The break-even point is determined by analyzing the ratio of indicators, sales volume how to calculate
O.V. Grishchenko
Management Accounting
Lecture notes. Taganrog: TTI SFU, 2007.
6. USE OF ACCOUNTING INFORMATION IN THE PROCESS OF MANAGEMENT DECISION-MAKING
6.2. One-component break-even analysis
Break-even analysis is a rather simple in form and deep in content tool for planning and making managerial decisions in a commercial organization. The basis for making decisions regarding production activities is the consideration of options for possible changes in the market situation. Since the enterprise plan is a system of indicator values that the enterprise intends to achieve in the future, its implementation will depend on many factors. In the process of drawing up plans, the management of the enterprise will have to solve the following tasks:
- determine the volume of production, which will not only cover the costs, but also allow you to get the desired level of profit;
– determine the level of costs that allows you to remain competitive in the market.
Break-even analysis allows to solve these problems. There are other names for this procedure in the literature, for example: “critical sales volume method”, “dead point method”, “zero profit point method”, “operational analysis”, “marginal method”, “costs - volume - profit” method ”, or CVP analysis (Cost - Volume - Profit).
The essence of the method is to determine for each specific situation the volume of output that ensures break-even activity.
One-component break-even analysis.
The simplest is the break-even analysis of single-product production, i.e. production that produces only one type of product. In the general case, excluding tax effects, the operating profit of the enterprise (P) for the reporting period is formed as follows:
P \u003d VR - Zpost - Zper;
where BP is the company's revenue for the period in monetary units, BP = c × Q;
q - selling price of a unit of production, rub.;
Q - sales volume in physical terms, pieces, kg, etc.;
Zpost - fixed costs, rub.;
Zper - total variable costs, rub.
If we designate specific variable costs in rubles. - zper, then the formula can be represented in the following form:
P \u003d (c - zper) × Q - Zpost.
Break even(Qcr)- this is an indicator characterizing the volume of sales of products, at which the company's revenue from the sale of products (works, services) allows you to cover all costs and reach a zero level of profit (P = 0). The break-even point can be found from the equation:
Another important value that characterizes the cost structure of an enterprise is the value marginal incomeor contribution enterprises. Marginal income at manufacturing enterprises is the difference between the company's revenue from the sale of products (works, services) and the variable costs incurred by the enterprise in the process of producing these products (works, services). Distinguish the value of the total marginal income (MD):
MD \u003d VR - Zper \u003d c × Q - zper × Q \u003d (c - zper) × Q
and specific marginal income ( md):
md\u003d c - zper.
There is another way to determine the amount of marginal income. The value of marginal income can be determined by adding the fixed costs and profits of the enterprise:
MD = Zpost. + P.
The dependence model of the indicators under consideration can be built graphically (Figure 6.2).

Rice. 6.2. Break even chart
A widely accepted and highly illustrative representation of earnings growth above the break-even point is shown in Figure 2. 7.3. On this graph, the line 3 full is the x-axis. The y-axis reflects the amount of "divergence" between the straight lines "Revenue" And Wfull, i.e. the amount of profit. When issuing below Qcr, the value on the y-axis will be negative (which corresponds to losses), and above Qcr - positive (profit). The slope of this graph to the x-axis will be equal to specific marginal income, and its intersection with the y-axis is the value Wfast, which is understandable - at zero output, losses are equal to the amount of fixed costs.

Rice. 6.3. Dependence of profit on the volume of output
The volume of production Qkr corresponds to the amount of revenue BPkr, which, by analogy with the release, is also called break-even point, in monetary units only:
![]()
or otherwise:
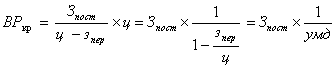 ,
,
Where umd- the share of marginal income in the price.
The conclusion follows from the second formula: the higher the share of variable costs in the selling price of the product (ratio zper / c), the higher the break-even point. Otherwise, the lower the share of marginal income in revenue, the more products the company should produce in order to cover fixed costs and start making a profit.
