Н28МЗДЗТ, | ||
|
EI943, EP591) |
|
Standard designation |
||
|
GOST 5950-73 |
||
|
15X11MF (1X11MF, EP369) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
25Х13Н2 (2Х14Н2, ЭИ474) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
09X16N4B (1X16N4B, EP56, 1X17N4B) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
Kh15N5D2T (EP225, VNS-2, EP410) * Neresist (Zh4NDKh | ||
|
80X20NS (EI992) * | ||
|
(X18N10E, EP47, EI452, EI453) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
0Х18Н12ТФ (ЭИ953) * | ||
|
10Х11Н20ТЗР |
GOST 5950-73 |
|
|
(Kh12N20TZR, EI696), Kh12N20T2R (EI696A), |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
12Х25Н16Г7АР |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
(Х25Н16Г7АР, ЭИ835) 36Х18Н25С2 |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
13X14NZV2FR |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
1Х15Н4АМЗ (EP310, VNS-5) * | ||
|
Х20Н6МД2Т (EP309) * 31Х19Н9МВБТ | ||
|
(ЭИ 572) 37Х12Н8Г8МФБ |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
(4Х12Н8Г8МФБ, |
GOST 5632-72 |
Continuation of table. 6
|
Standard designation |
||
|
40X15N7G7F2MS | ||
|
(4X15N7G7F2MS, EI388) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
0X20N12ABF * | ||
|
(Kh12N22TZMR, EPZZ) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
GOST 5632-72 |
||
|
(Kh21N28V5MZBAR, | ||
|
EP126, VZh 100) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
KhNZOVMT (VK 102, EP437) * | ||
|
48AN1 (XI8N22V2T2) * | ||
|
KhN35VT (EI 612) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
KhN35VTYu (EI 787) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
KhN38VT (EI 703) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
12Х12Н12Г6 (ЭИ 429, Н12ХГ) |
GOST 9124-85 |
|
|
40N, 42N, (N42, EP 318), 45N |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
50N, 52N (EI676) |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
GOST 10994-74 |
||
|
GOST 10994-74 |
||
|
19NX, 20NG, 24NX |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
GOST 10994-74 |
||
|
GOST 10994-74 |
||
|
77НМД (ЭП 233) |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
GOST 10994-74 |
||
|
GOST 10994-74 |
||
|
49K2F (50KF, EP 207) |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
TU 14-1-4487-88 |
||
|
EX9K15M2 (EX9K15M) |
TU 14-1-4487-88 |
|
|
52K5F (52KF5) * | ||
|
52K7F (52KF7) * | ||
|
52K9F (52KF9) * | ||
|
52KF12 (52KFB) |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
36N (N36, N36L) |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
32NKD (EI 630A, N30K4D) |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
GOST 10994-74 |
||
|
30NKD (N30K13D) |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
ZZNK (NZZK17, EP 139) |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
47НХР (Н47ХР, Н47ХБ) |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
GOST 10994-74 |
||
|
47NX (N47X, EI 677, EI563) |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
42NA (Feni 42, EPZZZ) |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
Standard designation |
||
|
40KHNM (K40HNM) |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
36НХТЮ (ЭИ 702) |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
(36NKHTYUM5, EP51) |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
(36NKHTYUM8, EP52) |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
42НХТЮ (Н41ХТ), | ||
|
44НХТЮ (Н43ХТ) |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
97 NL (EI 996) |
GOST 10994-74 |
|
|
NIM025 (EI 639) * | ||
|
Kh20N46B (EP 350) * | ||
|
KhN60VT (EI868) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
KhN78T (EI 435) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
KhN60Yu (EI 559A) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
KhN70Yu (EI 652) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
KhN77TYUR (EI 437B, | ||
|
EI 437, EI437A) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
ХН80ТБЮ (ЭИ 607) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
KhN75TBYU (EI 869) * | ||
|
KhN67VMTYu (EP202) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
KhN70VMYUT (EI 765) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
KhN70VMTYu (EI 617) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
KhN70MVTYUB (EI598) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
KhN65VMTYu (EI893) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
KhN70VMTYu (EI826) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
KhN75MBTYu (EI602) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
KhN73MBTYu (EI698) * | ||
|
KhN56VMTYu (EP199) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
KhN55VMTKYU (EI929) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
KhN56VMKYU (EP109) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
ХН62МВКЮ (ЭИ867) |
GOST 5632-72 |
|
|
GOST 10994-74 |
||
|
GOST 10994-74 |
||
|
VKS210 (EP637) * | ||
|
GOST 5950-73 |
||
|
40G18YUZF (EP112) * | ||
|
4X2V2MFS (EP641, | ||
|
GOST 5950-73 |
||
Continuation of table. 6
|
Standard designation |
||
* According to the normative and technical documentation approved in accordance with the established procedure.
