Functions of the trade union committee in the organization. The main functions of trade unions. The status of trade unions in modern society
union trade union function
The functions of trade unions are the directions of their activities.
Protective function trade unions, is traditional for Soviet trade unions. Due to the fact that historically it arose earlier than other functions, its content is characterized by significant and complex changes.
The task of protecting the rights and interests of workers in a socialist society by trade unions is constituent activity part of the entire system of organizations of Soviet society, and above all of the Communist Party and the socialist state. The peculiarities of the protective function of trade unions in comparison with the protection of the rights and interests of workers by other organizations of Soviet society is that, firstly, trade unions are called upon to protect the rights and interests of workers and employees, mainly in the field of social labor relations; secondly, the main goal of trade unions in this case is to prevent (prevent) possible violations of the specified rights and interests; thirdly, in protecting the rights and legitimate interests of workers and employees, trade unions use such ways and means that are inaccessible to the state apparatus.
FUNCTION REGULATIONS. In conditions when trade unions do not have (according to Russian legislation) the right to legislative initiative, they actively implement their participation in the rule-making process through proposals and amendments to draft laws that are sent to the Committees of the State Duma of the Russian Federation, through the RTK, through the association of trade unions of Russia (FNPR) and etc.
Implementing this function, trade union committees, formulating a reasoned opinion on a particular local legal act educational institution, carries out essentially an examination and in-depth analysis of it in order to protect the members of the Trade Union from the negative consequences of the introduction of a normative act into life
FUNCTION CONTROL. In accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, trade unions are granted the right to monitor compliance by employers and their representatives with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms.
Trade union legal and technical inspectors, authorized (authorized) persons for labor protection in an educational institution have the right to freely visit organizations in which union members work to conduct inspections of compliance with labor legislation, labor protection standards, as well as compliance with the terms of the collective agreement, agreement.
FUNCTION CO-CONTROLS. The main forms of participation of trade union organizations in management at the level of an educational institution are: taking into account the opinion of the trade union body in cases stipulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a collective agreement; consultations with the employer (administration) on the adoption of local regulations containing labor law norms; obtaining information from the employer on issues directly affecting the interests of employees; discussion with the employer of questions about the work of the institution, making proposals for its improvement; participation in the development and adoption of collective agreements; other forms determined by the constituent documents of the organization, collective agreement or local regulation organizations.
One of the important forms of co-management is the receipt by the trade union committee from the administration of the necessary information on such issues as: reorganization or liquidation of the organization; the introduction of technological changes, entailing a change in the working conditions of workers; vocational training, retraining and advanced training of employees; on other issues stipulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, federal laws, constituent documents of the organization, collective agreement. As part of the co-management function, the trade union committee has the right to submit proposals on the above issues to the management bodies of the organization and to participate in the meetings of these bodies during their consideration. The implementation of the co-management function is an important mechanism for the trade union organization in the implementation of the statutory goals and objectives.
TRAINING FUNCTION. Determination of the content of trade union training, development of the most effective methods and organizational forms of training of trade union activists, their improvement are the main problems in the activities of trade union training committees. When forming your own asset preparation system, you should actively introduce non-standard models for their preparation. It is advisable to include rhetoric, logic and other unusual components in educational programs, along with traditional questions, that expand the possibilities of a trade union activist, especially in the context of broad social partnership. It is important in the organizations of the Trade Union to create a learning environment that would actively contribute to the formation and development of the necessary qualities, abilities, and skills. it difficult task requires constant attention to itself and participation in its resolution of all structures of the Trade Union.
ORGANIZING FUNCTION. The organizational function permeates all areas of activity of trade union organizations, elected bodies in the trade union and is implemented at four levels.
- 1. Organizational (practical) level:
- - provision of activities higher bodies trade union organization;
- - ensuring the activities of collegial elected trade union bodies;
- - organization of the work of the standing committees of the trade union committee;
- - holding meetings, conversations, " round tables", Business negotiations, conferences, etc .;
- - organization and use of oral and visual-artistic information (lectures and speeches, trade union corners, information stands trade union committee, announcements, information sheets, exhibitions, etc.);
- - organization and holding of cultural and sports events (evenings, sports competitions, etc.);
- - organization of recreation (weekend trips, organization of family leisure, etc.);
- - health-preserving measures (preventive medical examinations, organization of spa treatment), etc.