Another indicator is calculated as part of the break-even analysis - safety threshold(otherwise called marginal margin of safety).This indicator is calculated asdifference between real volume and breakeven point andindicates how much output can be reduced before the company begins to incur losses. As already noted, the larger the output, the higher the profit. The higher the volume of production, the less fearful the enterprise is of fluctuations in market conditions - the more fluctuations in costs and revenues it can painlessly endure, remaining in the "profit zone".
Obviously, each specific volume of output has its own volume of security.
Consider the methodology of break-even analysis using an example.
Example.
The production enterprise "Zarya" is engaged in the production of dumplings. To develop a work plan for the next quarter, a break-even analysis of this one-product production is carried out. The planned variable costs for the finished product of the enterprise are Z per = 39 rubles. Fixed expenses for the quarter will be W post = 480,000 rubles. The selling price of dumplings is planned at the level of q = 67.5 rubles. Break even
![]() .
.
Such a volume of production will cover all costs and reach zero profit. If the production for the quarter does not reach, the financial result of the enterprise will be negative, and the activity will be unprofitable.
Based on the level of annual profitability desired by the owners of the enterprise, the following level of target profit is set - 100,000 rubles. Calculate how much output will allow you to get such a profit.
Having studied the market situation and the possibilities of their own enterprise, the management of Zarya planned the output of Q dumplings for the next quarter -. With this volume of production, the level of profit will be:
P \u003d (c - zper) × Qkr - Zpost. \u003d (67.5 - 39) × 20,000 - 480,000 \u003d 90,000 rubles.
Break even
Safety threshold:
The flexible budget of the company provides for the possibility of an unfavorable situation in the planning period, which may lead to an increase in rent, and, accordingly, fixed costs by 40,000 rubles. The managers of the organization do not consider it possible to increase the selling price of dumplings, since it is determined by the market. The easiest way to maintain the estimated level of profit is to cut variable costs. What savings in variable costs (v*per) will help to cope with an unfavorable situation?
Therefore, the enterprise should achieve savings in variable costs in the amount of (39 - 37) = 2 rubles. on products. However, technologists and employees of the supply department, having studied all the possibilities for saving variable costs, came to the conclusion that it was impossible to achieve savings of more than 1.3 rubles. How much fixed cost savings would such a situation require?
Z * post \u003d (c - s * lane) × Qplan - P \u003d (67.5 - 37.7) × 20,000 - 90,000 \u003d 506,000 rubles.
506,000 - 40,000 \u003d 466,000 rubles.
480,000 - 466,000 \u003d 14,000 rubles.
Thus, in order to compensate for a possible increase in rent, the managers of the enterprise should, in addition to saving variable costs in the amount of 1.3 rubles. on products, it is necessary to find an opportunity to save 14,000 rubles in the existing structure of fixed costs.
Sales volume is the main indicator of the company's performance. It can be expressed in the actual number of units sold or in the total amount of funds received by the firm after the sale of goods. In economic analysis, gross, net, target and critical OP are calculated. The indicator is used in the analysis of profit, costs, break-even point. The source of information is financial reports, primary accounting documents, management accounting data.
The central indicator reflecting the performance of any company is the volume of sales. It shows how many products, works and services the company has created and sold. The profit and value of the business depends on the result obtained.
Volume of sales(Sales volume - SV, OP) is an indicator of the result of the company's functioning, which is represented by the total amount of revenue received for a certain period of sales of products, works, services. Often it is called the volume of sales of products and is considered as a synonym for revenue.
Reference! The volume of sales in financial analysis is expressed in value units (rubles, dollars, euros, etc.). However, for the purposes of management accounting, the possibility of using natural units (pieces, kg, m, etc.) is not excluded.
The SV indicator is most conveniently viewed as the actual amount of funds received in the company's accounts over a certain period.
Break even analysis
In the future, other indicators of economic analysis are calculated on its basis.
- If you subtract the cost of production from the OP, then you can get a gross profit - a more accurate reflection of the efficiency of the business entity.
- If we compare the indicator with fixed and variable costs, we can calculate the break-even point.
Important point! When analyzing the OP, it is impossible to compare it with the indicator of other companies or the industry average. It is compared with the results of the same company for previous periods or planned targets.