** According to the replaced GOST 5950-63.
*** According to table 7 of this standard.
Notes:
1. In charge ingots, the following deviations in terms of the minimum and maximum content of alloying elements from those indicated in table are allowed. 5 and in the standards given in table. 6:
± 0.2% - for chromium with its content up to 10%;
± 0.5% - for chromium when its content is over 10%;
± 0.15% - for nickel with its content up to 5%;
± 0.4% - for nickel with its content exceeding 5%;
± 0.1% - for tungsten with its content up to 2%;
± 0.25% - for tungsten when its content is over 2%;
± 0.05% - for molybdenum with its content up to 1%;
± 0.15% - for molybdenum when its content is over 1%.
2. In the designations of steel grades given in table. 5 and 6, the last letter A for high quality steel has been omitted. Steels of high quality grades are included in the same waste group as steels of these grades of normal quality.
Old designations of steel grades are indicated in brackets.
3. The designation of alloyed scrap and waste of a certain type and group consists of the type number and the designation of the group.
For instance:
steel scrap and waste No. 2 of B26 group will have the designation 2B26.
Alloyed scrap and waste of a certain type have a seven-character code, in which the code of the waste group or the code of the metal grade is added to the general code of the class, category and type.
For instance:
steel scrap and waste No. 2 of B26 group will have the code 1212026, steel scrap and waste Nq 2 of grade X15N60-1212191.
2.11. Scrap and waste of two-layer steels, which are alloyed according to the average chemical composition, are distributed in accordance with the requirements of Table. 7.
Table 7
|
Designation two-layer |
Main layer steel grade |
Cladding steel grades |
Average chemical composition of the mass of two-layer steel,% |
Designation of the corresponding waste group |
|
VStZ, 10, 20K, 09G2, 09G2S (M), 16GS (ZN) |
08X13 (ЭИ 496, 0X13) |
Chromium - 1.3-1.5 | ||
|
VSTZ, 20K, 10 |
Chromium - 1.7-1.9 | |||
|
08X13 (ЭИ 496, 0X13) |
Chromium - 1.5-2.5 Nickel - up to 0.30 Molybdenum - 0.3-0.6 | |||
|
VSTZ, 20K, 09G2T (M) |
08X18N YuT, 12X18N10T |
Chromium - 1.3-2.0 Nickel - 0.8-1.5 Manganese - up to 1.3 | ||
|
VSTZ, 20K, 09G2S, 16GS |
Chromium - 2.4-2.8 | |||
|
10HSND (SHL-4) |
08X18N YUT, 12X18NYUT |
Chromium - 2.2-2.7 Nickel - 1.0-2.0 Copper - 0.3-0.6 | ||
|
08X18N YUT (0X18NYUT, EI914) |
Chromium 2.0-2.6 Nickel - 0.8-1.2 Molybdenum - |
Blotted |
||
|
20K, 09G2S, VStZ |
YUH17N13M2T, 08Х17Н15МЗТ |
Chromium - 1.6-2.0 Nickel - 1.2-1.8 Molybdenum - 0.2-0.4 | ||
|
VSTZ, 16GS |
Chromium - 2.2-2.6 Nickel - 2.6-3.0 Molybdenum - 0.2-0.4 Copper - 0.2-0.4 |
Blotted |
||
|
Chromium - 1.5-1.8 Nickel - 6.0-6.8 Molybdenum - 1.4-1.8 Tungsten - 0.2-0.5 |
Blotted |
Continuation of table. 7
3. RULES OF ACCEPTANCE
3.1 Secondary ferrous metals are presented for acceptance in lots.
3.2. A batch is the amount of secondary ferrous metals of one type and one group or brand, shipped in one unit of vehicles and accompanied by one quality document.
A lot of scrap and waste of high-alloy steel and special alloys is the amount of scrap and waste shipped in one packaging unit.
