Modern approaches to organizing the release of personnel. The concept and types of staff release. According to this criterion, three types of layoffs can be distinguished
RELEASE OF STAFF
The release of personnel is a kind management activities, providing for a set of measures for the observance of legal norms and organizational and psychological support from the administration when dismissing employees. This is the final stage in the formation of the organization's personnel.
The employer must consider the severity and importance of the dismissal from an industrial, social and personal perspective.
The release of personnel depends on the following factors:
- ? a release initiator;
- ? the reasons for the release;
- ? planned release (planned, emergency);
- ? the quality of vacated posts;
- ? the number of laid off workers (mass, large and medium batch, single).
Initiator and reasons for release. The reasons for the release can be very different: related to the personal life of the employee (relocation, maternity leave, reaching retirement age, enrolling in school, etc.), with his dissatisfaction with the changed organizational environment (deterioration of the socio-psychological climate, conflict, change in working conditions, etc.), with violation of the organization or employee of performance labor contract, with changed conditions for the functioning of the organization. The reasons for such changes can be positive (application of new technologies, diversification, reengineering) and negative (crisis, decline in business activity, bankruptcy, withdrawal from the market). The result of the influence of these reasons is a change in the number and (or) staff of the organization.
The reasons for the release may not depend on the employee or organization. Force majeure reasons for the release will not be considered in this work.
The most painful for the organization is care for employee initiative, those. that kind of release, which is practically not predicted by the administration and, as a rule, occurs unexpectedly for it. However, from the point of view of the employee, the ego is the mildest kind of release: the employee is ready to leave the organization, and this kind of release is psychologically easier for him.
When an employee leaves the organization on their own it is necessary to conduct a final interview with him, the main objectives of which are to analyze bottlenecks in the organization, an attempt to influence the change in the decision to dismiss (if this is a valuable employee for the organization and leaves of his own free will), the removal of mutual claims.
If an employee leaves of his own free will, then you need to prepare for the final interview and collect the following data:
- ? the nature of the relationship of the quitting employee with colleagues;
- ? his attitude to work;
- ? level vocational training a quitting employee;
- ? the presence of conflicts of a personal and official nature;
- ? previously expressed wishes to change jobs;
- ? access to information, including that constituting a commercial secret, and assess the likely period of obsolescence of this information for the organization;
- ? the expected future place of work of the employee.
A final interview should be conducted after collecting information. The venue is usually office premises. That interview can be either official or confidential based on the actual situation. The final interview is usually conducted by HR or a specialist, as they are experienced in conducting such interviews with maximum informational benefit to the organization.
However, the veracity of the reasons for the dismissal given by the employee during the exit interview remains an issue. Many employees believe that open criticism of negative aspects in the activities of the organization they leave may damage their interests in the future. To increase the reliability of the data, experienced managers recommend convincing the resigning person that the information received from him will be used exclusively in a constructive and not at all vengeful manner. This is also facilitated by the standardization of the questions included in the interviews and the cross-checking of the reasons for the employee's dismissal by comparison with information received from higher-level personnel and other employees. When conducting exit interviews, the resigner is seen as someone who discovered flaws in the organization's work that he could not come to terms with, and therefore his answers to questions become an extremely important source of information about the reserves, which may not be seen by management. This attitude is expressed in questions such as: what do you like most in the work of the organization, what do you like least in the work of the organization, how fair is the work in the organization, how do you assess the situation in the organization.
Clarify many assessments and views former employee it is advisable by means of a “weekend” interview conducted in person or by telephone 2-3 months after the employee is fired. By this time, the employee becomes more independent from former leadership and can become more outspoken. In addition, he has the opportunity to compare his position in the previous job with the new one, therefore, his assessments can become more objective.
Of course, this kind of activity takes a lot of time and effort, so it is extremely important to ensure its effectiveness. To do this, it is necessary, on the basis of data analysis and processing, to implement measures to prevent turnover, which are associated with a more careful selection of workers in the organization and purposeful retention within it.
Despite the reasons for dismissal, the employee must leave the organization without resentment, irritation, revenge, without humiliation. The main goal is that after finishing work in this organization, the employee does not have a feeling of suffering, and the employer does not feel uncomfortable.
Dismissal initiated by the organization can be predicted by the leadership of the administration. From the point of view of employees, this is a painful kind of release, which is difficult for them to predict and sometimes psychologically accept.
Sometimes, in the current economic conditions, an organization is faced with the need for mass, large-scale and small-scale dismissal of workers, which is an objective necessity. The reasons that led to this type of release, from the point of view of the organization, are both positive and negative. However, from the point of view of workers, this kind of release is stressful.
The downsizing process should not be chaotic. It needs to be well planned and prepared. As a rule, the administration of the organization makes a decision, determines the timing and total people to be fired. The campaign to reduce personnel, in addition to "the need to bring the number in line with the production load", is also justified ideologically, the management demonstrates the social orientation of personnel and social policy and care for the team - ego preservation of personnel potential, improving the management structure, eliminating unnecessary links, attracting young specialists and workers to ensure continuity.
The organization should develop a mechanism for releasing personnel. First of all, the number of released workers is established, which depends on the reasons for the release.
The second stage of the release is the determination of the timing of the reduction. As a rule, this is a phased reduction of the number of employees to the established number. The interval between stages can be from one month to six months. This approach, especially in the case of mass release, allows this process to be carried out with the least problems both for the organization and for the region where it is located, to avoid social upheavals, etc. The region receives additional time in order to employ the freed up workers. For economically sufficiently prosperous regions, this period can be shortened as much as possible. In depressed areas, as well as in the case when the organization is city-forming, the maximum possible interval between the reduction stages is established.