Sales volume reflects not only the results of the company's work, but also the situation on the market: if the demand for products decreases, a high-quality substitute has appeared, legislative restrictions have come into force, it will be reduced.
Sales volume: classification
In the modern practice of economic analysis, several varieties of the OP indicator are used:
- Gross - cumulative sales for the reporting period at full prices, excluding returns, discounts and other adjustments.
- Net - gross OP minus returns, benefits, discounts and other concessions to customers, which allows it to be used in assessing the effectiveness of the company's functioning and forecasting.
- Target - the planned indicator obtained by calculation on the basis of information about the target profit.
Critical - the minimum amount of income, which, even with unfavorable demand, allows the company to avoid losses.
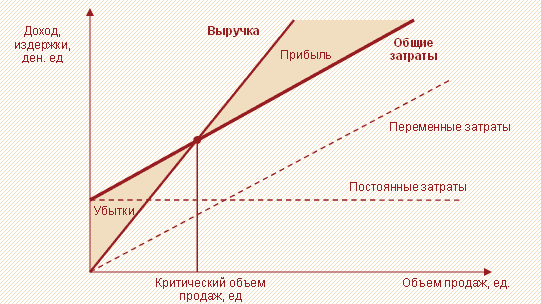
Figure 1. Break-even point and critical sales volume
Formula for calculating sales volume
To determine the volume of product sales, it is not enough to use data from the company's public financial statements: it will be necessary to accumulate information from primary accounting documents and internal management accounting documents.
The formula for estimating SV in general can be represented as an identity:
OP \u003d (VPF + EBIT) / (Ced - Pred), where:
CPL - the amount of conditionally fixed costs;
EBIT - profit before taxes;
Tsed - the cost of a unit of production;
Pre - variable costs for each unit of goods.
Reference! Semi-fixed costs are costs that remain the same even if output varies. These include depreciation of buildings and structures, enterprise management costs, rental payments, etc. Variable costs, on the contrary, change along with an increase or decrease in the amount of products produced.
The meaning of the indicator and its analysis
Since the OP formula takes into account costs and profit, this indicator is used in the analysis:
- Dynamics of the actual volume of sales.
- Price level changes.
- Volatility of production and distribution costs.
- marginal income.
- market demand, etc.
Important point! The total volume of sales is an absolute indicator. It can be compared with the performance of competing firms when it comes to assessing market shares. In other cases, the dynamics of Sales volume is analyzed, as well as its proximity to the target value.
There is no general standard value for the SV indicator. Each company determines for itself the critical volume of sales and target values, which become guidelines for changing the indicator.
Reference! To determine the critical OP, the formula KOP = CPI / (Ced - Prev) is used, since the profit at the breakeven point is zero.
The process of assessing the dynamics of the company's sales is presented in the video
Coefficient Calculation Examples
In order to understand the practical application of the sales volume calculation formula, the analysis of this indicator, it is worth considering a ready-made example of calculating this indicator for the Cube company, which sells a typical model of DVRs.
Important point! If a company sells several types of products with different costs and prices, then SV is calculated separately for each type of product.
Conclusion! For three years, the Kub company has been declining OP. This negative trend takes place against the backdrop of rising EBIT and unit prices. Consequently, the reason for the reduction could only be the fall in the physical value of sold products.
It should be noted that the critical volume of output of the enterprise under study varies over the years. However, it is below the obtained value and is 6.5, 6.1 and 6, respectively.
Conclusion! Until the actual SV value approaches a critical value, no action can be taken, but an unfavorable trend should be monitored.
A detailed scheme for calculating the volume of sales of goods, works, services and its critical value is given in a sample compiled on the basis of the toolkit of the spreadsheet editor Excel.
Questions and answers on the topic
No questions have been asked for the material yet, you have the opportunity to be the first to do so
Break Even Point Calculation in Excel with Examples
The break-even point reflects the volume of production, sales of goods and services, which covers all the costs of the enterprise.
CVP analysis: calculation of marginal income and break-even point
In an economic sense, this is an indicator of a critical situation when profits and losses are equal to zero. This indicator is expressed in quantitative or monetary units.