- 2. Level of union rule-making:
- - development and adoption of the Regulation on the organization;
- - formation and adoption of decisions of the higher and executive bodies of trade union organizations (in the form of resolutions);
- - formation of a motivated opinion trade union committee and etc.;
- - formation and adoption of decisions by individual elected trade union bodies (chairmen of organizations in the form of orders);
- - preparation and adoption of resolutions, statements, appeals, open letters on one or another urgent social and labor problems in the team;
- - the formation of representations, appeals and claims to the inspection bodies, trade union bodies and courts, etc.
- 3. The level of analytical and creative activity of the trade union committee:
- - development of plans, determination of the prospects for the development of the trade union organization, clarification of goals and specification of tasks;
- - development of a draft collective agreement, labor protection agreement, etc .;
- - development of scenarios for events, promotions;
- - generalization of the practice and experience of the work of commissions, trade union activists (drawing up information certificates);
- - analysis of the state and results of the activities of elected trade union bodies in various areas (statistical and other reports);
- - preparation of teaching materials;
- - preparation of newsletters, visual information, etc.
- 4. Technological level:
- - adaptation of various methods of organizational and statutory work of the trade union committee; - adaptation of methods and recommendations for holding collective actions, strikes, etc.
- - development of measures for the use of experience and the introduction of new forms of work of trade union organizations into practice (trade union circles, experience in developing target projects for the activities of the primary organization, etc.);
- - development of criteria for assessing the activities of standing committees and assets, identifying the effectiveness of the activities of trade union organizations, etc.
A trade union is a voluntary public association of citizens bound by common industrial, professional interests by the nature of their activities, created in order to represent and protect their social and labor rights and interests. All trade unions enjoy equal rights.
Every person who has reached the age of 14 and carries out labor (professional) activities has the right, at his discretion, to create trade unions to protect their interests, join them, engage in trade union activities and leave trade unions. Russian trade unions are not limited to citizens Russian Federation residing both on the territory of Russia and outside its territory, but also foreign citizens and stateless persons residing in the territory of the Russian Federation, with the exception of cases established by federal laws or international treaties of the Russian Federation.
Trade unions can create their own associations (associations) on the sectoral, territorial or other basis, taking into account professional specifics - all-Russian associations (associations) of trade unions, interregional and territorial associations(associations) of trade union organizations (Article 2 of the Trade Union Law).
The primary trade union organization unites members of trade unions, as a rule, of one enterprise, organization regardless of the form of ownership and subordination, acts on the basis of a provision adopted in accordance with the charter, or on the basis of general position about the primary trade union organization of the respective trade union.
Trade unions are independent in their activities from the executive authorities, bodies local government, the employer, their associations (unions, associations), political parties and other public associations are not accountable to them and are not controlled by them. Interference of state authorities, local self-government bodies and their officials in the activities of trade unions, which may entail restriction of the rights of trade unions or hinder the legal implementation of their statutory activities (Article 5 of the Law on Trade Unions), is prohibited.
Trade unions, their associations (associations) independently develop and approve their charters, their structure, organize their activities. These acts regulate relations within the trade union itself with its members and trade union bodies. They are not sources of law, as it is an act of the public.
The legal personality of a trade union as legal entity arises from the moment of their state (notification) registration with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation or its territorial body in the subject of the Russian Federation at the location of the corresponding trade union body. But trade unions have the right not to register, then they do not acquire the rights of a legal entity (Article 8 of the Law on Trade Unions). It is forbidden to condition the hiring, promotion at work, as well as the dismissal of a person by affiliation or non-affiliation with a trade union.
The reorganization or termination of the activity of a trade union or a primary trade union organization may be carried out only by decision of their members in the manner determined by the charter of the trade union, the statute on the primary trade union organization, and their liquidation as a legal entity in accordance with federal law.
In the event that the activities of a trade union contradict the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the Constitutions (charters) of the constituent entities of the Federation, federal laws, it may be suspended for up to six months or prohibited by a decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation or the corresponding court of a constituent entity of the Federation at the request of the Prosecutor General of the Russian Federation, the prosecutor of the corresponding constituent entity of the Federation. Suspension or prohibition of the activity of the trade union by decision of any other bodies is not allowed.