Consider the categories of workers that fall under iodine reduction in the first place. The possibility of dismissal of each of the categories is characterized from two sides: moral and economic. The economic side refers to the need of the organization itself. When it comes on the moral side of the issue, the problem is considered from the point of view of the dismissed workers.
Violators must leave the organization first. labor discipline, then unskilled workers can be fired. In an economic sense, the loss of this category is painless, but in a moral sense, problems may arise that should be solved in the same way as with all other categories of workers.
Further - the rest of the workers. There can be only one criterion for their dismissal - the desire and ability to fulfill the duties assigned to them. However, in some organizations, risk categories are emerging. The risk category includes retirees, workers with little work experience in this unit or organization, newly hired youth and students.
It is especially worth emphasizing that from an economic point of view, there is one criterion for differentiating personnel during mass layoffs - this is their qualifications. The organization must take all possible steps to retain the best people in the organization, the rest is acceptable to "sacrifice".
From a moral point of view, a fairly large number of factors can be considered, which include the so-called everyday circumstances, for example, the age of the staff. First of all, the youngest workers should be laid off, provided that they do not have families and small children. This is explained, on the one hand, by the fact that they are more adaptable to the labor market, and therefore it is easier for them than for older people to find new job... On the other hand, they are the most mobile part of the population, therefore, they are more likely to find work in another region, etc. However, all these factors should be taken into account only after considering the factors of professionalism, other things being equal.
The most predictable type of staff release from the organization, both from the point of view of the organization and from the point of view of the employee, is retirement. However, from a psychological point of view, this kind of release is sometimes difficult. Thus, statistics say that the largest number of deaths in men occurs at the age of 61 years. This is explained by the fact that retirement is more difficult for men than for women, since this process is associated with a change in the worker's status, income level, the emergence of a significant amount of free time, and all these changes are noticeable to others.
Therefore, this process should be closely monitored by the administration and personnel management services. They must conduct certain activities with retiring workers. Such activities include adaptation preparatory retirement courses; rolling pension, g.e. the transition from a full-fledged working life to final retirement. For this, a time frame is established within which employees move to a part-time work week, to an incomplete working day, to certain changes in wages. At the same time, the organizational status of workers of pre-retirement age can be gradually changed, for example, an employee from the position of a manager moves to the position of a consultant, expert, instructor.
There are also various types of release that soften this process, which have been successfully applied in foreign practice, when mass release and retirement were combined.
In the United States, a method was used to stimulate voluntary dismissal or retirement. The administration, but for a clearly defined contingent (age, division, work experience), encourages retirement or dismissal of their own free will, offering for some time an increased severance pay or preferential conditions for retirement.
Various variants and modifications of this method are used: the “open window” method, the “selective reduction” method, and “intimidation tactics”.
The "open window" method used in the case when it was required to carry out a significant reduction in the apparatus. So, the firm "DuPont" in the 1980s. invited managers, starting with the middle management, to retire, having not 27 years of work experience, but 22 years. The effect was unexpected. The organization's management wanted to fire 6,500 people, but received twice as many applications from those wishing to retire, of which 400 people held key positions in the firm.
Specificity of "selective reduction" lies in the fact that the submitted applications from employees are valid for several years and the administration itself selectively carries out dismissals depending on the situation. During this period of time, the employee gets used to the idea of leaving the organization, manages to find another occupation for himself, and the release process takes place according to a softer scheme.
Intimidation tactics is used to encourage voluntary redundancies. So, the ATT company in the mid-1980s. began to report the ratings of employees. Those workers whose ratings were low preferred to quit on their own initiative, without waiting for layoffs.
Dismissals in the organization occur constantly, and in case of dismissal on the initiative of the administration, the psychological situation can carry elements of personal drama, and possibly tragedy. Therefore, it is necessary to follow certain recommendations in order to “culturally” fire an employee. Here you can follow the recommendations of Stephen A. Jessef, vice president of the recruiting firm, who, based on professional experience and long-term observation, has summarized the following recommendations for dismissal.
- 1. Do not notify employees of layoffs at the end of the week or the day before a holiday when they have extra time to think. This does not apply to immediate layoffs, i.e. those violations that are associated with theft and other serious negative actions of employees. Be considerate and don't fire an employee on their birthday, wedding anniversary, or organization anniversary. If possible, do not fire a woman when she is pregnant or divorcing or sick, or after the recent death of a family member.
- 2. Do not express the reason for the termination in your own words and do not give the employee to be fired an opportunity to think that you simply do not like him. State the reason officially, with accurate and well-reasoned facts of poor performance by subordinates or the plight of the organization. Never humiliate a person, regardless of the reason for being fired.
- 3. Do not provide conflicting information: tell the dismissed employee about one reason, and other employees about another. To avoid conflict, some managers inform their employees that their position has been cut (eliminated), and then tell those who remain that the person was simply not doing their job. This management tactic opens the door to illegal activities and makes the remaining workers wonder if the manager is honest with them.
- 4. Do not tell anyone other than those who need to know that the employee will be fired. If such information is disseminated, the ego can create panic throughout the organization and increase the feeling of resentment of the person being fired.
- 5. Do not notify too early about dismissal due to unemployment or liquidation of the position.
- 6. Do not ask the worker to release immediately workplace and leave the office. The time after work or the weekend is the most appropriate time for the dismissed ego to do.
- 7. Except in the event of fraud or theft, do not use the organization's security services to escort the dismissed person out of the building.
- 8. Don't expect people to be laid off to behave reasonably after being told that there is no longer work for them.
- 9. Do not forget the "golden rule": if you do not understand something about a person's behavior, imagine yourself in his place.