3.3. Acceptance of secondary ferrous metals should be carried out by metal weight. The weight discount for contamination with harmless impurities and oil should be made in accordance with the actual contamination determined during acceptance.
3.4. To check the compliance of secondary ferrous metals with the requirements of this standard in terms of their composition, purity, dimensions, weight, density, crumbling and limiting content of alloying elements, five bags or briquettes are taken from the batch, and for other types of scrap and waste, sampling is carried out by agreement of the parties.
3.5. Upon receipt of unsatisfactory test results for at least one of the indicators for it, repeated tests are carried out on a doubled number of samples or a doubled sample taken from the same batch. Retest results are final and apply to the entire batch.
4. TEST METHODS
4.1. The composition of the batch of secondary ferrous metals presented for acceptance is checked visually.
4.2. The contamination of secondary ferrous metals with harmless impurities and oil is determined by agreement between the consumer and the supplier by methods that ensure the correct determination of the amount of contamination.
The contamination is checked by weighing the taken samples.
4.3. The contamination of bags and briquettes with harmless impurities and oil is checked after destruction by breaking or cutting.
4.4. To determine the dimensions and mass of secondary ferrous metals, they are measured and weighed. The density of bags and briquettes is defined as the ratio of the mass of a bag or briquette to its volume.
4.5. To determine the crumbling of briquettes, they are thrown three times (by free fall) from a height of 1.5 m onto a metal or concrete slab, while they should not crumble by more than 10%. Out of five discarded briquettes, at least four briquettes must withstand the test. If the test results are unsatisfactory, eight briquettes should withstand the test from 10 re-dumped briquettes.
4.6. To determine the content of alloying elements and other elements limited in the relevant standards, samples are taken from at least five locations in the batch.
The permissible deviation in chemical composition in the content of an individual element in two samples should not exceed 15% of the lower or upper limits of the studied group indicated in table. 5.
The arithmetic mean of the results of all determinations, which should be within the study group, is taken as the result of the analysis.
Note. Sampling in bags and briquettes is carried out from the outer and inner parts after the cut.
4.7 The chemical composition of secondary ferrous metals is determined according to GOST 12344-88, GOST 12345-88, GOST 12346-78, GOST 12347-77, GOST 12348-78, GOST 12349-83, GOST 12350-78, GOST 12351-81, GOST 12352 -81, GOST 12353-78, GOST 12354-81, GOST 12355-78, GOST 12356-81, GOST 12357-84, GOST 12358-82, GOST 12359-81, GOST 12360-82, GOST 12361-82, GOST 12362 -79, GOST 12363-79, GOST 12364-84, GOST 12365-84 for steel), GOST 28473-90 and GOST 2604.1-77, GOST 2604.2-86, GOST 2604.3-83, GOST 2604.4-87, GOST 2604.5- 84, GOST 2604.6-77, GOST 2604.7-84, GOST 2604.8-77, GOST 2604.9-83, GOST 2604.10-77, GOST 2604.11-85, GOST 2604.13-82, GOST 2604.14-82 (for cast iron) or other methods providing the required accuracy of determination.
4.8. If alloying elements not specified in this group are found in a sample or sample, the batch belongs to this group if the content of each of these elements does not exceed the upper limit provided for steel grades by the relevant standards or other regulatory and technical documentation.
5. MARKING, PACKAGING, TRANSPORTATION
AND STORAGE
5.1. Each batch of secondary ferrous metals must be accompanied by a document certifying their compliance with the requirements of this standard and including:
a) the name of the shipping company;
c) date of dispatch;
d) car number;
A batch of secondary ferrous metals shipped from enterprises using radioactive substances in the production process must be accompanied by a decontamination document.
In the shipping documents, an inscription must be made: for alloyed scrap and waste - "Doped scrap for remelting" or "Doped scrap for processing", for carbon ones - "Carbon scrap for remelting" or "Carbon scrap for recycling".
(Modified edition, Amendment No. 3).
5.2. Scrap and waste of high-alloy steel and special alloys must be shipped packed in specialized containers in accordance with the normative and technical documentation. At the same time, in addition to the shipping and accompanying documents, a marking label is applied to the batch of scrap and waste, which indicates the mass, group of waste or metal grade.
Transport marking - in accordance with GOST 14192-77.
(Modified edition, Amendments No. 3, 4).
