Opening of a nuclear power plant. How does a nuclear power plant work? Nuclear energy in Ukraine
In the middle of the twentieth century, the best minds of mankind worked hard on two tasks at once: on the creation of an atomic bomb, and also on how to use the energy of the atom for peaceful purposes. This is how the first in the world appeared. What is the principle of NPP operation? And where in the world are the largest of these power plants located?
History and features of nuclear power
"Energy is the head of everything" - this is how the well-known proverb can be paraphrased, taking into account the objective realities of the XXI century. With each new round of technical progress, mankind needs more and more of it. Today, the energy of the "peaceful atom" is actively used in the economy and production, and not only in the energy sector.
Electricity produced in so-called nuclear power plants (the principle of operation of which is very simple in nature) is widely used in industry, space exploration, medicine and agriculture.
Nuclear power is a branch of heavy industry that extracts heat and electricity from the kinetic energy of the atom.
When did the first nuclear power plants appear? The principle of operation of such power plants was studied by Soviet scientists back in the 40s. By the way, in parallel, they also invented the first atomic bomb. Thus, the atom was both "peaceful" and deadly.
In 1948, IV Kurchatov suggested that the Soviet government begin to carry out direct work on the extraction of atomic energy. Two years later, the construction of the very first nuclear power plant on the planet began in the Soviet Union (in the city of Obninsk, Kaluga Region).
The principle of operation of all is similar, but it is not at all difficult to understand it. This will be discussed further.
NPP: principle of operation (photo and description)
Any work is based on a powerful reaction that occurs when the nucleus of an atom fissions. In this process, uranium-235 or plutonium atoms are most often involved. The nucleus of atoms divides a neutron that enters them from the outside. In this case, new neutrons appear, as well as fission fragments, which have enormous kinetic energy. This energy is the main and key product of the activity of any nuclear power plant.
This is how the principle of operation of a nuclear power plant reactor can be described. In the next photo, you can see how it looks from the inside.

There are three main types of nuclear reactors:
- high-power channel reactor (abbreviated as RBMK);
- water-water reactor (VVER);
- fast neutron reactor (BN).
Separately, it is worth describing the principle of operation of the NPP as a whole. How it works will be discussed in the next article.
The principle of NPP operation (diagram)
Works under certain conditions and in strictly defined modes. In addition to (one or several), the NPP structure includes other systems, special structures and highly qualified personnel. What is the principle of NPP operation? It can be briefly described as follows.
The main element of any nuclear power plant is a nuclear reactor in which all the main processes take place. We wrote about what happens in the reactor in the previous section. (as a rule, most often it is uranium) in the form of small black pellets is fed into this huge boiler.

The energy released during the reactions taking place in an atomic reactor is converted into heat and transferred to the coolant (usually water). It is worth noting that the coolant also receives a certain dose of radiation during this process.
Further, the heat from the coolant is transferred to ordinary water (through special devices - heat exchangers), which, as a result, boils. The steam generated in this process drives the turbine. A generator is connected to the latter, which generates electrical energy.
Thus, according to the principle of operation of a nuclear power plant, it is the same thermal power plant. The only difference is how the steam is generated.
Geography of nuclear power
The top five countries for the production of nuclear energy are as follows:
- France.
- Japan.
- Russia.
- South Korea.
At the same time, the United States of America, generating about 864 billion kWh per year, produces up to 20% of all the planet's electricity.
In total, there are 31 states in the world that operate nuclear power plants. Of all the continents of the planet, only two (Antarctica and Australia) are completely free from nuclear energy.
Today there are 388 nuclear reactors in the world. True, 45 of them have not been generating electricity for a year and a half. Most of the nuclear reactors are located in Japan and the United States. Their full geography is shown on the following map. Countries with operating nuclear reactors are indicated in green, and their total number in a particular state is also indicated.

Development of nuclear power in different countries
In general, as of 2014, there is a general decline in the development of nuclear power. Three countries are the leaders in the construction of new nuclear reactors: Russia, India and China. In addition, a number of states that do not have nuclear power plants are planning to build them in the near future. These include Kazakhstan, Mongolia, Indonesia, Saudi Arabia and a number of North African countries.

On the other hand, a number of states have embarked on a course towards a gradual reduction in the number of nuclear power plants. These include Germany, Belgium and Switzerland. And in some countries (Italy, Austria, Denmark, Uruguay), nuclear power is prohibited at the legislative level.
The main problems of nuclear power
There is one significant environmental problem associated with the development of nuclear power. This is the so-called environment. Thus, according to many experts, nuclear power plants generate more heat than thermal power plants of the same capacity. Thermal pollution of waters is especially dangerous, which disrupts the life of biological organisms and leads to the death of many species of fish.
Another acute problem associated with nuclear energy concerns nuclear safety in general. For the first time, mankind seriously thought about this problem after the 1986 Chernobyl disaster. The principle of operation of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant was not much different from that of other nuclear power plants. However, this did not save her from a major and serious accident, which entailed very serious consequences for the whole of Eastern Europe.