- TO). Assign one of your closest employees to contact the laid-off worker until he finds another job.
The sequence and nature of the termination procedures must strictly comply with the requirements labor legislation, do not contradict the collective agreement, personnel regulations, job description, labor agreement(to the contract). The collective agreement usually defines the procedure for dismissing personnel in the event of a decrease in the business activity of the organization and the procedure for hiring previously dismissed workers in the event of an increase in business activity. If possible, the employee is given severance pay, letter of recommendation, provide assistance in employment, retraining, etc.
The process of announcing termination of employment depends on the law, except for gross violations of labor discipline. But both parties can negotiate other terms fixed by the contract. Articles 77-84 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulate the legal aspects of the process of dismissing an employee from an organization.
When releasing personnel, it is necessary to remember the costs associated with this process, when both the organization and the employee bear mutual direct and indirect costs, a list of which is presented in table. 2.6.
Table 2.6
Dependence of the cost of release from its initiator and reasons
|
Release initiator | ||||
|
indirect |
||||
|
worker |
organization |
worker |
organization |
|
|
Worker Of my own free will |
Large (costs for urgent vacancy filling) |
Medium (decrease in attractiveness in the labor market) |
||
|
Due to violation of the employment contract by the employer |
(penalties costs pa legal actions) |
Medium (decrease in attractiveness in the labor market |
||
|
Organization Due to violation of an employment contract by an employee |
Large (costs of compensation for losses, fines, penalties, looking for another job) |
Average (legal support costs) |
||
The most costly for the organization is release on the initiative of the employee, since the dismissal of this type is practically not planned by the management and, as a rule, occurs unexpectedly for her and, accordingly, is associated, on the one hand, with a decrease in overall labor productivity, and on the other, with the impossibility of optimizing the costs of urgently closing a vacancy.
Release due to non-fulfillment of the labor contract by the organization is associated for the organization with the costs of paying compensation to the employee and legal costs.
Dismissal due to non-fulfillment of an employee's labor contract does not entail any costs for the organization.
As you can see from the table. 2.10, the least preferable for both the employee and the employer is the release of personnel due to changes in the number and (or) staff. If, with positive reasons for changes in the working conditions of the organization, it becomes necessary to redistribute personnel with single or medium-series layoffs, then with negative reasons for changes in its financial position it may turn out that the preservation of the previous volume of production (performance of work, provision of services) will become impossible not only at the present time, but also in the future. In this case, the organization's management may decide to carry out measures to massively reduce the number of personnel.
Costs are influenced by and quality of vacated posts. If an organization vacates a job that implies high wages for skilled labor, then when such an employee is fired, the severance pay will be high. When this employee is fired on his own initiative, the cost of hiring a new employee increases dramatically.
The cost depends on the number of laid off workers, moreover, if the release concerns workers of a higher level of professionalism and their number is large, then this sharply increases the costs of the release.
Usually, the collective agreement defines the procedure for releasing personnel. If possible, the employee is given a severance pay, a letter of recommendation, assistance in employment, retraining, etc. However, there is also a legislatively enshrined practice of dismissals during mass redundancies and and.
- 1. The minimum period between the decision of the management to change the conditions or terminate the contract with the employee and its actual implementation is two months. At the same time, the costs of the organization become the salary paid to the employee and the payments transferred according to the rates of insurance funds. Indirect costs for this period are a decrease in the labor productivity of the dismissed employee and technologically related other workers.
- 2. The employer, with the written consent of the employee, has the right to terminate the employment contract with him without warning of dismissal two months in advance with the simultaneous payment of additional compensation in the amount of two months' average earnings (Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The costs of the organization in this case will be the payment of compensation.
This option for reducing the number and staff is the most economical for the organization. For an employee, it is beneficial only if the employee is confident in quickly finding a new, higher-paid job.
3. Termination employment contract with an employee on the initiative of the management entails additional costs for the payment of severance pay (and. 2 Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) to the dismissed employee in the amount of the average monthly earnings. In addition, the employee retains the average monthly earnings for the period of employment, but not more than two months from the date of dismissal (including severance pay). In exceptional cases, the average monthly salary is retained for the dismissed employee for the third month from the date of dismissal by decision of the employment service body, provided that within two weeks after the dismissal the employee applied to this body and was not employed by it (Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
There are different situations that precede the dismissal, for example, the employee in the period preceding the dismissal worked in the normal working hours; the employee in the period preceding the dismissal, worked part-time; the employee was idle during the six months preceding the dismissal (through no fault of his own); the employee in the period preceding the dismissal was on leave without pay. In these cases, it is necessary to strictly follow the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation to reduce the likelihood of significant costs for the release of personnel.
Questions and tasks for verification
- 1. Highlight the factors influencing the organization's need for personnel.
- 2. Give the definition of hiring personnel.
- 3. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of using internal and external labor markets when hiring personnel.
- 4. What sources of personnel attraction are there? Consider their pros and cons when hiring.
- 5. List the main parameters of the vacancy announcement.
- 6. What selection methods are there? Describe the advantages and disadvantages of using them.
- 7. List the cost items when hiring personnel.
- 8. Give a definition to the concept of "release of personnel". What are the consequences of errors in its implementation?
- 9. What methods are available to mitigate the process of releasing personnel?
- 10. What types of staff release are there?
- 11. Describe the organizational-economic, legal and socio-psychological aspects of the release of the organization's personnel.
Introduction
reduction in layoffs
Relevance term paper... V modern society a person is highly dependent on his labor activity and therefore, upon dismissal, the employee should be provided with the softest exit from the organization, which greatly affects not only his financial situation, but also his spiritual state.
The purpose of the course work. To study the main types of release of the organization's personnel.
