Break even. Formula. Example of model calculation in Excel. Advantages and disadvantages
Let's talk about the break-even point of the enterprise, the formula and algorithm for calculating it in an analytical and graphical form.
Business break-even point(English CVP-point) shows what should be the volume of production of goods and services, as well as their sales in order to cover all costs and expenses. The break-even point can be expressed in terms of the number of products produced, in monetary terms, or the possible size of future profits.
Behind the break-even point, as with any financial indicator, one should see the economic meaning. So the break-even point serves as an indicator that shows what size of production of goods / services is critical for the enterprise, at which profit and loss are equal to zero. The break-even point is used to analyze the financial condition of the enterprise, the higher the volume of production and sales above this critical point, the better its solvency and financial strength.
The model for calculating the break-even point of an enterprise
In calculating the break-even point, enterprises use the following assumptions and simplifications of reality:
- Output and costs have a linear relationship (have a linear trend of change);
- Variable costs and product prices are constant over the future period under review;
- Production capacities are constant, the structure of products does not change;
- Stocks of finished goods are not significant and will not be able to distort the estimate of the company's break-even point. In other words, the size of production equals the volume of sales;
- Variable costs can be predicted and accurately estimated in the future period;
As we can see, the conditions for estimating the break-even point are taken as ideal: stable market, production and organizational conditions. In reality, output, sales and costs are affected by many external factors that are difficult to predict in the planning period. Nevertheless, consider the ideal model for calculating the break-even point of an enterprise.
Stages of calculating the break-even point according to A.D. Sheremet
Domestic economist A.D. Sheremet singled out the main 3 stages to determine the break-even point of an enterprise.
- Gathering the necessary information for analysis. Evaluation of the level of production volume, product sales, profit and loss.
- Calculation of the size of variable and fixed costs, determination of the break-even point and safety zone.
- Assessment of the required level of sales / production to ensure the financial sustainability of the enterprise.
The task of the enterprise is to determine the lower limit of its financial stability and create opportunities to increase the security zone.
Break even. 2 calculation formulas
The formulas for calculating the break-even point of an enterprise are given below. As a rule, use the break-even point expressed in the volume of production and the monetary equivalent of the generated income.
The formula for calculating the break-even point of an enterprise in monetary terms
It should be noted that variable costs are calculated per unit of output, not total.
The formula for calculating the break-even point of an enterprise in physical terms
An example of calculating the break-even point in Excel
fixed costs (FC) are costs that are independent of production. For example, this can be rent for premises, lease payments, taxes, salaries of administrative staff, etc.
Variable costs (AVC) are costs that vary with the volume of production. Variable costs include: the cost of raw materials and materials, fees for energy, fuel, wages of workers, etc.
Price per item (MR)- is the selling price of the output.
In Excel, fill in the main indicators. Fixed costs amount to 150 rubles, variable costs 50 rubles. and the selling price of 70 rubles. per unit of production.
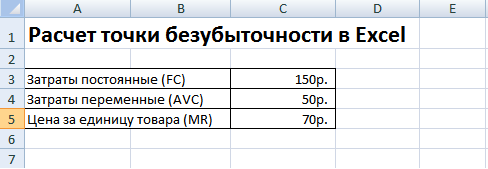
Break even. main parameters
At the next step, we calculate how the size of net profit will change depending on production, and determine at what volume of product sales the break-even point will come. Let's create a table with the following columns.
Column fixed costs=C3
variable costs=A10*$C$4
General costs = Variable + fixed costs= B10+C10
Income= A10*$C$5
Marginal income \u003d Income - Variable costs \u003d E10-C10
Net profit=E10-C10-B10
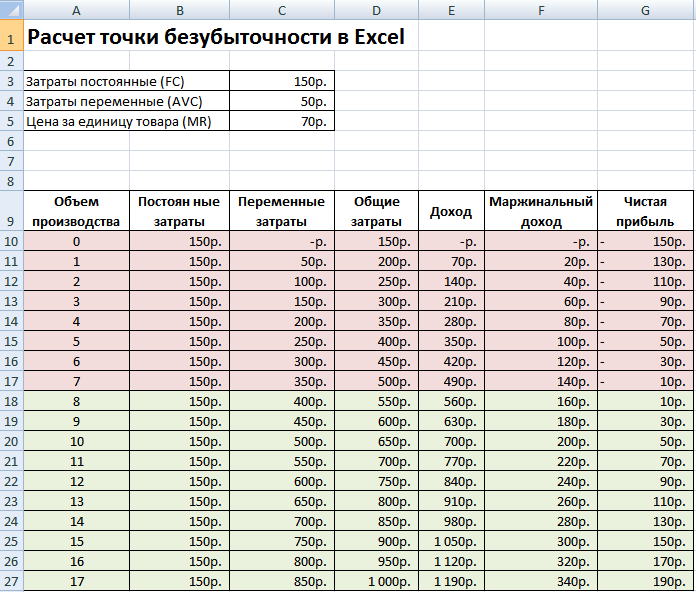
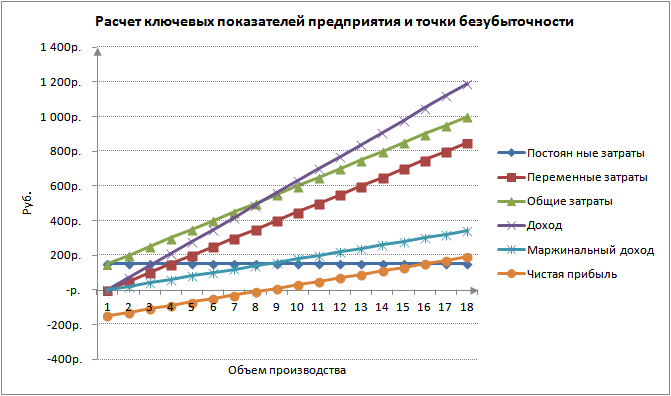
As we can see, starting from the 8th production, net profit became positive, and on the 7th production it was still negative. The break-even point is equal to a production volume of 8 pcs. and income from sales in the amount of 560 rubles.