Thus, trade unions enter the political system of society as a specific public organization with their own tasks and functions, determined by their charters. The main tasks of trade unions are related to the implementation of their functions - to protect the rights and interests of workers in the labor sphere and other relations directly related to it.
The functions of trade unions are the directions of their activities. Since trade unions arose to protect the rights and interests of workers, therefore, their main function is protective. The need to protect the rights and interests of workers in the world of work is especially relevant in the modern period, which has exposed socio-economic contradictions. The relations of trade unions with employers on social and labor issues are regulated by labor legislation at all levels of social partnership relations, from production to the federal level, while using their protective function, as well as their second most important function - representing the interests of employees. For the effective implementation of these functions, the state has assigned to trade unions a number of rights and guarantees in rule-making, law enforcement and monitoring compliance with labor legislation and labor protection rules.
The protective function of trade unions is the activity of trade union bodies, as well as labor and asset inspections under their jurisdiction, aimed at preventing violations and restoring violations of the rights and legitimate interests of workers in the world of work, as well as bringing their violators to justice.
The functions of employee representation are directly enshrined in Art. 29 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, according to which the representatives of workers in a social partnership are trade unions and their associations, other trade union organizations provided for by the charters of all-Russian trade unions. Federal Law of the Russian Federation "On trade unions, their rights and guarantees of activity" in Art. 11 "The right of trade unions to represent and protect the social and labor rights and interests of workers" and in Art. 1 brings together these two essential functions of trade unions with their respective rights.
But in addition to these two, trade unions also carry out a cultural and educational function to educate their members in the spirit of patriotism and a political one by their participation in the elections of state authorities and local self-government bodies.
The implementation of the protective and representation function of trade unions is facilitated by the social regulation of social relations into which they enter in the course of their activities. Relations with the participation of trade unions, as a rule, are governed by various types of social norms - morality, tradition, etc.
However, legal regulation is also possible to ensure the representation and protection of the rights and legitimate interests of employees.
Limits legal regulation relations with the participation of trade unions depend on the state of social relations, the degree of their development, socio-economic and political conditions in which they develop.
The main functions of trade unions also include the following:
- 1. Organizational, or function of organizing social practices.
- 2. Function of regulation of social and labor relations.
- 3. Protective function.
- 4. Representative function.
- 5. Control function.
- NS Organizational function trade unions is that they organizationally provide a number of long-term and repetitive social practices. These are the practices:
- - resolution of industrial labor conflict;
- - implementation of social partnership;
- - holding mass actions;
- - carrying out the activities of intra-union bodies and organizations;
- - securing membership;
- - implementation of international contacts and relations, etc.
- Ш The function of regulating social and labor relations is carried out by trade unions on an equal footing with the main social partners: the state and entrepreneurs. Trade unions do not directly control the processes in the field of social and labor relations, but participate in their regulation at the level of their competence and in the interests of different groups wage labor.
- Ш The protective function of trade unions is the activity of trade union bodies, as well as labor and asset inspections under their jurisdiction, aimed at preventing violations and restoring violations of the rights and legitimate interests of workers in the world of work, as well as bringing their violators to justice.
Trade unions exert their influence, to a greater or lesser extent, on the following aspects of social and labor relations:
- * salary;
- * conditions, organization and regulation of labor;
- * labor protection and safety (including environmental);
- * employment and unemployment;
- * privatization;
- * taxes and budgets in terms of social labor.
Working in conjunction with legislative and executive bodies authorities (not excluding lobbying), with employers to regulate social and labor relations - this is the field where trade unions in practice can demonstrate their social usefulness, as they are involved in the creation of a regulatory and legal system that is mandatory for all social activists.
- Ш The representative function is that trade unions are legally given the right to act on behalf of and on behalf of various professional groups workers, labor collectives, workers employed in one or more industries, workers living in the same territory, to express and defend their interests.
- Ш The control function of trade unions is considered as one of the forms of civil public control over the actions of the authorities and employers in the field of social and labor relations, as well as over the activities of the trade union bodies and organizations themselves. The lack of proper control during the period of economic reform, when the trade unions for various reasons were curtailed in the rights of control over many processes, gave rise to a large extent to numerous violations labor standards from which the whole society suffers.