Moreover, the danger of nuclear power is not limited only to possible technogenic accidents. So, big problems arise with the disposal of nuclear waste.
Benefits of nuclear power
Nevertheless, proponents of the development of nuclear power also name the clear advantages of operating nuclear power plants. So, in particular, the World Nuclear Association recently published its report with very interesting data. According to him, the number of human victims accompanying the production of one gigawatt of electricity at nuclear power plants is 43 times less than at traditional thermal power plants.

There are other, equally important, advantages. Namely:
- low cost of electricity production;
- ecological cleanliness of nuclear power (with the exception of only thermal pollution of waters);
- the absence of a strict geographic reference of nuclear power plants to large sources of fuel.
Instead of a conclusion
In 1950, the world's first nuclear power plant was built. The principle of operation of nuclear power plants is the fission of an atom using a neutron. As a result of this process, a tremendous amount of energy is released.
It would seem that nuclear energy is an exceptional blessing for humanity. However, history has proven otherwise. In particular, two major tragedies - the accident at the Soviet Chernobyl nuclear power plant in 1986 and the accident at the Japanese power plant Fukushima-1 in 2011 - have demonstrated the danger posed by the "peaceful" atom. And many countries of the world today began to think about a partial or even complete rejection of nuclear energy.
Modern nuclear power plants are widespread throughout the world because of their high power and performance. First nuclear power plants inferior to the latest nuclear power plants in many respects. The construction of the first nuclear power plants began in the middle of the last century.
Launch of the first nuclear power plant in the USSR
The development of the plan for the first nuclear power plant began after the successful test of the first atomic bomb in the USSR, when plutonium was produced at the nuclear reactor, and the production of enriched uranium was also organized. A large-scale discussion of the prospects and main problems of launching nuclear power plants for energy production took place in the autumn of 1949.
Work on the construction of the first nuclear power plant was launched in the middle of the 20th century. During 4 years, from 1950 to 1954, the first nuclear power plant was built. The first nuclear power plant was officially put into operation on June 27, 1954 on the territory of the Soviet Union, in the city of Obninsk. The operation of this nuclear power plant was ensured thanks to the AM-1 reactor, the maximum power of which was only 5 MW.
This power plant has been operating without interruption for almost 48 years. In April 2002, the plant's reactor was shut down. The decision to stop the station was made due to economic considerations and the inexpediency of its further use. Obninsk NPP became not only the first launched, but also the first shutdown nuclear power plant in Russia.
Significance of the first nuclear power plant
The first nuclear power plants in the USSR were able to open the way for the use of atomic energy for peaceful purposes. The operation of the very first nuclear power plants also allowed the accumulation of engineering and scientific experience necessary for the further design and construction of larger plants. 
The nuclear power plant erected in Obninsk was transformed during the construction period into a kind of school for training personnel, operating personnel and research workers. Obninsk NPP performed this role for several decades in the course of industrial use and a large number of experiments carried out on it.
First nuclear power plants in different countries
The long-term experience of operating the first Soviet nuclear power plant has confirmed almost all engineering and technical solutions put forward by professionals in this field. This made it possible to build and successfully launch the Beloyarsk NPP in 1964, with a capacity of 300 MW. 
In Britain, the very first nuclear power plant was officially launched only in October 1956. Outside the territory of the Soviet Union, this facility became the first industrial station in its category. The capacity of the power plant built in the British settlement of Calder Hall was 46 MW at the time of launch. Several years later, construction began on several more large nuclear power plants.
The first nuclear power plant in the United States began operations in 1957. The 60 MW power plant is located in the US state of Shippingport. The United States halted construction of the reactors in 1979 following the global accident at the Three Mile Island nuclear power plant. The construction of two new reactors on the basis of the former station is planned only for 2017.
The major one that happened in 1986 had a serious impact on the world and forced a number of related issues to be reconsidered. Experts from different countries actively began to solve the safety problem and thought about the importance of international cooperation in order to ensure the maximum safety of nuclear power plants.
Today, in countries such as India, Canada, Russia, India, Korea, China, the USA and Finland, programs for the further development of nuclear energy are being actively developed and implemented. In modern conditions, around the world, 56 reactors are under construction, and another 143 reactors are expected to be built by 2030. 
Advantages and disadvantages of using a nuclear power plant
All over the world it is constantly increasing. At the same time, the growth in consumption is increasing at a faster pace than energy production, and the practical application of modern promising technical solutions in this area, for many reasons, will begin in a few years. The solution to this problem is the improvement of nuclear energy and the construction of new nuclear power plants. The following advantages of operating nuclear power plants can be highlighted:
- High energy intensity of the used fuel resource. When fully burned out, one kilogram of uranium releases an amount of energy comparable to the result of burning about 50 tons of oil, or twice as many tons of coal
- The ability to reuse the resource after processing. Fissioned uranium, unlike waste fossil fuels, can be reused to generate energy. Further development of nuclear power plants presupposes a full-fledged transition to a closed cycle, which will help ensure that no hazardous waste is generated
- The nuclear power plant does not contribute to the formation of the greenhouse effect. Nuclear power plants help to avoid the emission of about 600 million tons of carbon dioxide every day. Nuclear power plants operating in Russia every year delay the release of more than 200 million tons of carbon dioxide into the environment
- Absolute independence from the location of fuel sources. The great remoteness of the nuclear power plant from the uranium deposit does not in any way affect the possibility of its operation. The energy equivalent of a nuclear resource is many times greater than that of fossil fuel, and the cost of its transportation is minimal.
- Low cost of use. For a large number of countries, generating electricity from nuclear power plants is not more expensive than other types of power plants
Despite the large number of positive aspects of operating nuclear power plants, there are several problems. The main disadvantage is the grave consequences of emergency situations, for the prevention of which power plants are equipped with rather complex safety systems with large reserves and redundancy. This ensures that damage to the central internal mechanism is avoided even in the event of a major accident. 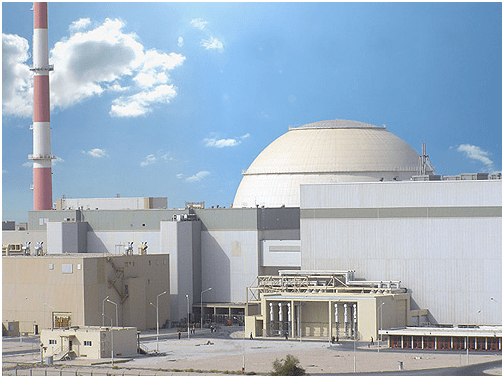
A big problem for the operation of nuclear power plants is also their destruction after the depletion of resources. The cost of their elimination can reach 20% of all costs of their construction. In addition, for technical reasons, it is undesirable for nuclear power plants to operate in maneuverable modes.
The first nuclear power plants in the world allowed to take a big step in the improvement of nuclear power. In modern conditions in Russia, about 17% of electricity is generated precisely with the help of nuclear power plants. Due to the benefits of operating nuclear power plants, many countries are starting to build new reactors and see them as a promising source of electricity.