Object of work: staff of the organization. Subject of work: the system of releasing the personnel of the organization.
Over the past couple of years, a number of large enterprises Russia has significantly reduced the number of staff. The workers who had worked in production for many years fell under the release. Practice shows that the listed tendencies are also typical for mass layoffs today. Factors That Cause Great Release work force currently common to many Russian regions. Mass layoffs are almost impossible to discourage, or impossible to prohibit through legal means. If the organization, or part of it, is no longer viable, and recovery seems unpromising, then appropriate conclusions should be drawn. The market economy does not allow one to save the life of economically sick organizations with its own hand. The curtailment of production and the restructuring of the economy are appropriate both for the stage of economic growth and for the period of general recession. As before, the following categories of citizens may be laid off: employees, disabled people who do not have the appropriate qualifications and work experience, as well as citizens up to retirement age and women. In other words, mass layoffs from enterprises in one city or region significantly alter the demand for labor.
Release of personnel
The concept of staff release
The release of staff for most firms is becoming a very significant function, supported by a well-developed organizational mechanism for its implementation. The system of special events accompanying, directly, the process of releasing staff, is very widely used at American enterprises, in contrast to Russian enterprises and organizations. To a lesser extent, this area of activity is widespread in European countries, although it has received considerable attention there lately. The problems arising from the release of staff are based on the value of labor, which is acquired in industrial society. Firstly, work is of great importance for material support of life, and secondly, it is useful and rational spending of an employee's free time, a means of satisfying the needs of the highest level, for example, self-realization. Third, labor has a social dimension. In the process of labor activity, social ties are established, social status person. The achievement of these goals can potentially be threatened by the very fact of the release of an employee. Many works of domestic and foreign authors are devoted to the release of staff. The issues related to the release of employees are studied from the standpoint of various scientific disciplines: social and organizational psychology, labor economics, organization management, personnel management, institutional economics, labor economics, labor law, sociology, personality psychology, conflictology.
Dismissal of staff - the movement of workers due to the destruction of jobs or such reorganization, in which the requirements for the profession (specialty) or qualifications of the employee change, as well as in connection with the termination of the employment contract on the initiative of one of the parties (employer or employee) or retirement ... The release of employees is carried out in accordance with the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws and must be accompanied by organizational and psychological support from the administration of the organization where the dismissed employee works. Dismissal of an employee is a procedure established by law for release from official duties upon termination of an employment contract.
Personnel release management is a type of activity carried out by the administration of the organization and its personnel management service in connection with the dismissal of employees within the framework of the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and determining the development and implementation of measures to optimize the number of personnel, socio-psychological and economic support for the dismissed employees. Considering the importance of such an event as leaving the organization, the main task of the personnel management services when working with leaving employees is to maximize the mitigation of the transition to a different socio-psychological, industrial, organizational, economic and socio-labor environment. This applies in particular to two types of layoffs: on the initiative of the employer and in connection with retirement.
Planning staff reductions or redundancies is essential in the process workforce planning.
The rationalization of production or management creates a surplus of human resources. Timely transfers, preparation of admission to vacancies, the implementation of a socially-oriented selection of candidates for dismissal allow regulating the intra-organizational labor market in the process of planning staff reduction.
Planning for work with leaving employees is based on a simple classification of types of layoffs. In this case, the classification criterion is the degree of voluntariness of the employee leaving the organization. According to this criterion, three types of layoffs can be distinguished:
Dismissal at the initiative of the employee (of his own free will);
Dismissal initiated by the employer (initiated by the administration);
Retirement.
It is relatively hassle-free to leave an employee on his own initiative. At the same time, the professional activity of the employee, the social environment does not change radically, or the employee is ready for such changes. In most cases, such a transition is viewed positively by the employee himself. Therefore, the need for support of this employee from the administration is usually insignificant.
Mass release is one of the most difficult consequences of technical and economic development society.
Mass release affects a whole range of social and economic problems, requires significant costs on the part of society, organizations and individuals. The main burden falls on those to be fired.
If downsizing as a result of individual interventions such as early retirement, cancellation agreements, or individual layoffs cannot be reliably enforced, all that remains is a mass layoff tool. Destruction labor relations contrary to wishes job seekers, can only be a last resort, since the loss of a job without personal involvement or one's own guilt often leads to the fact that the economic basis of the family's livelihood is threatened, up to the consequences for children (funding for studies, etc.).
The release principle, which, in the opinion personnel policy, must be observed, is the openness of the administration of the organization in relation to workers and employees, as well as to representatives of job seekers. Tipping points such as layoffs are not decisions that are made and enforced by the leadership of an organization alone. It should:
Explain to representatives of employers the reasons for the decline in employment;
Prove to them the extent of the staff cuts;
Explain to them the concept of recovery;
Introduce them timetable release.
This information as a basis for representatives of the interests of workers and employees should be made at a time when the representatives of workers and employees can still influence the conclusion, as well as comprehensive and truthful.
The planned measures should be explained to employees in a timely manner, for example, at extraordinary meetings of collectives of workers and employees. The sooner those targeted by these measures learn the truth, the sooner they will prepare for the upcoming situation and start looking for alternative work.
Mass release of workers associated with the rationalization of production, improvement of labor organization, liquidation, re-profiling of the organization, its structural divisions, complete or partial suspension of production at the initiative of the management body or the head, can be carried out only on condition of prior (not less than three months in advance) written notification relevant trade union bodies.
After informing the representatives of workers and employees and the staff of the organization, you should immediately contact the employment service. This service should know in a timely manner what it will face, as preparatory work may be required.