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted on http://www.allbest.ru/
Introduction
The trade union, abbreviated as a trade union, in accordance with the Federal Law of January 12, 1996 No. 10-FZ "On trade unions, their rights and guarantees of activity" , and in non-production areas, to protect the labor and socio-economic rights and interests of its members.
The role of trade unions in civil society:
· Protection of the legal rights and interests of employees.
· Participation in the establishment of an efficient economy that allows for the implementation of the principle of economic democracy and social justice.
Indicator public opinion, system element feedback to adjust the policy of the state.
· Representation of the economic interests of workers in the labor market.
The foundations for the creation of trade unions in Russia are laid down in Art. 30 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation: everyone has the right to association, including the right to form trade unions to protect their interests. The freedom of activity of public associations is guaranteed. No one can be forced to join or stay in any association, that is, the right to both free entry into trade unions and free exit is guaranteed.
The main functions of trade unions:
a) Representative - representing the interests of employees before the employer, municipal, regional and federal authorities.
b) Protective - protection of the labor rights of workers, their socio-economic interests.
c) Control - control: compliance with labor legislation, social sphere, collective agreement at the enterprise and agreements of the federal, regional and municipal levels; compliance with labor and industrial safety standards.
d) Organizational - organization of employees for joint actions to protect their rights and interests.
1. Organizational structure of Trade Unions
The organizational structure of the trade union is based on the primary trade union organizations. The Law on Trade Unions gives the following definition of a primary trade union organization: "voluntary association of trade union members working, as a rule, in one enterprise, in one institution, one organization, regardless of the form of ownership and subordination, acting on the basis of the provision on the primary trade union organization of the corresponding trade union" FZ "On Trade Unions", Art. 3.
If the subject of the federation has several primary organizations one trade union, they, as a rule, are united in the territorial organization of the trade union.
The Federation unites two types of member organizations:
a) all-Russian and interregional trade unions;
b) territorial associations of trade union organizations.
The territorial association of trade union organizations unites the territorial organizations of the all-Russian trade unions, members of the FNPR, which operate on the territory of the subject of the federation.
Functions of the territorial association of trade union organizations:
a) Representing the interests of the Federation of Independent Trade Unions of Russia in the constituent entities of the Federation.
b) Coordination of actions of trade union organizations in the subject of the Federation.
c) Ensuring the interaction of member organizations.
d) Regulation of social and labor relations on the territory of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
employment labor legislation trade union
2. Legal support trade union activities
The Federal Law "On Trade Unions, Their Rights and Guarantees of Activity" empowers trade unions to represent and defend the rights and interests of trade union members in matters of individual labor and labor-related relations, as well as the collective rights and interests of all workers, regardless of their membership in trade unions, if trade unions are endowed with such powers in established order.
The legal basis for the activities of trade unions in modern Russia are: the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the Federal Law "On trade unions, their rights and guarantees of activity", Labor Code Russian Federation:
a) the right of trade unions to represent and protect the social and labor rights and interests of workers;
b) the right of trade unions to promote employment;
c) the right of trade unions, primary trade union organizations to conduct collective bargaining, conclude collective agreements, agreements and control their implementation;
d) the right to participate in the settlement of collective labor disputes;
e) the right of trade unions to information (to receive it from the employer, public authorities, use state media);
f) the right to training and advanced training of trade union personnel;
g) the right to exercise control over the observance of labor legislation;
h) law in the field of labor protection and the environment;
i) the right to participate in the privatization of state and municipal property;
j) the right to social protection of employees;
k) the right to represent the interests of employees in labor dispute resolution bodies;
l) property rights of trade unions.
Guarantees for the activities of trade unions:
a) guarantees of property rights;
b) guarantees for elected employees;
c) guarantees for judicial protection;
d) guarantees from the employer.
Trade union responsibility:
a) for violation of constitutional norms;
b) for non-fulfillment of the collective agreement;
c) for organizing a court-recognized illegal strike.
Relationship with public authorities:
a) non-accountability;
b) a system of agreements;
c) suspension of the activity of trade unions only in court.
International principles and norms of law have a decisive influence on the formation of Russian legislation, including in matters of activity trade unions.