The lower the break-even point of production and sales, the higher the solvency and financial stability of the company.
Break Even Point Formula in Excel
There are 2 ways to calculate the break-even point in Excel:
- In monetary terms: (revenue * fixed costs) / (revenue - variable costs).
- In natural units: fixed costs / (price - average variable costs).
Attention! Variable costs are taken per unit of output (not total).
To find breakeven, you need to know:
Fixed costs (not dependent on the production process or implementation) - rent payments, taxes, salaries for management staff, lease payments, etc.
Variable costs (depending on production volumes) - the cost of raw materials and materials, utility bills in production facilities, wages of workers, etc.
The selling price of a unit.
Enter data into an Excel spreadsheet:

- Find the volume of production at which the company will receive a net profit. Establish a relationship between these parameters.
- Calculate the volume of sales of goods at which the break-even point will come.
To solve these problems, we compile the following table with formulas:

- Variable costs depend on the volume of products produced.
- Total costs are the sum of variable and fixed costs.
- Income is the product of the volume of production and the price of a good.
- Marginal income is the total income without variable costs.
- Net profit is income without fixed and variable production costs.
Let's fill in the table and see what output the company will make a "plus" on.
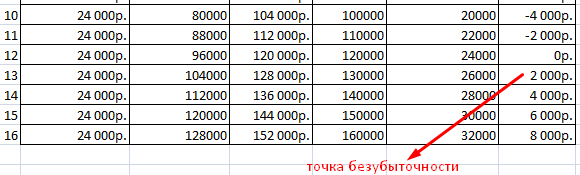
Starting from the 13th production, the net profit became positive. And at the breakeven point, it is zero. The volume of production is 12 units of goods. And the income from sales is 120,000 rubles.
How to Plot a Break Even Point Chart in Excel
To visually demonstrate the economic and financial condition of the enterprise, we will draw up a graph:
- Decide on the appearance of the chart and click the "Select data" button.
- To demonstrate, we need the columns "Total Cost", "Revenue", "Net Profit". These are the elements of the legend - "Rows". We enter manually the "Row name". And in the line "Values" we make a link to the corresponding column with data.
- The range of labels on the horizontal axis is "Production volume".
We get a graph like this:
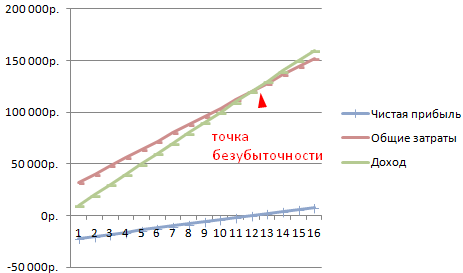
Let's change the graph (chart layout) a bit.
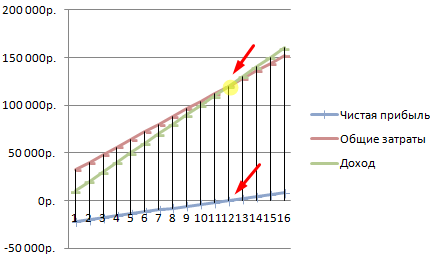
Such a demonstration allows you to see that the net profit at the break-even point is indeed “zero”. And it was after the twelfth release of products that “plus went”.
Where are such calculations needed?
The break-even point indicator is in demand in economic practice for solving the following problems:
- Calculation of the optimal price for the product.
- Calculation of the amount of costs at which the firm is still competitive.
- Drawing up a plan for the sale of goods.
- Finding the volume of output at which profitability will appear.
- Analysis of the financial condition and solvency of the enterprise.
- Finding the minimum production volume.
Ready-made calculations and templates for analyzing the company's break-even:
The results of such calculations are in demand by both internal and external users. Break-even is taken into account when making management decisions, gives an idea of the financial condition of the company. The use of such a model is a way to assess the critical level of production volume and the sale of goods and services.
Online break-even point calculator
What is a break-even point and how to calculate it yourself
Let's take a look at the instructions for self-calculation of the break-even point, with two test examples with formulas and graphs for retail and manufacturing activities.