Nuclear power is a modern and rapidly growing method of generating electricity. Do you know how nuclear power plants are arranged? What is the operating principle of a nuclear power plant? What types of nuclear reactors are there today? We will try to examine in detail the scheme of operation of a nuclear power plant, delve into the structure of a nuclear reactor and find out how safe the atomic method of generating electricity is.
How is a nuclear power plant arranged?
Any station is a closed area far from a residential area. There are several buildings on its territory. The most important structure is the reactor building, next to it is the turbine room, from which the reactor is controlled, and the security building.
The circuit is impossible without a nuclear reactor. An atomic (nuclear) reactor is an NPP device that is designed to organize a chain reaction of neutron fission with the obligatory release of energy during this process. But what is the operating principle of a nuclear power plant?
The entire reactor plant is placed in the reactor building, a large concrete tower that hides the reactor and, in the event of an accident, will contain all the products of a nuclear reaction. This large tower is referred to as containment, containment, or containment.
The containment area in the new reactors has 2 thick concrete walls - shells.
The outer shell, 80 cm thick, protects the containment area from external influences.
The inner shell, 1 meter 20 cm thick, has special steel cables in its device, which increase the strength of the concrete almost threefold and prevent the structure from crumbling. On the inside, it is lined with a thin sheet of special steel, which is designed to serve as additional protection of the containment and in the event of an accident, not to release the contents of the reactor outside the containment area.
Such a device of a nuclear power plant can withstand a plane crash weighing up to 200 tons, an 8-point earthquake, tornado and tsunami.
For the first time, a sealed enclosure was built at the American Connecticut Yankee nuclear power plant in 1968.
The total height of the containment area is 50-60 meters.
What does a nuclear reactor consist of?
To understand the principle of operation of a nuclear reactor, and hence the principle of operation of a nuclear power plant, you need to understand the components of the reactor. 
- Active zone. This is the area where the nuclear fuel (heat release) and moderator are placed. Fuel atoms (most often uranium is the fuel) undergo a fission chain reaction. The retarder is designed to control the fission process, and allows you to carry out the required reaction in speed and strength.
- Reflector of neutrons. The reflector surrounds the active zone. It consists of the same material as the retarder. In fact, it is a box, the main purpose of which is to prevent neutrons from leaving the core and entering the environment.
- Heat carrier. The coolant must absorb the heat that was released during the fission of fuel atoms and transfer it to other substances. The coolant largely determines how a nuclear power plant is arranged. The most popular heat carrier today is water.
Reactor control system. Sensors and mechanisms that drive the nuclear power plant reactor.
Fuel for nuclear power plants
What does the nuclear power plant operate on? Fuel for nuclear power plants are chemical elements with radioactive properties. At all nuclear power plants, uranium is such an element.
The design of the stations implies that nuclear power plants operate on a complex composite fuel, and not on a pure chemical element. And in order to extract uranium fuel from natural uranium, which is loaded into a nuclear reactor, you need to carry out a lot of manipulations.
Enriched uranium
Uranium consists of two isotopes, that is, it contains nuclei with different masses. They were named by the number of protons and neutrons isotope-235 and isotope-238. Researchers of the 20th century began to extract 235th uranium from the ore, because it was easier to decompose and transform. It turned out that there is only 0.7% of such uranium in nature (the remaining percent went to the 238th isotope). 
What to do in this case? They decided to enrich uranium. Uranium enrichment is a process when many necessary 235x isotopes and few unnecessary 238x are left in it. The task of uranium enrichers is to make almost 100% of uranium-235 from 0.7%.
Uranium can be enriched using two technologies - gaseous diffusion or gas centrifuge. For their use, uranium extracted from the ore is converted into a gaseous state. It is enriched in the form of a gas.
Uranium powder
The enriched uranium gas is converted into a solid state - uranium dioxide. Such pure solid 235 uranium looks like large white crystals, which are later crushed into uranium powder.
Uranium tablets
Uranium tablets are solid metal washers a couple of centimeters long. In order to mold such tablets from uranium powder, it is mixed with a substance - a plasticizer, which improves the quality of tablet pressing.
Pressed washers are baked at a temperature of 1200 degrees Celsius for more than a day to give the tablets special strength and resistance to high temperatures. How a nuclear power plant works depends directly on how well the uranium fuel is compressed and baked. 
The tablets are baked in molybdenum boxes, because only this metal is capable of not melting at "hellish" temperatures over one and a half thousand degrees. After that, the uranium fuel for the nuclear power plant is considered ready.
What are TVEL and TVS?
The reactor core looks like a huge disk or tube with holes in the walls (depending on the type of reactor), 5 times the size of a human body. These holes contain uranium fuel, the atoms of which carry out the desired reaction.
It's impossible to just throw fuel into the reactor, well, if you don't want to get an explosion of the entire station and an accident with consequences for a couple of nearby states. Therefore, uranium fuel is placed in fuel rods and then collected in fuel assemblies. What do these acronyms mean?
- TVEL is a fuel element (not to be confused with the same name of the Russian company that produces them). It is essentially a thin and long zirconium tube made of zirconium alloys, into which uranium pellets are placed. It is in fuel rods that uranium atoms begin to interact with each other, releasing heat during the reaction.
Zirconium was chosen as a material for the production of fuel rods due to its refractoriness and anti-corrosion properties.
The type of fuel rods depends on the type and structure of the reactor. As a rule, the structure and purpose of fuel rods does not change, the length and width of the tube may be different. 
The machine loads more than 200 uranium pellets into one zirconium tube. In total, about 10 million uranium pellets are simultaneously operating in the reactor.
FA - fuel assembly. NPP workers call fuel assemblies bundles.
In fact, these are several fuel rods, fastened together. Fuel assemblies are ready-made nuclear fuel, what a nuclear power plant operates on. It is the fuel assemblies that are loaded into a nuclear reactor. One reactor holds about 150 - 400 fuel assemblies.
Depending on the reactor in which the fuel assemblies will operate, they come in different shapes. Sometimes the beams fold in a cubic, sometimes in a cylindrical, sometimes in a hexagonal shape.
One fuel assembly for 4 years of operation generates the same amount of energy as when burning 670 coal wagons, 730 natural gas tanks or 900 tanks loaded with oil.
Today, fuel assemblies are produced mainly at factories in Russia, France, the USA and Japan.
To deliver fuel for nuclear power plants to other countries, fuel assemblies are sealed in long and wide metal pipes, air is pumped out of the pipes and delivered to cargo aircraft by special machines.
Nuclear fuel for nuclear power plants weighs prohibitively much, tk. uranium is one of the heaviest metals on the planet. Its specific gravity is 2.5 times that of steel.
Nuclear power plant: how it works
What is the operating principle of a nuclear power plant? The principle of operation of a nuclear power plant is based on a chain reaction of fission of atoms of a radioactive substance - uranium. This reaction takes place in the core of a nuclear reactor.
If you do not go into the intricacies of nuclear physics, the principle of operation of a nuclear power plant looks like this:
After starting a nuclear reactor, absorbing rods are removed from the fuel rods, which prevent uranium from reacting.
Once the rods are removed, the uranium neutrons begin to interact with each other.
When neutrons collide, a mini-explosion occurs at the atomic level, energy is released and new neutrons are born, a chain reaction begins to occur. This process generates heat.
Heat is transferred to the coolant. Depending on the type of coolant, it turns into steam or gas, which rotate the turbine.