5.3. The supplied charge ingots must be marked individually with the indication of the heat number.
5.4. Secondary ferrous metals should be stored separately by types and groups or brands.
During storage, scrap metal and waste should not be mixed with non-metallic materials.
5.5. The oily shavings should be disposed of in dumps in the area of the site equipped with sedimentation tanks for oil, or in bins with an oil drain.
5.6. Secondary ferrous metals, including packages, are transported in bulk.
5.7. Secondary ferrous metals are transported by all types of transport in open vehicles in accordance with the rules for the carriage of goods in force for this type of transport.
Secondary ferrous metals are loaded into wagons and placed in them in accordance with the technical conditions for loading and securing goods approved by the USSR Ministry of Railways.
5.6, 5.7. (Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 4).
6. REQUIREMENTS FOR ENSURING EXPLOSION PROTECTION
6.1. Enterprises, organizations and farms that procure, hand over, process and remelt secondary ferrous metals, as well as unload or reload them in ports and other points, must check all secondary ferrous metals for explosion safety and remove from them all items containing explosive flammable and flammable substances.
Scrap metal handed over by schools, hospitals, etc. institutions should be checked by procurement organizations.
6.2. Deactivated explosive items must meet the following requirements.
6.2.1. Ammunition (shells, mines, warheads, aerial bombs, etc.) must not have explosive devices, must have an open spectacle, an unscrewed bottom and an empty chamber; their inner surface must be cleaned of explosives and special compounds; in shrapnel machines and jet mines, the inner baffle (diaphragm) must be removed.
6.2.2. The barrels of artillery and small arms must be with open through channels or deformed at the end of the barrel and breech (receiver) to a complex bend.
6.2.3. Store boxes of artillery and small arms must be open and empty or bruised (to the point of cracking).
6.2.4. Artillery and small arms cases must not have means of ignition (capsule sleeves, galvanic and galvanic shock tubes, etc.) and the remains of powder charges.
6.2.5. All types of military equipment handed over for scrap by military units must be written off in accordance with the established procedure of the USSR Ministry of Defense, rejected, disassembled and freed from combustible and lubricants, and the ammunition, solid fuels, initiators and other explosives contained in them must be removed ; the fluid from the cylinders of hydraulic, brake, anti-rollback and other devices must be drained.
6.2.6. Vessels of all types and sizes (cylinders, barrels, etc.) and all hollow objects (engine cylinders, etc.) must be cleaned of contents (and in winter - from ice and snow) and are accessible for inspection of the inner surface ; the necks of the cylinders must be open, and a second hole must be cut on their body; the bottoms of barrels and other containers must be opened.
6.2.7. Capacities of machine units (engines, gearboxes, etc.) must be free of residues of combustible and lubricants.
6.2.8. Beds, pallets, metal structures and other massive objects subjected to explosive crushing must not have unexploded charges or their remains.
6.3. If non-neutralized ammunition is found, further work with scrap metal should be suspended and measures should be taken to remove, neutralize or destroy them by representatives of the military unit.
6.4. Inspection of scrap and waste of ferrous metals for explosion safety and removal of explosive objects from them (except for those specified in clause 6.3) must be carried out under the guidance of a person * who has undergone special training and has an appropriate certificate.
6.5. For the removal and transportation of explosive objects, workers who have passed special equipment must be allocated, who, before starting work, must be instructed in the prescribed manner about the precautions for carrying out these works.
6.6. Cutting and shipment of scrap metal specified in paragraphs. 6.2.1-6.2.5, must be produced separately from other scrap.
6.7. Every vehicle with recycled ferrous metals must be accompanied by a document certifying their explosion safety.
The form of a certificate of explosion safety of scrap and waste of ferrous metals is given in the mandatory Appendix 3.
6.8. Unloading and inspection of the scrap and waste received at the enterprise for explosion safety in accordance with the requirements set out in clause 6.2 should be carried out under the supervision of a pyrotechnician. The check must be recorded in the ledger
scrap received by the enterprise, indicating the name of the enterprise (organization) - the sender; consignment note numbers and explosion safety certificate, the name of the pyrotechnician with his signature. Explosion protection of packets is ensured by the sender.
6.9. Untested secondary ferrous metals should not be mixed with tested ones and cannot be accepted for processing or use as a metal charge.
6.10. All work related to the testing of secondary ferrous metals for explosion safety and their neutralization must be carried out with an illumination of at least 30 lux.