The goal of any business is to make a profit. Every businessman has to predict the development of production, which is especially important when planning any new directions in it. Therefore, before the start of implementation, it is necessary to understand how effective the conceived project will be, to evaluate the amount of investments, payback periods and financial risks. To conduct this assessment, there is an economic indicator - break-even point or, as it is also called break-evenpoint - BEP. Let's talk about this important economic tool, the need for its application and calculation methods.
Download two ready-made models for calculating the break-even point in excel format for retail and manufacturing activities. In the given examples, you can change the initial data to suit your numbers and calculate the VER directly for your project.
What does the break-even point mean, its significance in the functioning of the enterprise
The indicator determines the volume of sales necessary to cover the costs. Profit, which is the difference between revenue and expenses, is zero. Those. The break-even point is the level of sales at which there is no profit and no loss.
It is calculated both in natural units and in monetary terms. This economic tool determines the number of units of products, services or goods that need to be sold in order to cover costs and reach zero profit, as well as their cost. If the level of sales did not reach the calculated indicator VER, it means that the company incurs losses, and vice versa, its excess by sales volume indicates that the organization, having crossed the zero line, makes a profit.
What does the breakeven point show?
- According to the BEP indicator, such an important aspect of the company's functioning as its financial stability is determined. For example, an increase in the BEP value indicates objective or private problems in the company that led to more sales to achieve a zero profit threshold. The reasons for the growth of the indicator are the expansion and change in the structure of production, which invariably entails an increase in trade turnover, fluctuations in market prices, etc.
- The BEP value allows the company to analyze the feasibility of investing in a new project, comparing the rate of self-sufficiency with the required sales volume, and its fluctuations - to establish the causes of problems in the company and their timely elimination, if they are not of a global nature.
- The calculation of the break-even point of the project makes it possible to calculate the optimal changes in sales volumes and the cost of the product for a more comfortable and flexible business. For example, to calculate a non-critical value of a decrease in the amount of revenue in order to increase sales volumes, while operating without loss and creating sufficient reserves.
Key Metrics for Calculations
The calculation of the BEP is based on information from the production cost accounts. Here it is important to separate them into constants and variables. Fixed costs are expenses that do not change from month to month and do not respond to fluctuations in output and sales. It can be:
- depreciation of machine tools and equipment;
- the salary of the AUP and the social contributions accrued on it;
- rent, utilities and other payments of an unchanging nature.
Variable costs include:
- expenses for the purchase of raw materials and materials for the production process of the product;
- payment for fuel and energy resources involved in the work process;
- wages of shop workers (with deductions), etc.
Fixed costs may change due to various reasons, such as reduction/increase in production capacity, increase in energy prices, changes in rental payments, acquisition/disposal of equipment, inflation and other factors. The amount of variable costs varies depending on the volume of output and sales.
Formulas for calculating the break-even point
As already mentioned, the calculation can be made in kind and value terms. Consider the basic data required for calculations in units. Calculation data required:
- fixed costs for the full volume (Zpost);
- unit price of a product or commodity (Ced);
- variable costs per unit (Zper / unit).
VER formula in units: BEPed \u003d Zpost / (Ced- Zper / unit) shows the volume of sales in units to reach zero profit.
Calculation of the VER value in monetary terms will require the use of the following data:
- fixed costs for the full volume (Zpost);
- revenue (B);
- unit price of the product (Ced);
- variable costs for the full volume (Zper) and unit of goods (Zper / unit).
At the first stage of calculations, marginal income (Dm) is found, which is the difference between revenue and variable costs according to the formula: Dm \u003d B - Zper.
Based on it, calculate the coefficient (share) of marginal income in total revenue Kdm = Dm / V.
Using the coefficient, the value of VER is calculated in monetary terms: VERDEN = Zpost / Kdm
When forecasting new directions in business, it is sometimes impossible to calculate marginal income for the entire volume of sales. In this case, the values of price and variable costs per unit of product or commodity are used, based on the formula
Dm / unit \u003d C - Zper / unit, where Dm / unit - marginal income per unit.