The turbine drives an electric generator. It is he who, in fact, generates an electric current.
If you do not follow the process, uranium neutrons can collide with each other until they blow up the reactor and blow up the entire nuclear power plant to smithereens. The process is controlled by computer sensors. They detect temperature rise or pressure change in the reactor and can automatically stop reactions.
What is the difference between the principle of operation of a nuclear power plant and thermal power plants (thermal power plants)?
There are differences in work only in the first stages. In a nuclear power plant, the coolant receives heat from the fission of uranium fuel atoms, in a thermal power plant, the coolant receives heat from the combustion of fossil fuel (coal, gas or oil). After either uranium atoms or gas with coal have released heat, the operating schemes of nuclear power plants and thermal power plants are the same.
Types of nuclear reactors
How a nuclear power plant works depends on how its nuclear reactor works. Today, there are two main types of reactors that are classified according to the spectrum of neurons:
Slow neutron reactor, also called thermal reactor.
For its operation, 235th uranium is used, which goes through the stages of enrichment, creation of uranium pellets, etc. Today, there are overwhelming majority of slow neutron reactors.
Fast neutron reactor.
The future belongs to these reactors, since they work on uranium-238, which is a dime a dozen in nature and there is no need to enrich this element. The disadvantage of such reactors is only in very high costs for design, construction and launch. Today fast reactors operate only in Russia.
The coolant in fast reactors is mercury, gas, sodium or lead. 
Slow neutron reactors used by all nuclear power plants in the world are also of several types.
The IAEA organization (the international atomic energy agency) has created its own classification, which is used most often in the world atomic energy. Since the operating principle of a nuclear power plant largely depends on the choice of coolant and moderator, the IAEA based its classification on these differences.