When the entire organization is closed, as a rule, all employees are affected. Difficulties arise at a time when some qualified personnel must be transferred to another plant or to another organization in order to timely save them from layoffs. In this case, the problem of personal selection arises, especially when only part of the staff is subject to dismissal.
From the point of view of the organization, the choice looks different than from the standpoint of a collective of workers and employees. The firm would like to get rid of all employees with low productivity and retain young staff and employees with a higher level of knowledge. The opposite position is taken by a collective of workers and employees: the weakest in socially the employee should be able to stay, with the appropriate education and dynamic employees should look for a new job for themselves.
This conflict in many countries was resolved through a compromise. Those workers, whose further employment is absolutely necessary due to production and technical aspects, do not fall under the selection of personnel. Also, specialists and management personnel who are necessary for the continued existence of the company are not subject to dismissal.
The rest of the employees who do not belong to this area should be put into a hierarchical list according to social parameters, and only employees who perform exactly the same work can always be compared with each other. Only those employees who are least affected by the dismissal are subject to dismissal. These criteria are: age, length of service in the organization, maintenance obligation, health status, the ability to find a job in the labor market, as well as the income of other family members. At the same time, the consideration of production efficiency and the assessment of one's own qualities are not selection criteria.
A point system can be used to establish a sequence of redundancies, with the highest score being the best protection against dismissal.
They have proven themselves well in Russia different ways on curbing mass layoffs, accepted in world practice: employers' initiatives to extend the timeframes, reduce their scale and prevent them were supported.
In most regions, employers receive financial support for payments to employees who are on leave without retention wages working part-time.
The experience of regulating mass layoffs convinces us that the aforementioned measures by themselves are ineffective without strategic programs for the development of employment and prevention of mass layoffs. An active state policy in training and retraining workers, increasing their competitiveness in the labor market, supporting programs to create new jobs create conditions for a crisis-free development of the labor market. ...
The needs of an organization for employees change over time under the influence of a number of external and internal factors for the organization. Such changes do not always mean an increase or maintaining the demand for labor at a constant level. The introduction of new technologies, the termination of the production of certain types of products, a drop in demand for the services provided by the organization can lead to a decrease in demand, both for separate categories workers and the workforce in general. The problem of staff release arises, which is considered in the works of many domestic scientists dealing with the problems of personnel management.
It is necessary to distinguish between the concepts of "release" and "dismissal".
Release of personnel is the dismissal or suspension from work for a long period of one or more employees for reasons of economic, structural or technological nature in order to reduce the number of employees or change their professional qualifications.
The release of personnel is understood as a set of measures to comply with legal norms and organizational and psychological support from the administration of the dismissed employees.
Release of personnel- a type of activity that provides for a set of measures to comply with legal norms and organizational and psychological support from the administration in case of dismissal of employees.
The problems arising from the release of personnel arise from the functions of labor that develop in an industrial society.
Firstly, labor performs the direct function of material support of life. As a rule, it is the main source of income.
Secondly, labor in most cases is identified with the potential of a particular worker. Labor activity is associated not only with income, but also with the possibility of development, self-realization of the employee.
Thirdly, labor has a social dimension. In the process of labor activity, social ties are established, the social status of a person is formed. The implementation of the above functions can potentially be threatened by the fact of the release of an employee.
Dismissal - termination of an employment agreement (contract) between the administration (employer) and the employee.
Dismissal of personnel is one of the tools for regulating the organization's labor market.
In practice, the following options for reducing the number of personnel are used:
Termination of employment;
Moving to other free places;
Reduction of working hours;
Introduction of the shortened working week.
Types of layoffs
Planning for work with departing employees is based on a simple classification of types of dismissals. The classification criterion in this case is the degree of voluntariness of the employee leaving the organization.
According to this criterion, three types of layoffs can be distinguished:
Dismissal at the initiative of the employee (in Russian terminology - at will);
Dismissal on the initiative of the employer (in Russian terminology - on the initiative of the administration);
Retirement.
Dismissal of an employee on his own desire.
From the point of view of the organization, if we abstract from the subsequent problems of hiring and adapting new employees, this is a relatively hassle-free type of dismissal.
The decision is made by the employee himself, in most cases he is assessed positively, in fact he is ready for changes in professional activity and social environment, the need for support from the administration is usually small.
In this situation, the HR service can:
Conduct a final interview (verbally and in writing), during which the true reasons for dismissal are identified, as well as various aspects are assessed production activities(psychological climate, leadership style, growth prospects, objectivity of business assessment and remuneration, requirements for the workplace and working conditions, etc.);
Inform the employee about his rights and obligations upon dismissal, etc .;
Get information about the state of affairs in the organization through the feedback channel;
Partially or completely remove various claims of the parties to each other;
Identify shortcomings in work with personnel and prevent further mistakes in the relationship between administration and employees.
However, in most cases, upon dismissal, an employee is either not at all inclined to give any assessments, or does so with a great deal of subjectivity.
The main objectives of the final interview are usually: to try to influence the employee's decision to fire if necessary and to analyze the bottlenecks in the organization.
Dismissal initiated by the administration .
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation defines an exhaustive list of grounds for dismissal at the initiative of the administration.
Dismissal at the initiative of the employer most often occurs as a result of staff cuts or the closure of an organization and is going through hard, because it affects all the most important aspects of work (professional, social, personal-psychological, many feel fear, depression, confusion, as he is potentially, for an indefinite period , unemployment threatens), has negative consequences (loss of social relationships or status).
When dismissing personnel on the initiative of the administration, a special problem is the release of personnel during the liquidation of an enterprise, reduction of the number of employees and reorganization of production.
The system of measures for working with departing employees can be built both on an individual and group basis.