 |
★ (calculation of Sharpe, Sortino, Trainor, Kalmar, Modiglanchi beta, VaR ratios) + rate movement forecasting |
For greater clarity, we present a graph of changes in the net profit of the enterprise, depending on the volume of production / sales of products.
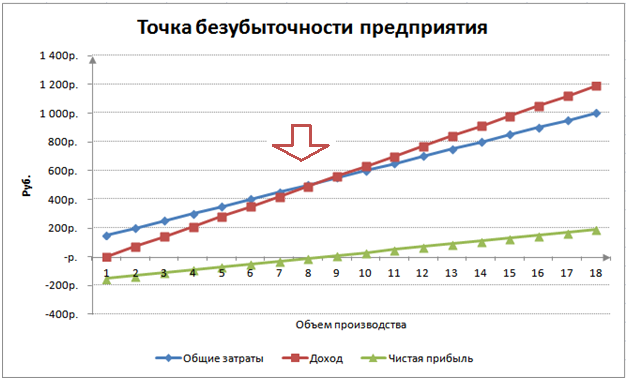
You can calculate and compare other calculated indicators, which are presented in the figure below. If the level of production / sales at the enterprise currently corresponds to 17 pcs. per month, the margin of safety is 190 rubles.
Break-even point and practice of its use
Break-even point analysis is used for various purposes. Let's consider some directions and purposes of using this indicator. The table below shows the purposes of the possible use of the break-even point indicator in economic practice.
| Users | Purpose of use |
|
Internal users |
|
| Development/Sales Director | Calculation of the optimal price per unit of goods, calculation of the level of costs when the company can still be competitive. Calculation and preparation of a sales plan |
| Owners/Shareholders | Determination of the volume of production at which the enterprise will become profitable |
| Financial analyst | Analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise and the level of its solvency. The further the enterprise is from the break-even point, the higher its threshold of financial reliability |
| Production director | Determination of the minimum required volume of production at the enterprise |
|
External Users |
|
| Lenders | Assessment of the level of financial reliability and solvency of the enterprise |
| Investors | Evaluation of the effectiveness of enterprise development |
| State | Enterprise sustainable development assessment |
The use of the break-even point model is used in management decisions and allows you to give a general description of the financial condition of the enterprise, assess the level of critical production and sales in order to develop a set of measures to increase financial strength.
Advantages and disadvantages of the break-even point model
Consider the main advantages and disadvantages of the break-even point model.
The advantages of this model lie in the ease of analysis and assessment of the required level of production and sales when the minimum critical level is reached. The disadvantages of the model lie in the conditions and limitations of building this model.
- Linearity of changes in the volume of production and sales. This does not take into account the various bursts and abrupt changes that often occur in real practice. Linearity is greatly influenced by the seasonality of output, changes in demand in the region, and the emergence of new competitors in the market. All this changes the demand in the future. Production is greatly influenced by new technologies, which also determines the volume of sales.
- The break-even point model is well applicable to markets with low competition and strong consumer demand for manufactured products. The globalization of markets creates more volatile demand for national products.
- The cost of raw materials during production can vary quite significantly.
- Many factors affect sales volume: product quality, dealer network size, seasonality, marketing, etc.
- Poorly used for small businesses that have an unstable sales pattern.
Summary
The break-even point model allows you to determine the minimum allowable limit of sales and production for the enterprise. This model can be well used for large enterprises with a stable market. The calculation of the break-even point allows you to determine the safety zone - the remoteness of the enterprise from the critical level at which profit is zero.
 Ready-made business plan with calculations using the example of a web studio
Ready-made business plan with calculations using the example of a web studio Registration of an internal memorandum: sample document and drafting rules
Registration of an internal memorandum: sample document and drafting rules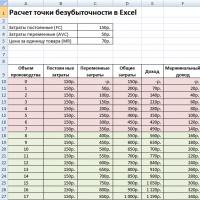 Break even. Formula. Example of model calculation in Excel. Advantages and disadvantages
Break even. Formula. Example of model calculation in Excel. Advantages and disadvantages Advance report is ... Advance report: sample filling
Advance report is ... Advance report: sample filling How to stitch documents with threads by hand?
How to stitch documents with threads by hand? Disciplinary sanction for non-fulfillment of official duties
Disciplinary sanction for non-fulfillment of official duties Binding your book
Binding your book