From a chemical point of view, deuterium oxide is an ideal moderator and coolant, because its atoms most effectively interact with uranium neutrons in comparison with other substances. Simply put, heavy water performs its task with minimal losses and maximum results. However, its production costs money, while the usual "light" and familiar to us water is much easier to use.
A few facts about nuclear reactors ...
It is interesting that one NPP reactor has been built for at least 3 years!
To build a reactor, equipment is needed that operates on an electric current of 210 kilo Amperes, which is a million times higher than the current that can kill a person.
One shell (structural element) of a nuclear reactor weighs 150 tons. In one reactor there are 6 such elements.
Pressurized water reactor
We have already figured out how the nuclear power plant works as a whole, in order to put everything on the shelves, let's see how the most popular pressurized water nuclear reactor works.
All over the world today, pressurized water reactors of generation 3+ are used. They are considered the most reliable and secure.
All pressurized water reactors in the world for all the years of their operation in total have already managed to gain more than 1000 years of trouble-free operation and have never given serious deviations. 
The structure of a nuclear power plant based on pressurized water reactors implies that distilled water, heated to 320 degrees, circulates between the fuel rods. To prevent it from going into a vaporous state, it is kept under a pressure of 160 atmospheres. The NPP scheme calls it primary circuit water.
The heated water enters the steam generator and gives off its heat to the water of the secondary circuit, after which it "returns" to the reactor again. Outwardly, it looks like the pipes of the primary circuit water are in contact with other pipes - the water of the secondary circuit, they transfer heat to each other, but the water is not in contact. The tubes are in contact.
Thus, the possibility of radiation getting into the water of the secondary circuit, which will further participate in the process of generating electricity, is excluded.
NPP Operational Safety
Having learned the principle of operation of a nuclear power plant, we must understand how safety is arranged. The device of a nuclear power plant today requires increased attention to safety rules.
The cost of nuclear power plant safety is approximately 40% of the total cost of the plant itself. 
4 physical barriers are laid in the NPP scheme, which prevent the release of radioactive substances. What should these barriers do? At the right time, to be able to stop the nuclear reaction, to ensure constant heat removal from the core and the reactor itself, to prevent the release of radionucleids outside the containment (pressurized zone).
- The first barrier is the strength of uranium pellets. It is important that they are not destroyed by high temperatures in a nuclear reactor. To a large extent, how a nuclear power plant works depends on how uranium tablets were "baked" at the initial stage of production. If the uranium fuel pellets are baked incorrectly, the reactions of uranium atoms in the reactor will be unpredictable.
- The second barrier is the tightness of the fuel rods. Zirconium tubes must be tightly sealed, if the tightness is broken, then at best the reactor will be damaged and work is stopped, at worst everything will blow up.
- The third barrier is a strong steel reactor vessel a, (the same big tower - hermetic zone) which "holds" in itself all radioactive processes. The hull will be damaged - radiation will be released into the atmosphere.
- The fourth barrier is the emergency protection rods. Above the core, rods with moderators are suspended on magnets, which can absorb all neutrons in 2 seconds and stop the chain reaction.
 If, despite the design of a nuclear power plant with multiple degrees of protection, it is not possible to cool the reactor core at the right time, and the fuel temperature rises to 2600 degrees, then the last hope of the safety system comes into play - the so-called melt trap.
If, despite the design of a nuclear power plant with multiple degrees of protection, it is not possible to cool the reactor core at the right time, and the fuel temperature rises to 2600 degrees, then the last hope of the safety system comes into play - the so-called melt trap.
The fact is that at such a temperature the bottom of the reactor vessel will melt, and all the remnants of nuclear fuel and molten structures will drain into a special "glass" suspended above the reactor core.
The melt trap is cooled and refractory. It is filled with the so-called "sacrificial material" that gradually stops the chain reaction of fission.
Thus, the NPP scheme implies several degrees of protection, which practically completely exclude any possibility of an accident.