When calculating the coefficient, this indicator is also used, comparing its value with the price of the product, because it is revenue in the sale of a unit of goods:
Kdm \u003d Dm / unit / Zed, and get the value of the coefficient exactly the same as when calculating the entire volume of sales.
So, the break-even point in value terms is calculated by the formula
VERDEN = Zpost / Kdm.
This indicator is also called the profitability threshold, which is very true, since by crossing this threshold - the amount covering the invested costs, the company goes to make a profit.
Let's analyze examples of calculating the break-even point for companies of different types of activities.
Example #1: Calculating the Break Even Point for a Retail Business
Let's calculate the profitability threshold for a women's clothing store. The range of the outlet is usually quite wide, so the practice of calculating it in terms of money is used here.
The fixed costs of a trade enterprise include the costs associated with the work process:
- payment for rent of retail space, communication services, security, utilities, etc.;
- sellers' wages and deductions to off-budget funds;
- advertising costs.
Variable costs consist of the volume of sales and the purchase price per unit of goods. Consider the presented table, which contains data for calculating the profitability threshold broken down into variable and fixed costs, calculated marginal income and its share in total revenue, and also calculated the required sales volume to reach zero profit.
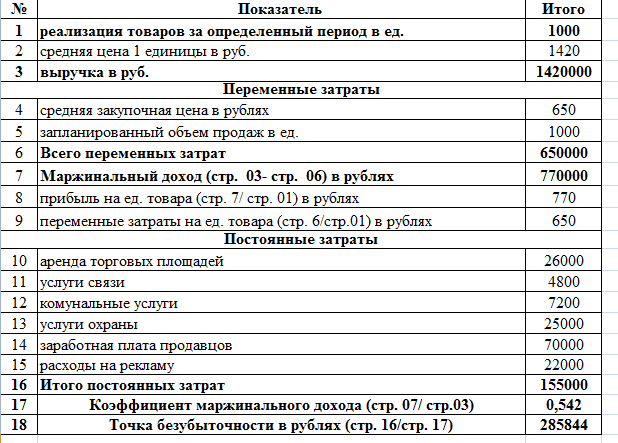
According to the formulas, after calculating the fixed and variable costs, we calculate:
- marginal income Dm \u003d B - Zper. \u003d 1,420,000 - 650,000 \u003d 770,000 rubles
- margin ratio Kdm = Dm / V = 770,000 / 1,420,000 = 0.542
- break-even point VERDEN \u003d Zpost / Kdm \u003d 155,000 / 0.542 \u003d 285,844 rubles.
Conclusion: to cover investments, sales in the amount of 285,844 rubles will have to be made, and the sale of goods above this level will begin to make a profit.
Download break-even point calculation in excel for retail.
Features and methods for calculating the break-even point
The low complexity of the calculations of the previous example is due to the ideal conditions of the implied environment, not taking into account the constantly changing market.
What is a break-even point and how to calculate it
The calculations of our examples allow the constancy of such situations:
- the company does not change the price of products with an increase in sales;
- costs (both types) do not change. In reality, an increase in sales usually causes an increase in costs and expenses;
- the volume of production implies full implementation, which is also rare in the course of activity.
Of course, this does not happen in real life, but we give a correct calculation algorithm, and the businessman himself has to correct the calculations in accordance with the current market situation. There are different break-even point calculation methods:
- mathematical (presented in example No. 1);
- graphic (more visual).
Both methods are very effective in calculating the indicator and are quite simple. Let's look at them in the following example.
Example #2: Calculating the BEP value for a manufacturing plant
Product-specific industries often produce a limited range of homogeneous products, such as prefabricated parts of a single assembly. This method of production planning saves costs and greatly facilitates the calculation of the break-even point. For companies that produce a small number of titles, it is easier to calculate the BEP indicator in physical terms. Extended production provides for the association of product groups. In the presented example - a small enterprise that produces five types of products.