6.11. Explosive objects discovered during the inspection of secondary ferrous metals (except those specified in clause 6.3) must be removed and sent, accompanied by pyrotechnics, for temporary storage or disposal.
6.12. Upon detection of explosive objects, an act must be drawn up, the form of which is given in the mandatory Appendix 4.
6.13. The explosion safety of the supplied scrap metal is ensured by the sender, and the explosion safety of the received scrap (excluding packages) is ensured by the recipient.
6.14. Scrap metal to be processed by various methods (gas and scissor cutting, batching, crushing, etc.) must be checked for explosion safety in accordance with the requirements set out in clause 6.2.
6.15. Immediately before loading into troughs, scoops and buckets, scrap and waste must be checked for explosion safety in accordance with the requirements set out in clause 6.2. An entry must be made about the check in the metal charge book with the signature of the pyrotechnician who performed the check.
6.1-6.15. (Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 2).
6.16. The storage of explosive items (except for those specified in clause 6.3) is carried out in storage facilities built in accordance with the requirements of the "Unified Safety Rules for Blasting Operations" approved by the USSR Gosgortekhnadzor.
Storage facilities should be located at a distance of at least 30 m from buildings, structures and communication lines. Shelf life - no more than 15 days.
In storage facilities and at a distance of less than 30 m from them, it is prohibited to use open fire and perform gas-electric welding work.
The storehouses must be provided with lightning protection and fire-fighting equipment in accordance with the applicable rules and regulations.
(Modified edition, Amendments No. 2, 3).
6.17. Explosive objects that entered storage facilities must be placed in a stable position, excluding the possibility of their falling.
6.18. Neutralization or destruction of military explosive scrap metal and cylinders with unknown content must be carried out by the appropriate military units in the prescribed manner.
6.17, 6.18. (Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 2).
APPENDIX 1 Reference
GROUPS AND BRANDS OF ALLOYED SCRAP AND WASTE INTENDED FOR PREPARATION OF SEPARATE TYPES OF SECONDARY FERROUS METALS
|
Type name |
Group designation and brand |
|
Briquettes No. 1 and 2 from steel shavings Packages No. 1 and scrap for packaging No. 1 Steel ropes and wire |
BZ, B4, B5, B13, 38X2MYUA (38HMYUA) Any group or brand specified in this standard B1, B2, BZ, B4, B5, B6, B8, B9, B10, B11, B12, B13, B15, B16, B18, B19, B21, B24, B25, B26, B32, BZZ, B34, B37, B42, B43, B53, B59, 38Kh2MYuA (38KhMYuA), Kh12M, EP589, 95X18 (9X18, EI229), EP609, 25Kh13N2 (2Kh14N2, EI474), 80Kh20NS (EI922), EP263, 0Kh18N12TF, EP128173 ), 40Kh15N7G7F2MS (4Kh15N7G7F2MS, EI388), 10Kh11H23T3MP (Kh12N22TZMR, EPZZ, 40N, 42N (N42, EP318), 45N, 36N (N36, N36L), 36KHNTU (EI702), NKHTYU NIM025 (EI639), KhN78T (EI435), Kh15N60, N20N80 |
(Modified edition, Amendment No. 2).