The production of electricity using a nuclear chain reaction in the Soviet Union took place for the first time at the Obninsk nuclear power plant. Compared to today's giants, the first nuclear power plant had only 5 MW of capacity, and the world's largest operating nuclear power plant "Kashiwazaki-Kariva" (Japan) - 8212 MW.
Obninsk NPP: from start-up to museum
At the end of their military programs, Soviet scientists headed by IV Kurchatov immediately set about creating an atomic reactor with the aim of using thermal energy to convert it into electricity. The first nuclear power plant was developed by them in the shortest possible time, and in 1954 an industrial nuclear reactor was launched.
The release of potential, both industrial and professional, after the creation and testing of nuclear weapons allowed I.V. Kurchatov to tackle the problem of obtaining electricity entrusted to him by mastering heat release during a controlled nuclear reaction. Technical solutions for the creation of a nuclear reactor were mastered during the launch of the very first experimental uranium-graphite reactor F-1 in 1946. The first nuclear chain reaction was carried out on it, practically all theoretical developments in recent years were confirmed.
For an industrial reactor, it was necessary to find design solutions related to the continuous operation of the installation, heat removal and supply to the generator, circulation of the coolant and its protection from radioactive contamination.
The team of laboratory No. 2, headed by IV Kurchatov, together with NIIkhimmash under the leadership of NA Dollezhal, worked out all the nuances of the structure. Physicist E.L. Feinberg was entrusted with the theoretical development of the process.
The launch of the reactor (reaching critical parameters) was carried out on May 9, 1954, on June 26 of the same year, the nuclear power plant was connected to the grid, and already in December it was brought to its design capacity.
After the Obninsk NPP had been operating as an industrial power plant for almost 48 years, it was shut down in April 2002. In September of the same year, the unloading of nuclear fuel was completed.
Even while working at the nuclear power plant, many excursions came, the station worked as a training class for future nuclear scientists. Today, a memorial museum of nuclear energy has been organized on its basis.
The first foreign nuclear power plant
Nuclear power plants, following the example of Obninsk, did not immediately, but began to be created abroad. In the United States, the decision to build its own nuclear power plant was made only in September 1954, and it was only in 1958 that the Shippingport nuclear power plant in Pennsylvania was launched. The shippingport nuclear power plant has a capacity of 68 MW. Foreign experts call it the first commercial nuclear power plant. The construction of nuclear power plants is quite expensive; the nuclear power plant cost the US treasury $ 72.5 million.

24 years later, in 1982, the station was shut down, fuel was unloaded by 1985 and the dismantling of this huge structure weighing 956 tons for subsequent disposal began.
Prerequisites for the creation of a peaceful atom
After the discovery of uranium fission by German scientists Otto Hahn and Fritz Strassmann in 1938, studies of chain reactions began.
IV Kurchatov, pushed by AB Ioffe, together with Yu. B. Khariton drew up a note to the Presidium of the Academy of Sciences on nuclear problems and the importance of work in this direction. IV Kurchatov worked at that time at the Leningrad Physico-Technical Institute, headed by AB Ioffe, on problems of nuclear physics.

In November 1938, based on the results of the study of the problem and after IV Kurchatov's speech at the Plenum of the Academy of Sciences (Academy of Sciences), a note was drawn up to the Presidium of the Academy of Sciences on the organization of work in the USSR on the physics of the atomic nucleus. It traces the rationale for the generalization of all scattered laboratories and institutes in the USSR, belonging to different ministries and departments, dealing, in fact, with the same problem.
Suspension of work on nuclear physics
Some of these organizational work was done even before the Second World War, but the main progress began to occur only in 1943, when IV Kurchatov was offered to head the atomic project.
After September 1, 1939, a kind of vacuum began to form around the USSR. Scientists did not immediately feel this, although the agents of Soviet intelligence immediately began to warn about the classification of the speeding up of work on the study of nuclear reactions in Germany and Great Britain.
The Great Patriotic War immediately made adjustments to the work of all scientists in the country, including nuclear physicists. In July 1941, LPTI was evacuated to Kazan. IV Kurchatov began to deal with the problem of demining sea vessels (protection against sea mines). For work on this topic in wartime conditions (three months on ships in Sevastopol until November 1941, when the city was almost completely under siege), for organizing a demagnetization service in Poti (Georgia), he was awarded the Stalin Prize.
After a severe cold, upon arrival in Kazan, only by the end of 1942, IV Kurchatov was able to return to the topic of a nuclear reaction.
Atomic project led by I. V. Kurchatov
In September 1942, IV Kurchatov was only 39 years old; by age standards of science, he was a young scientist next to Ioffe and Kapitsa. It was at this time that Igor Vasilyevich was appointed to the post of project manager. All nuclear power plants in Russia and plutonium reactors of this period were created within the framework of the atomic project, which was headed by Kurchatov until 1960.