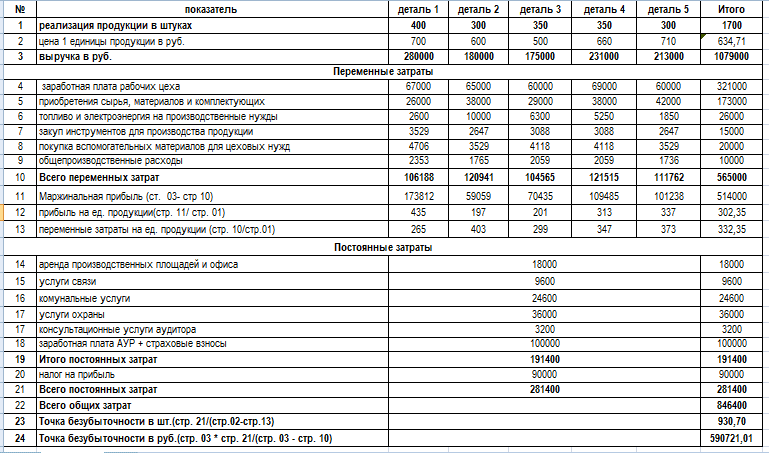
The break-even point calculation involves expenses grouped according to variable and fixed characteristics. We calculate the VER indicator in natural terms according to the formula:
BEPed \u003d Zpost / (Ced - Zper / unit) \u003d 281,400 / (674.71 - 332.35) \u003d 930.7 units.
To calculate the indicator in monetary terms, you can use the following formula:
VERden \u003d B * Zpost / (B - Zper) \u003d 1,079,000 * 281,400 / (1,079,000 - 565,000) \u003d 590,721.01 rubles.
Conclusion: in order to reach a zero level of profit, having covered the invested costs, 930.7 units should be sold. products in the amount of 590,721.01 rubles. Subsequent sales will already be profitable and will start to make a profit.
A graphical method for determining the value of VER has a greater clarity. To do this, you need to build a graph by grouping the necessary data into a table.
The graph is built in the classical system, plotting data on the volume of production along the horizontal axis, and revenue along the vertical axis. Using tabular information, build lines of revenue and costs.
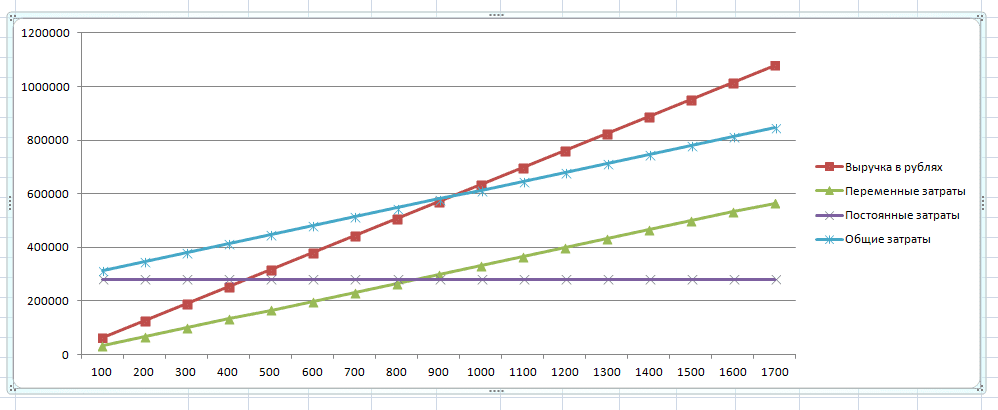
The point of intersection of the line of received (or planned) revenue with the line of total costs is the break-even point. If you lower the perpendicular to the sales volume axis, you can find out the number of products required for sale in order to achieve a state of no loss and no profit. The value of this point is determined by drawing a perpendicular to the vertical axis. The graph clearly confirms the correctness of mathematical calculations - 930.7 units should be sold. in the amount of 580,721.01 rubles to reach zero losses.
Downloadable model for a manufacturing plant.
If you have any clarifying questions about the calculation method or any difficulties with applying the formulas, ask them on the forum, we will help you figure it out.
Break even
Break even- the volume of sales at which the company covers all its expenses without making a profit.