3. Social partnership
Social partnership is a civilized system of public relations in the social and labor sphere, based on the coordination and protection of the interests of employees, employers, entrepreneurs, public authorities and local governments on the basis of contracts, agreements, reaching a compromise, consensus on topical issues of economic and socio-political life of society.
The main principles of social partnership are:
a) - equality of the parties;
b) - respect and consideration of the interests of the parties;
c) - the parties' interest in participating in contractual relations;
d) - assistance of the state in strengthening and developing social partnership on a democratic basis;
e) - observance by the parties and their representatives of labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms;
f) - the authority of the representatives of the parties;
g) - freedom of choice when discussing issues related to the sphere of work;
h) - voluntary acceptance of obligations by the parties;
i) - the reality of the obligations assumed by the parties;
j) - the obligation to comply with collective bargaining agreements, agreements;
k) - control over the implementation of the adopted collective agreements, agreements;
l) - the responsibility of the parties, their representatives for non-fulfillment through their fault of collective agreements, agreements.
The parties to the social partnership are employees and employers represented by duly authorized representatives.
State authorities and local self-government bodies are parties to social partnership in cases when they act as employers, as well as in other cases provided for by labor legislation.
Trade unions act as representatives of the workers' side. By protecting the interests of union members, they act in the interests of all workers.
A collective agreement is a form of employee participation in the management of an organization and ensures the protection of their labor rights and socio-economic interests.
The parties to the social partnership are mutually responsible.
4. Provision of employment and decent wages
Employment is understood as the activity of citizens related to the satisfaction of personal and social needs, which does not contradict the legislation of the Russian Federation and brings them, as a rule, earnings, labor income. At the same time, citizens have the exclusive right to dispose of their abilities for productive, creative work. Compulsion to work in any form (physical, psychological, moral) is not allowed, unless otherwise provided by law.
The participation of trade unions in promoting employment and decent wages is guaranteed by regulatory legal acts:
a) create new jobs with good conditions work and decent wages;
b) strive for compliance with the law when laying off workers and reducing jobs at the enterprise;
c) promote retraining, advanced training of employees;
d) contribute to the creation of conditions for the development of the vocational education system.
Position of trade unions on the labor market: “Effective employment - necessary condition for decent work ”.
The ideology of trade unions is based on the thesis: "Decent pay for decent work."
Position of trade unions on pay issues
a) The minimum wage should not be lower than the subsistence minimum in the region and in the Russian Federation.
b) The average wage is not less than four living wages.
c) Indexing wages depending on the rise in inflation.
d) Establishment of a wage system at the enterprise that promotes wage growth, incentives for workers for high labor productivity.
e) Protection of wages.
f) Establishing a constant (base) part of wages at a level not lower than 70% of the total wages.
5. Social protection of employees and their family members
Social protection is a set of targeted legal, economic and organizational measures to protect citizens from negative manifestations of the social environment, mitigate their consequences, to support the most vulnerable segments of the population.
Social protection of workers and their families is one of the main areas of activity of trade unions.
Social insurance is the foundation social protection workers.
Trade unions use various forms their activities in order to protect the social rights and interests of employees:
a) Participation in the development of normative legal acts regulating the social sphere.
b) Participation in the management of off-budget social funds.
c) Ensuring social protection of workers through a system of agreements and collective agreements.
d) Organization and implementation of collective actions of trade unions for social guarantees.
The solution to the problems of social protection of workers is achieved primarily by increasing wages.
6. Ensuring labor protection of employees
The participation of trade unions in labor protection is enshrined in international and national legislation, regional and sectoral regulations.
At the federal level
a) Participation in the development and implementation public policy in the field of labor protection.
b) Participation in the development of regulatory legal acts.
c) Participation in the formation of government programs.
G) Public control over the observance of the rights and interests of workers in the field of labor protection.
At the enterprise
a) Develop and conclude a collective agreement and monitor its implementation (there is a section on labor protection in the collective agreement).
b) Represent the side of employees in the labor protection commission.
c) Contribute to the identification and require the elimination of hazardous working conditions.
d) Participate in the examination of working conditions and certification of workplaces.
e) Participate in the investigation of accidents and compensation for damage to the employee by the enterprise.
f) Participate in the development of financial justifications for labor protection measures.
g) Provide advice to employees, inform them about dangerous conditions and preventive measures.
Occupational safety issues are an integral part of agreements and collective agreements.