From the point of view of today, it is impossible to imagine that exactly when 60% of the industry was destroyed in the occupied territories, when the main population of the country worked for the front, the leadership of the USSR made a decision that predetermined the development of nuclear energy in the future.
After evaluating the intelligence reports on the state of affairs with work on the physics of the atomic nucleus in Germany, Great Britain, and the United States, Kurchatov became clear about the scope of the lag. He began to gather scientists around the country and active fronts who could be involved in the creation of a nuclear potential.
Lack of uranium, graphite, heavy water, and the absence of a cyclotron did not stop the scientist. Work, both theoretical and practical, resumed in Moscow. The high level of secrecy was determined by the GKO (State Defense Committee). For the production of weapons-grade plutonium, a reactor was built (a "boiler" in the terminology of Kurchatov himself). Work was underway to enrich uranium.
Lagging behind the United States from 1942 to 1949
On September 2, 1942, a controlled nuclear reaction was carried out in the United States, at the world's first nuclear reactor. In the USSR by this time, apart from the theoretical developments of scientists and intelligence data, there was practically nothing.
It became clear that the country would not be able to catch up with the United States in a short time. To train (save) personnel, create prerequisites for the rapid development of uranium enrichment processes, the creation of a nuclear reactor for the production of weapons-grade plutonium, and the restoration of the operation of plants for the production of pure graphite - these are the tasks that had to be done during the war and post-war times.
The course of a nuclear reaction is associated with the release of a colossal amount of thermal energy. US scientists - the first creators of the atomic bomb used this as an additional damaging effect in an explosion.

Nuclear power plants of the world
Today, nuclear power, although it generates a colossal amount of electricity, is widespread in a limited number of countries. This is due to the huge capital investments in the construction of a nuclear power plant, from geological exploration, construction, creation of protection and ending with the training of employees. Payback can occur in tens of years, provided that the station is constantly in operation.
The feasibility of building a nuclear power plant is determined, as a rule, by the governments of the countries (of course, after considering various options). In the context of the development of industrial potential, in the absence of own internal reserves of energy resources in large quantities or their high cost, preference is given to the construction of a nuclear power plant.

By the end of 2014, nuclear reactors were operating in 31 countries around the world. The construction of nuclear power plants has begun in Belarus and the United Arab Emirates.
P / p No. | Country | Number of operating nuclear power plants | Number of reactors in operation | Generated power |
Argentina | ||||
Brazil | ||||
Bulgaria | ||||
Great Britain | ||||
Germany | ||||
Netherlands | ||||
Pakistan | ||||
Slovakia | ||||
Slovenia | ||||
Finland | ||||
Switzerland | ||||
South Korea | ||||
Nuclear power plants of Russia
Today there are ten nuclear power plants operating in the Russian Federation.
NPP name | Number of working units | Reactor type | Installed capacity, MW |
Balakovskaya | |||
Beloyarskaya | BN-600, BN-800 | ||
Bilibinskaya | |||
Kalininskaya | |||
Kola | |||
Leningradskaya | |||
Novovoronezh | VVER-440, VVER-1000 | ||
Rostov | VVER-1000/320 | ||
Smolensk |
Today, Russian nuclear power plants are part of the State Atomic Energy Corporation Rosatom, which unites all structural divisions of the industry, from uranium mining and enrichment and nuclear fuel production to the operation and construction of nuclear power plants. In terms of power generated by nuclear power plants, Russia is in second place in Europe after France.
Nuclear energy in Ukraine
Nuclear power plants in Ukraine were built during the Soviet Union. The total installed capacity of Ukrainian NPPs is comparable to Russian ones.
NPP name | Number of working units | Reactor type | Installed capacity, MW |
Zaporizhzhya | |||
Rivne | VVER-440, VVER-1000 | ||
Khmelnitskaya | |||
South Ukrainian |
Before the collapse of the USSR, the nuclear power industry of Ukraine was integrated into a single industry. In the post-Soviet period, before the events of 2014, industrial enterprises were operating in Ukraine, producing components for Russian nuclear power plants. Due to the severance of industrial relations between the Russian Federation and Ukraine, the start-ups of power units under construction in Russia scheduled for 2014 and 2015 have been delayed.
Nuclear power plants in Ukraine operate on fuel rods (fuel elements with nuclear fuel, where the nuclear fission reaction takes place), manufactured in the Russian Federation. Ukraine's desire to switch to American fuel nearly led to an accident at the South Ukrainian nuclear power plant in 2012.
By 2015, the state concern "Nuclear Fuel", which includes the Eastern Mining and Processing Plant (mining of uranium ore), has not yet been able to organize a solution to the issue of producing its own fuel rods.
Nuclear energy prospects
After 1986, when the Chernobyl accident occurred, nuclear power plants were shut down in many countries. Improving the level of safety has brought the nuclear power industry out of a state of stagnation. Until 2011, when the accident at the Japanese nuclear power plant "Fukushima-1" occurred as a result of the tsunami, nuclear power was developing steadily.