The main emphasis in this work is placed on the transmission of the letter of resignation to the employee and the conduct of advisory work on the new vocational guidance and further development of personnel.
The implementation of this system of measures allows us to solve several target tasks:
- from an organizational point of view- optimization of costs arising from dismissal; analysis and identification of bottlenecks in employee training and professional behavior; visibility of the dismissal process for the remaining staff of the organization.
- from the point of view of the employee- tasks can be divided into monetary, socio-psychological, career.
In a number of cases, in management practice, there is a massive layoff of workers, representing a special case of layoff, the main criteria of which are indicators of the number of laid off employees in connection with the liquidation of an organization or a reduction in the number or staff of employees for a certain calendar period.
Conditional release of workers represents a saving in labor as a result of improving the management system, combining professions, increasing labor productivity and equipment productivity. Conditional release is expressed as a calculated value derived from the value of the potential savings in working time resulting from an increase in labor productivity.
Lockout is the mass layoff of workers in the event of bankruptcy of an enterprise or with the aim of suppressing or preventing a strike.
Outplacement - a form of termination of an employment contract between enterprises and employees, providing for the involvement of specialized organizations in order to provide assistance to interested persons in employment.
The services of the intermediary organization are paid by the company with which the dismissed employee terminates the agreement. Participation in the termination of the employment contract of an independent third party allows you to relieve tension and find a compromise solution.
End of the contract
Dismissal of an employee in connection with the expiration of the term of the contract can be initiated by the employer (category “dismissal initiated by the administration”) or initiated by the employee.
Retirement- the third type of dismissal is characterized by a number of features:
- Firstly can be foreseen and planned in advance;
- Secondly, is associated with specific changes in the personal sphere;
- third, changes in a person's lifestyle are visible to his environment;
- fourthly, a certain duality, discord with oneself is inherent in man.
Factors associated with the release of staff
In practice modern governance a method of assessment has been worked out economic efficiency measures to combat unnecessary staff movement or departure. It is based on comparing the costs of creating a stable, cohesive team with the savings obtained as a result of reducing losses associated with a drop in labor productivity from workers leaving.
These losses add up due to:
A drop in productivity in the period after the decision to dismiss and the issuance of documents for resignation (from two weeks to a month);
Losses associated with insufficiently high labor productivity in the period after entering a new job (due to new working conditions, equipment, technology, familiarization with the team - up to 2-3 months);
Losses due to a break in work experience between dismissal and employment (25 days or more);
Losses incurred by the state and the company in connection with the costs of training employees (if a person changes his profession, then the previously made costs in this area disappear, and, moreover, he must be taught again) and with their adaptation to new jobs (marriage, equipment breakdown, downtime, etc.).
The layoff process has an impact not only on the released employees, but also on those who remain in the organization. They observe the process of managing the release, the relationship between the administration, immediate managers and employees in the process of dismissal and compare real actions with the officially proclaimed policy. The information obtained through such observation affects further work motivation. Thanks to professional actions in the process of releasing personnel, the administration tries, to the maximum extent possible for this situation, to reconcile the interests of personnel policy with the interests of employees.
Lecture plan:
Personnel release concept
Reasons for the release of personnel
Types of staff release
Ways of partial release of personnel
Types of absolute staff release
Measures taken by the organization to mitigate the situation of dismissal
Staff turnover and its causes
Personnel release concept
Release personnel is the scope of management activities to reduce the number of employees.
Reasons for the release of personnel
The main reasons for the release of the person.
automation and other types of production improvement, entailing a reduction in labor costs;
reducing the scope of the organization;
inadequate assessment of staffing requirements when hiring.
Types of staff release
There are 2 main types of employee release:
absolute release (dismissal) of employees;
partial (internal) release, which consists in reducing the volume of work performed while maintaining the number of employees.
Ways of partial release of personnel
There are the following methods for the partial release of personnel:
the introduction of a part-time working day, a reduction in the working week, the provision of temporary unpaid leave to employees;
the termination of the hiring of new employees with the expectation of a gradual reduction in their number;
transfer of workers from labor-surplus divisions to labor-deficient ones, equal distribution of workers between divisions;
diversification of the company's activities, development of new types of work to create new jobs.
Types of absolute staff release
The existence of different types of absolute release (dismissal) of personnel due to such reasons as:
dismissal at the initiative of an employee, that is, of their own free will, dismissal due to institutional changes in the life of an employee, for example, having a child, leaving for the army, entering an institute;
dismissal initiated by the administration. Such dismissals can be caused by the inadequacy of the employee to his position or associated with the need to reduce the number of employees.
Measures taken by the organization to mitigate the situation of dismissal
If it is necessary to reduce the number of personnel the organization usually takes the following measures to mitigatesituationslayoffs:
pays monetary compensation;
applies the procedure of "layoffs", which consists in the temporary layoff of workers during the period of recession in production;
applies the "outplacement" method, which implies the conduct of vocational guidance and psychologically rehabilitative classes with the dismissed by special counseling services;
organizes early retirement to ensure employment among young people and middle-aged people.
Staff turnover and its causes
Staff turnover is a phenomenon characterized by frequent and massive layoffs of employees , occurring on the initiative of the employees themselves or on the initiative of the administration, dissatisfied with their work behavior.
The main reasons for staff turnover are:
unsatisfactory conditions, labor protection and maintenance;
unsatisfactory work organization;
labor conflicts associated with tensions in the team and with management;
lack of prospects for career advancement and professional growth.
Planning for the release or reduction of personnel is essential in the workforce planning process. The rationalization of production or management creates a surplus of human resources. Timely relocations, retraining, termination of hiring for vacant jobs, as well as the implementation of a socially-oriented selection of candidates for dismissal (depending on age, work experience, marital status and the number of children, the possibility of getting a job at foreign market labor, etc.) allow you to regulate the intra-organizational sphere of work in the process of planning staff reductions.