Control over the observance of workers' rights in the field of labor protection is carried out by state and trade union technical labor inspectors. In accordance with Article 370 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, they have a number of rights, including:
a) freely visit the organizations where the members of this trade union work;
b) monitor compliance with regulatory legal acts;
c) conduct an independent examination and participate in the investigation of accidents;
d) receive information from the employer about the state of labor conditions and labor protection at the enterprise;
e) protect the rights and interests of members of the trade union on the issues of compensation for harm caused to their health;
f) send instructions on elimination of detected violations;
g) apply to state labor protection authorities.
Employers are responsible for the state of labor protection at work and are obliged to compensate the employee for the damage caused:
a) The employer's obligation to compensate the employee is based on federal law.
b) Compensation is carried out in the form of: benefits for temporary incapacity for work, lump sum payments, monthly insurance payments, additional expenses for rehabilitation.
Trade unions influence government bodies and employers in the development and implementation of policies in the field of labor protection, the creation of normal and safe working conditions at the enterprise.
7. Monitoring compliance with labor legislation and protection of labor rights of workers
The main document regulating relations in the labor sphere is the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, adopted on December 30, 2001, as amended and supplemented on June 30, 2006 No.
The rights of trade unions to exercise control over the observance of labor rights of workers are provided for in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the Federal Law "On Trade Unions, Their Rights and Guarantees of Activity."
Types of trade union control:
a) preliminary - prevention of violations of labor legislation;
b) current (periodic) - checking working conditions;
c) subsequent - restoration of violated rights of employees.
To monitor compliance with labor legislation, trade unions have the right to receive free and unhindered information and make proposals.
Human rights activities of trade unions in the world of work are carried out through trade union technical and legal inspectorates. They:
a) organize inspections of compliance with labor laws and other regulations;
b) seek to eliminate the identified violations;
c) take part in labor dispute commissions as employee representatives;
d) represent the interests of employees - members of the trade union in court;
e) conduct legal expertise of draft laws and regulations on social and labor issues;
f) interact with judicial, law enforcement agencies, state labor inspectorate;
g) keep records and summarize statistical data on violations and measures to prevent them.
Participation of trade unions in ensuring the legality of changes in the terms of an employment contract:
a) advising an employee to whom the employer proposed changes to the terms of the employment contract;
b) determining the legality of the changes proposed by the employer to the employee, negotiating with the employer;
c) participation in the resolution of a labor dispute in a labor dispute commission or in court as a representative of an employee who is a member of a trade union;
d) verification by a legal labor inspector of the presence of violations of labor legislation at the enterprise during scheduled inspections and sending the relevant instructions to the employer;
e) taking into account the opinion of the elected trade union body when adopting local regulations;
f) the conclusion of a collective agreement, the terms of which apply to employees and regulate the peculiarities of work at a particular enterprise;
g) legal assistance to members of the trade union;
h) negotiations with the employer on the issues of the employment contract.
When adopting local regulations, the employer must take into account the opinion of the elected trade union body.
A written employment contract between an employee and an employer is a mandatory document governing social and labor relations.
8. Resolution of labor disputes
Labor dispute - unresolved disagreements between employees and employers regarding the establishment and change of working conditions.
Labor disputes are individual and collective.
Individual labor disputes are resolved through labor dispute commissions with the participation of trade unions on the side of the employee who is a member of the trade union.
The role of the trade union organization in the creation and formation of the CCC (Labor Dispute Commission)
a) - clarification of the expediency of creating a CCC in the organization;
b) - preparation and holding of a general meeting (conference) of employees;
c) - selection of candidates to the CCC for election at a meeting (conference).
In a collective labor dispute, a trade union organization acts as a representative body of workers, participates in mandatory conciliation procedures.
If the resolution of the labor dispute is not reached, an effective legal measure of influence on the employer is a strike.
The parties to a collective labor dispute bear disciplinary and material responsibility.
Conclusion
Trade unions can exist and perform their functions only in a certain legal space. It is necessary that the trade union leader in modern conditions has necessary knowledge in the field of labor legislation, legislation on labor protection and trade unions. It is within the framework of laws that trade unions must be able to defend the interests of workers. This area of activity includes the control of trade unions for timely and full payment of labor, for the creation of normal working conditions, compliance with legislative norms when hiring and firing, and preventing violations production process by the employer.