Its value plays an important role in the stability and solvency of the company. The degree of excess of sales volumes over the break-even point determines the margin of financial strength (margin of stability) of the enterprise. In turn, how profit grows with a change in revenue is shown by the Operating leverage (operating leverage).
Break Even Point Formula
To calculate the break-even point, you need to divide the costs into two components:
- variable costs- increase in proportion to the increase in production (the volume of sales of goods).
- fixed costs- do not depend on the quantity of manufactured products (sold goods) and on whether the volume of operations is growing or falling.
Let us introduce the notation:
| IN | — | sales revenue. |
| pH | — | sales volume in physical terms. |
| Zper | — | variable costs. |
| Zpost | — | fixed costs. |
| C | — | price per piece |
| ZSper | — | average variable costs (per unit of output). |
| Tbd | — | break-even point in monetary terms. |
| tbn | — | break-even point in physical terms. |
The formula for calculating the break-even point in monetary terms:
(in rubles, dollars, etc.)
Tbd \u003d V * Zpost / (V - Zper)
The formula for calculating the break-even point in physical terms:
(in pieces, kilograms, meters, etc.)
Tbn \u003d Zpost / (C - ZSper)
Break-even point calculation example
Look at the Excel spreadsheet
with a wide range"
Calculation and graphs
The same data on the chart. Break-even point Tbn = 20 pieces
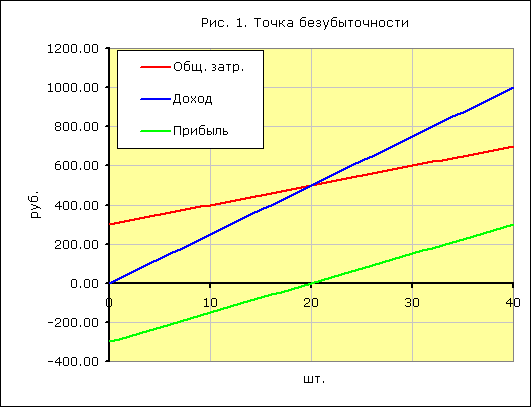
At the break-even point, the income line crosses and goes above the total cost line, the profit line crosses 0 - it moves from the loss zone to the profit zone.
How fixed costs, variable costs and price affect the break-even point, see Break-even point calculation, examples and graphs.
At first glance, the formula for calculating the break-even point is quite simple and should not be difficult to calculate. But in fact, everything is not so simple.
Four Important Assumptions When Calculating the Break Even Point
- We are talking about revenue (sales volume), so we believe that all produced or purchased products. Warehouse stocks are not taken into account.
- Variable costs are directly proportional depend on sales volume. This is not always the case.
The procedure and rules for calculating the break-even point
For example, the case when a new workshop had to be built to increase the volume of output will have to be calculated in a more complicated way.
- Fixed costs do not depend from sales volume. This also does not always happen. If, in order to increase the output, it was necessary to build a new workshop, hire more management personnel, increase utility bills - this case also does not fit the general formula.
- The breakeven point is calculated for the enterprise as a whole or for some average product.
When calculating the break-even point, perhaps the most important limitation is assumption 4. To make a calculation for each product separately, you need to know what proportion of fixed costs falls on each of the products. If there are many products, calculating break-even points separately for each product turns into a complex task that requires a lot of calculations.
Look at the Excel spreadsheet
"Breaking Point and Break-Even Analysis
with a wide range"
Profitability, Min. markup, Marginal profit, Margin of safety
Calculation and graphs
 Ready-made business plan with calculations using the example of a web studio
Ready-made business plan with calculations using the example of a web studio Registration of an internal memorandum: sample document and drafting rules
Registration of an internal memorandum: sample document and drafting rules Break even. Formula. Example of model calculation in Excel. Advantages and disadvantages
Break even. Formula. Example of model calculation in Excel. Advantages and disadvantages Advance report is ... Advance report: sample filling
Advance report is ... Advance report: sample filling How to stitch documents with threads by hand?
How to stitch documents with threads by hand? Disciplinary sanction for non-fulfillment of official duties
Disciplinary sanction for non-fulfillment of official duties Binding your book
Binding your book