The release of personnel is a type of activity that provides for a set of measures to comply with legal norms and organizational and psychological support from the administration when employees are dismissed.
In the specialized literature on management labor resources the concepts of “release” and “dismissal” of workers differ. Dismissal is the termination of an employment agreement (contract) between the administration (employer) and an employee.
Liberation is a broader concept that contains, as mentioned above, a set of complex measures for conflict-free cardinal changes in the living conditions of individuals. The layoff of personnel is the dismissal or suspension from work for a long period of one or more employees for reasons of economic, structural or technological nature in order to reduce the number of employees or change their professional qualifications.
Dismissal of staff is one of the tools for regulating the number of employees. In practice, the following options for reducing the number of personnel are used: termination of hiring, moving to other vacant places, reducing the duration of working hours, introducing a shortened working week.
The problems arising from the release of personnel arise from the functions of labor that develop in an industrial society. First, labor fulfills the direct function of providing material support for life. As a rule, it is the main source of income. Secondly, labor in most cases is identified with the potential of a particular employee. Labor activity is associated not only with income, but also with the possibility of development, self-realization. Third, labor has a social dimension. In the process of labor activity, social ties are established, the social status of a person is formed. Through labor, the individual determines his place in social integration.
The achievement of these goals can potentially be threatened by the fact of the release of an employee. The starting point for making a decision on the release of personnel should be the recognition of the seriousness and importance of the very fact of dismissal, both from an industrial, and from a social and personal point of view, since the process of releasing personnel is ambiguous in its consequences. For leaving employees, the positive aspects are the expected growth in income, career prospects in a new place 1. New opportunities for promotion appear for the remaining employees, but the workload is increasing, the socio-psychological climate is changing. For the organization, staff mobility makes it easier to get rid of outsiders, makes it possible to attract people with new views, but, on the other hand, generates additional costs associated with the recruitment and training of newcomers, leads to loss of working time, a drop in discipline.
Planning for work with leaving employees is based on a simple classification of layoffs. The classification criterion is the degree of voluntariness of the employee leaving the institution. In accordance with this, there are three types of layoffs, which are presented in table 6.
1. Dismissal at the initiative of an employee (in Russian terminology - at will). From the point of view of the institution, this is a relatively hassle-free form of dismissal. The decision is made by the employee himself, in most cases he is assessed positively, in fact he is ready for changes in professional activity and social environment. The need for support from the administration is usually small.
Table 6
Layoff classification
1 See: Bazarova T.Yu., Eremina B.L. Personnel management: Textbook, for universities. M., 2011.
- 2. Dismissal on the initiative of the employer (in domestic terminology - on the initiative of the administration). Dismissal on the initiative of the employer most often occurs as a result of staff reductions and is an extraordinary event for any employee. Dismissal on the initiative of the employer is especially difficult, since it affects all the most important aspects of work - professional, social, personal and psychological. The professional labor role of the employee is in danger, since he is potentially, and for an indefinite period, facing unemployment. Therefore, it depends on how the dismissal process is organized, what impact this event will have on the employee - it will either aggravate or mitigate the situation.
- 3. Retirement. The third type of dismissal is characterized by a number of features that distinguish it:
- - can be foreseen and planned with sufficient time accuracy;
- - associated with specific changes in the personal sphere;
- - changes in a person's lifestyle are visible to his environment;
- - in assessing the upcoming retirement, a person is characterized by some duality, discord with himself.
The process of retirement, as well as finding a person in a new social role in civilized countries are the object of quite close attention. This attention comes both from the state and from the institution where the person worked and contributed to the common cause.
In view of the importance of such an event as leaving the institution, the main task of personnel management services when working with leaving employees is to mitigate the transition to a different production, social, personal situation as much as possible. This applies in particular to two types of layoffs: on the initiative of the employer and in connection with retirement.
In modern conditions, managing the dismissal process means not only strictly observing the requirements of the law, but also providing people with psychological support, since dismissal causes a high level of stress and leads to emotional trauma.
Depending on the situation, layoffs can be individual or massive.
With the individual release of personnel, carried out upon dismissal of employees on the initiative of the administration or upon the expiration of the term of the employment contract, a comprehensive program of measures is drawn up. The personnel management service is trying to find the available opportunities (methods) for this. These include:
- - legal advice on emerging claims and compensations;
- - assistance provided to future employers in the process of making inquiries about an employee;
- - psychological consultations and support in carrying out organizational measures related to the release of an employee;
- - formation new system target aspirations, new schemes of professional and service promotion as a condition for the successful professional reorientation of the consulted employee.
The main focus of the program is on communicating the resignation to the employee and advising on the new vocational guidance.
V general view such a system can include three stages:
- 1) preparatory;
- 2) transmission to the employee of a message (notice) of dismissal;
- 3) counseling.
The third stage - consulting - is the central link in the entire process of personnel release management. It is characterized by a set of measures aimed at legal and psychological counseling of employees, at the formation of new targets and professional relevance of dismissed employees. At this stage, the dismissed employees are assisted in finding a new job. It includes three phases:
- - through consultations, an attempt is made to consider all the failures of work in previous positions and outline new professional and personal goals;
- - a new job search scheme is being formed (for example, Required documents, networks of contacts for job search are created, training is organized on participation in an interview, etc.);
- - search for jobs (assistance in choosing one of the various job offers, taking into account individual settings).
The mass layoff of personnel is understood as a reduction in the number of employees in connection with the liquidation, reorganization, re-profiling of an enterprise. The procedure for releasing personnel consists of several stages.