The Trade Union will constantly and purposefully actively advocate for the improvement of living standards and the realization of the rights of the members of the Trade Union, whose interests it represents.
Literature
2. FZ "On trade unions, their rights and guarantees of activity" No. 10-FZ dated January 12, 1996 (as amended on May 9, 2005)
3. Labor Code of the Russian Federation. M., 2007.
4. Isaicheva E.A. "Handbook of Labor Law" M. "Gorodets" 2005
5. Mikheev V.A. "Fundamentals of social partnership" M. "Exam" 2001
6. Snigireva I.O. Trade unions and labor law. M., 1993
Posted on Allbest.ur
...Similar documents
Characteristics of the totality of the rights and obligations of trade unions under Russian law. The activity of trade unions in the field of employment. Classification of rights and the main forms of influence of trade unions on management labor process at the enterprise.
abstract added on 11/27/2014
The concept and essence of trade unions, legal regulation of their activities. Social and legal problems in increasing the role of trade unions in protecting the rights and interests of workers. Examples from judicial practice in cases of labor disputes with the participation of trade unions.
course work, added 01/02/2017
Protection of labor rights and interests of workers as the goal of creating trade unions. Powers of trade unions to participate in the rule-making activities of state authorities and local self-government. Trade union rights in the world of work and guarantees of their activities.
term paper added on 04/06/2014
Regulatory framework for the activities of trade unions to protect the rights and interests of workers. Legal status trade unions in the world of work. Guarantees and methods of protecting the rights of trade unions, their responsibility and measures to prevent possible violations.
test, added 06/28/2010
The right to association is one of the fundamental human and civil rights. The human rights nature of trade unions in the world of work. Participants and parties of social partnership. Description of protective, representative and collaborative functions. Trade union powers.
term paper, added 12/26/2012
Legal status trade unions in the world of work. Classification of the fundamental rights of trade unions. Guarantee of property rights to those exempted from the main job union workers, on the creation of conditions by the employer for the implementation of trade union activities.
term paper, added 07/02/2015
term paper, added 10/13/2014
Legal framework for trade unions: protection of the interests of workers in the field of labor protection; their powers in the field of monitoring compliance with labor legislation and legal relations with the employer to fulfill the obligations of the Collective Agreement.
test, added 11/06/2012
Concept, status of trade unions, their protective function. Guarantees of the rights and activities of trade unions. Classification and principles of creating trade union bodies on various grounds, legal basis activities. The role of trade unions in the modern legal space.
test, added 06/08/2009
The concept and essence of ensuring the protection of labor rights in Russia to the present stage... Bodies of supervision and control over the observance of labor legislation. Forms of implementation of the protective function of trade unions and the Federal Labor Inspectorate. Problems of judicial protection.
Union- a voluntary public association of citizens bound by common industrial, professional interests by the nature of their activities, created in order to represent and protect their social and labor rights and interests. All trade unions enjoy equal rights.
Every person who has reached the age of 16 and carries out labor (professional) activities has the right, at his discretion, to create trade unions to protect their interests, join them, engage in trade union activities and leave trade unions. Russian trade unions may include not only citizens of the Russian Federation living both in the territory of the Russian Federation and outside its territory, but also foreign citizens and stateless persons living in the territory of the Russian Federation, with the exception of cases established by federal laws or international treaties of the Russian Federation.
Trade unions can create their own associations (associations) according to industry, territorial or other characteristics that take into account professional specifics: all-Russian associations (associations) of trade unions, interregional and territorial associations (associations) of trade union organizations (Article 2 of the Law on Trade Unions).
The primary trade union organization unites the members of trade unions, as a rule, of one enterprise, organization regardless of the form of ownership and subordination, acts on the basis of a regulation adopted in accordance with the charter, or on the basis of a general regulation on the primary trade union organization of the respective trade union.
Trade unions are independent in their activities from the executive authorities, local self-government bodies, the employer, their associations (unions, associations), political parties and other public associations, they are not accountable and not controlled by them. Interference of state authorities, local self-government bodies and their officials in the activities of trade unions, which may entail restricting the rights of trade unions or hinder the legal implementation of their statutory activities (Article 5 of the Law on Trade Unions), is prohibited.