INTENDED FOR USE AS A METAL CHARGE IN DIFFERENT MELTING UNITS
|
Melting aggregates |
Types of secondary ferrous metals |
Conditional designation |
|
|
1. Converters |
Steel scrap i |
l waste No. 3 | |
|
Packages No. 1 1 Packages No. 2 g without shavings Packages No. 3 J | |||
|
Briquettes No. 1 from steel shavings | |||
|
Steel scrap and waste No. 3 | |||
|
Packages No. 1 | |||
|
Packages No. 2 Packages No. 3 Briquettes No. 1 from steel shavings |
9A 10A 6A, 6B |
||
|
Briquettes No. 2 from steel shavings | |||
|
Steel shavings No. 2 | |||
|
Steel ropes and wire | |||
|
3. Electric arc furnaces: | |||
|
a) with a capacity of up to 20 tons |
Steel scrap and waste No. 2 | ||
|
Steel scrap and waste No. 4 | |||
|
Briquettes No. 1 from steel shavings | |||
|
Packages No. 1 |
Sizes no more | ||
|
Packages No. 2 |
> 600 * 600 * 800 mm, | ||
|
Packages No. 3 |
without shavings | ||
|
b) with a capacity |
Steel scrap and waste No. 3 | ||
|
Briquettes No. 1 from steel shavings | |||
|
Briquettes No. 2 from steel shavings | |||
|
Packages No. 1 Packages No. 2 |
Sizes no more | ||
|
Packages No. 3 |
600 * 600 * 800mm, | ||
|
Steel ropes and wire | |||
|
4. Electric induction furnaces: | |||
|
e) for smelting |
Steel scrap and waste No. 1 | ||
|
Steel scrap and waste No. 4 | |||
|
Briquettes No. 1 from steel shavings | |||
Continuation
|
Melting aggregates |
Types of secondary ferrous metals |
Conditional designation |
|
b) for you floating |
Steel scrap and waste No. 1 | |
|
ki cast iron |
Steel scrap and waste No. 2 | |
|
Steel scrap and waste No. 4 | ||
|
Briquettes No. 1 from steel shavings | ||
|
Briquettes No. 2 from steel shavings | ||
|
Steel shavings No. 1 | ||
|
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 1 | ||
|
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 2 | ||
|
Cast iron briquettes | ||
|
Cast iron shavings | ||
|
5. Cupola |
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 1 | |
|
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 2 | ||
|
Pig iron scrap and waste No. 3 | ||
|
Steel scrap and waste No. 1 | ||
|
Briquettes No. 1 from steel shavings | ||
|
Briquettes No. 2 from steel shavings | ||
|
Cast iron briquettes | ||
|
6. Domain |
Blast furnace | |
|
Rolling and forging mill scale | ||
|
Welding slag | ||
|
7. Ferroalloy |
Steel shavings No. 1 | |
(ministry, department)
Drawn up in duplicate. One copy with the invoice is sent to the recipient, and the second remains with the sender.
CERTIFICATE No._
on explosion safety of scrap and waste of ferrous metals
Recipient of scrap and waste _
Scrap and waste name _
Mass_tons
Wagon (car) No._ consignment note No._
The specified scrap and waste meet the requirements of GOST 2787-75, are explosion-proof and can be approved for processing and use as a metal charge.
Responsible representative
delivery company _ _
(signature,
(initials and surname)
(ministry, department)
(name of the delivery company)
Drawn up in triplicate.
Sent: one copy - to the sender with copies of his invoice and explosion safety certificate, the second - to the sender's technical labor inspector, and the third - remains at the enterprise.
"APPROVED" Chief Engineer
on the detection of explosive objects when checking scrap and waste of ferrous metals
Scrap and waste shipper _
Name of scrap and waste_
Mass_tons
Wagon (car) No._
Invoice #_ date of arrival "_" 19_year.
Explosion protection certificate No._of "_" 19
Checking established: _
(describe each explosive item in detail) Administration representative
recipient company _ _
Pyrotechnic _ _
(signature) (initials and surname)
Appendices 3, 4 (Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 2).
Editor R. G. Goverdovskaya Technical editor N. S. Grishanova Proofreader N. I. Gavrishchuk Computer layout A. P. Finogenova
Ed. persons. No. 02354 of 14.07.2000 Signed for printing on 11.04.2002. Uel. print l. 3.02. Uch.-ed. l. 2.90. Circulation 89 copies. S 5171. Zak. 325.
IPK Standards Publishing House, 107076, Moscow, Kolodezny per., 14. Branch of the IPK Standards Publishing House - type. "Moscow printer", 103062 Moscow, Lyalin per. 6 PLR No. 080102
 What to do in case of unsuccessful attempts to find a job
What to do in case of unsuccessful attempts to find a job Information about welded joints
Information about welded joints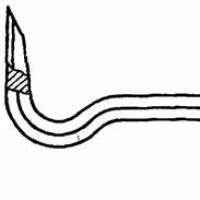 Gost scrap of ferrous metals (download) Scrap for construction gost 1405 83
Gost scrap of ferrous metals (download) Scrap for construction gost 1405 83 How many kilometers is the Moscow Ring Road in a circle?
How many kilometers is the Moscow Ring Road in a circle? Where did the Moscow sparrows disappear: the conclusion of ornithologists Why did the sparrows disappear?
Where did the Moscow sparrows disappear: the conclusion of ornithologists Why did the sparrows disappear? How to make money on homemade toys?
How to make money on homemade toys? Creative business: making handmade toys
Creative business: making handmade toys