At the stage of justifying the need to reduce personnel, specific economic, financial, technical calculations are carried out, proving the objectivity of the reasons for the massive layoffs of employees. In order to preserve and make rational use of the organization's professional potential, it is advisable to analyze all possible alternatives to downsizing.
To eliminate the surplus number of personnel, less painful than mass layoffs, directions of personnel rationalization are used, that is, a flexible employment policy is applied.
The final stage the procedure for the release of personnel is to work with the dismissed employees. Psychologists have developed a number of recommendations for conducting a final interview with a released employee. Employment authorities can assist employers by:
- - Conducting group and individual consultations with the released employees on issues related to their training and subsequent employment;
- - conducting, together with the head of the institution, a questionnaire survey among the released employees to determine the number and professional qualifications of employees in need of appropriate vocational training.
The issues of releasing employees of the penal system are regulated by the Regulations on service in the internal affairs bodies Russian Federation and the Instruction on the procedure for applying the Regulations on service in the internal affairs bodies of the Russian Federation in institutions and bodies of the penal system. According to the specified regulatory legal acts, the grounds for termination of service in the internal affairs bodies are:
- a) dismissal from the internal affairs bodies;
- b) termination of the citizenship of the Russian Federation;
- c) recognition of an employee of the internal affairs bodies in established order missing;
- d) death (death) of an employee of the internal affairs bodies.
Police officers may be dismissed from
services on the following grounds:
- a) of their own free will;
- b) reaching the age limit established by article 59 of the regulation;
- c) length of service, which gives the right to a pension;
- d) the end of the service life stipulated by the contract;
- e) due to violation of the terms of the contract;
- f) to reduce staffing during the liquidation or reorganization of the internal affairs body in the event that it is impossible to use an employee of the internal affairs bodies in the service;
- g) illness (on the basis of the decision of the military medical commission on unfitness for service);
- h) other grounds listed in Article 58 of the Regulation.
Before submitting employees for dismissal, the data on their service are clarified, the periods subject to credit for seniority for the appointment of a pension in calendar terms and separately in preferential terms are confirmed. According to the law, the length of service is calculated for the appointment of a pension, which is announced to the employee.
Employees are notified of the upcoming dismissal from service by a notification handed to the employee against receipt in compliance with the terms established by the regulation. If the employee refuses to receive a notification, the personnel department draws up an appropriate act about this in the prescribed manner, and an official notice of dismissal from the penal system is sent by registered mail.
In addition, a conversation is held with the employee, during which he is informed about the grounds for dismissal, benefits, guarantees and compensation, employment issues, material and household support and other issues are explained. At their request, representatives of the personnel, legal, medical and financial departments may be invited to participate in conversations with the dismissed. If, during the conversation with the dismissed employees, questions are raised that cannot be resolved by the relevant institutions or bodies of the UIS, the leaders conducting the interviews report these questions for the decision of the superior direct superior.
When determining the grounds for dismissal of an employee, his age, state of health, working capacity, length of service for assigning a pension, attitude towards service, as well as benefits, guarantees and compensations provided depending on the grounds for dismissal in accordance with the legislative and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation are taken into account. and position.
If there are grounds for the application of two or more wordings for the dismissal of a positively certified employee, with his consent, the one that gives the right to receive the greatest guarantees and compensations is indicated.
The heads of institutions and bodies of the penal system and personnel departments are responsible for correctly determining the grounds for dismissal of employees.
The dismissal of employees during the period of their being on vacation or during the period of illness, being held as a hostage, unknown absence (until they are recognized as missing or declared dead in accordance with the procedure established by law) is not allowed.
Dismissal from service of pregnant women, women with children under the age of three, as well as those with disabled or disabled children from childhood until they reach the age of 18, single mothers with children under the age of 14, is not allowed, except in cases where when employees are subject to dismissal from service on the grounds provided for in subparagraphs "b", "d", "f", "g", "h", "k", "l" and "m" of Article 58 of the Regulation.
Women who are on maternity leave or parental leave cannot be dismissed, except in the case of liquidation of this institution and the penal system in which they served, and their refusal to continue serving in another institution, body.
A citizen dismissed from the penal system has the right, within one month from the date of delivery of the order of dismissal, to appeal it in court (article 62 of the provision), as well as the right, before sending a complaint to the court, to apply to a higher institution or body of the penal system for clarification or a decision on the issue of reinstatement on service in the manner prescribed by article 66 of the regulation.
- See: V.R. Vesnin. Personnel Management. Theory and practice.
- See: Motivation of labor activity / Ed. V.P. Pugacheva.
- See: V.K. Potemkin. Personnel management: Textbook, for universities. SPb., 2010.
- See: V.N. Sidorenko Release of personnel as an element of modern personnel policy of organizations: Textbook. M., 2011.
 From a student of a FZU school to a director and a minister (Hero of Socialist Labor V
From a student of a FZU school to a director and a minister (Hero of Socialist Labor V Law on public organizations of the Russian Federation
Law on public organizations of the Russian Federation Votkinsk machine-building plant: history, products, address Votkinsk machine-building plant
Votkinsk machine-building plant: history, products, address Votkinsk machine-building plant Founder's decision to appoint a director of sample ltd
Founder's decision to appoint a director of sample ltd Sample notification of the start of business
Sample notification of the start of business What is a journal-order accounting system in accounting
What is a journal-order accounting system in accounting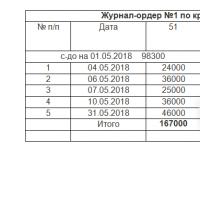 Journal-order: sample filling
Journal-order: sample filling