Trade unions, their associations (associations) independently develop and approve their charters, their structure, organize their activities. These acts regulate relations within the trade union itself with its members and trade union bodies. They are not sources of law, as they are acts of the public.
Legal personality of a trade union as a legal entity arises from the moment of their state (notification) registration with the Ministry of Justice of Russia or its territorial body in the subject of the Russian Federation at the location of the corresponding trade union body. But trade unions have the right not to register, and then they do not acquire the rights of a legal entity (Article 8 of the Law on Trade Unions). It is prohibited to condition the recruitment, promotion at work, as well as the dismissal of a person by affiliation or non-affiliation with a trade union.
The reorganization or termination of the activity of a trade union or a primary trade union organization may be carried out only by decision of their members in the manner determined by the charter of the trade union, the statute on the primary trade union organization, and their liquidation as a legal entity - in accordance with federal law.
If the activity of a trade union contradicts the Constitution, constitutions (charters) of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, federal laws, it can be suspended for up to six months or prohibited by a decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation or the corresponding court of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation but a statement by the Prosecutor General of the Russian Federation, the prosecutor of the corresponding constituent entity of the Russian Federation. Suspension or prohibition of the activity of the trade union by decision of any other bodies is not allowed.
Thus, trade unions enter the political system of society as specific public organizations with their tasks and functions, determined by their statutes. The main tasks of trade unions are related to the implementation of their function - to protect the rights and interests of workers in the labor sphere and other relations directly related to it.
Functions of trade unions- these are the directions of their activities. Since trade unions arose to protect the rights and interests of workers, their main function is protective. The need to protect the rights and interests of workers in the world of work is especially relevant in the modern period, which has exposed socio-economic contradictions. The relations of trade unions with employers on social and labor issues are regulated by labor legislation at all levels of social partnership - from production to the federal level, while using their protective function, as well as their second most important function - representation of the interests of employees. For the effective implementation of these functions, the state has assigned to trade unions a number of rights and guarantees in rule-making, law enforcement and control over compliance with labor and labor protection legislation.
The protective function of trade unions is the activity of trade union bodies, as well as labor and asset inspections under their jurisdiction, aimed at preventing violations and restoring violated rights and legitimate interests of workers in the world of work, as well as bringing their violators to justice.
The function of representing the interests of employees is directly enshrined in Art. 29 of the Labor Code, according to which the representatives of workers in social partnership are trade unions and their associations, other trade union organizations provided for by the charters of all-Russian, interregional trade unions, or other representatives elected by workers in cases provided for by the Labor Code. In Art. 1 paragraph 11 of the Law on Trade Unions combines these two most important functions of trade unions with their respective rights.
But, in addition to these two functions, the trade unions also carry out cultural and educational function to educate its members in the spirit of patriotism and political function on their participation in the elections of bodies of state power and bodies of local self-government.
The implementation of the protective function and the function of representing the interests of employees is facilitated by the social regulation of social relations, into which they enter in the course of their activities. Relations with the participation of trade unions, as a rule, are governed by various types of social norms (morality, tradition, etc.). However, legal regulation is also possible to ensure the representation and protection of the rights and legitimate interests of employees.
The limits of legal regulation of relations with the participation of trade unions depend on the state of social relations, the degree of their development, socio-economic and political conditions in which they develop.
 Comments Off Order 8 tsz ojsc rzd read
Comments Off Order 8 tsz ojsc rzd read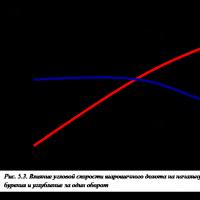 Peculiarities of determining the cruising speed when drilling with shells cs How to calculate the mechanical speed of drilling
Peculiarities of determining the cruising speed when drilling with shells cs How to calculate the mechanical speed of drilling Automated electric drive course of lectures
Automated electric drive course of lectures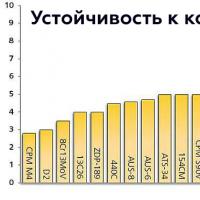 Powder steel crucible cpm s30v
Powder steel crucible cpm s30v How to open a medical center from scratch?
How to open a medical center from scratch? Comic, funny scenes for teenage and adult audiences
Comic, funny scenes for teenage and adult audiences Diploma templates blank download
Diploma templates blank download