Today, constant (both minor and major) accidents at nuclear power plants will slow down the decision-making on the construction or reactivation of facilities. The attitude of the world's population to the problem of generating electricity by a nuclear reaction can be defined as wary and pessimistic.
It's always nice to be the first in something. So our country, while still a part of the USSR, was the first in many endeavors. A striking example is the construction of a nuclear power plant. It is clear that many were involved in its design and construction. Still, the world's first nuclear power plant was located on the territory that is now in Russia.
Prehistory of the NPP
It began with the use of the atom for military purposes. Before the world's first nuclear power plant was built, many doubted that nuclear energy could be used peacefully.
First, the atomic bomb was created. Everyone knows the sad experience of using it in Japan. Then the test of the atomic bomb created by Soviet scientists was carried out at the test site.
After some time, the USSR began to produce plutonium in an industrial reactor. All conditions have been created for the production of enriched uranium on a large scale.
It was at this time, in the fall of 1949, that an active discussion began on how to organize an enterprise where nuclear energy would be used to generate electricity and heat.

The theoretical development and creation of the project was entrusted to Laboratory "B". At that time it was headed by D.I. Blokhintsev. A supervised scientific council proposed a nuclear reactor that ran on enriched uranium. Beryllium was used as a moderator. Cooling was carried out using helium. Other reactor options were also considered. For example, using fast and intermediate neutrons. Other cooling methods were also allowed.
In the spring of 1950, a resolution of the Council of Ministers was issued. It stated that it was necessary to build three experimental reactors:
- the first is uranium-graphite with water cooling;
- the second is helium-graphite, which was supposed to use gas cooling;
- the third is uranium-beryllium also with a gas cooler.
The remainder of the current year was allocated for the creation of the technical project. Using these three reactors, the power of the world's first nuclear power plant was about 5000 kW.
Where and by whom were they created?
Of course, in order to erect these buildings, it was necessary to determine the location. Thus, the first nuclear power plant in the world was built in the city of Obninsk.
The construction work was entrusted to the Khimmash Research Institute. At that moment it was led by N. Dollezhal. By education, he is a construction chemist who was far from nuclear physics. But still, his knowledge was useful during the construction of structures.
By joint efforts, and a little later several more institutes were involved in the work, the world's first nuclear power plant was built. She has more than one creator. There are many of them, because such a large-scale project cannot be created alone. But the main developer is called Kurchatov, and the builder is Dollezhal.
Construction progress and launch preparation
In parallel with the creation of the world's first nuclear power plant, stands were developed in the laboratory. They were prototypes that were later used on nuclear submarines.

In the summer of 1950, preparatory work began. They lasted for one year. The result of all the work was the very first nuclear power plant in the world. Her original design has remained largely unchanged.
The following adjustments were made:
- the uranium-beryllium reactor was built with a lead-bismuth cooler;
- The helium-graphite reactor was replaced by a pressurized water reactor, which formed the basis of all subsequent nuclear power plants, and was also used on icebreakers and submarines.
In June 1951, a decree was issued to build an experimental power plant. At the same time, all the necessary materials were delivered for the uranium-graphite reactor. And in July, the construction of a water-cooled nuclear power plant began.
The first launch, providing electricity to settlements
The loading of the reactor core began in May 1954. Namely, the 9th. In the evening of the same day, a chain reaction began in it. uranium happened in such a way that it was supported independently. This was the so-called physical start-up of the station.
A month and a half later, in June 1954, the power plant was launched. This consisted in the supply of steam to the turbine generator. The world's first nuclear power plant started working on June 26 at half past five in the evening. It has functioned for 48 years. Its role was to give impetus to the emergence of similar power plants around the world.
The next day, an electric current was given to the city of the world's first nuclear power plant (1954) - to Obninsk near Moscow.
The impetus for the emergence of other nuclear power plants around the world
It had a relatively small power, only 5 MW. One load of the reactor was enough to operate it at full power for 3 months.

And despite this, it attracted the attention of people from all over the world. Numerous delegations came to the city of the world's first nuclear power plant. Their goal was to see firsthand the miracle created by the Soviet people. You don't need to use a turbine generator to get electricity without coal, oil or gas. And the nuclear power plant provided electricity to the city with a population of about 40 thousand people. At the same time, only His amount was spent, equal to 2 tons per year.
This circumstance was the impetus for the construction of similar stations almost all over the world. Their power was enormous. And yet the beginning was here - in small Obninsk, where the atom became a hard worker, throwing off his military uniform.
When did the nuclear power plant finish work?
The first nuclear power plant in Russia was shut down in 2002 on April 29. There were economic prerequisites for this. Its capacity was not large enough.
During her work, data were obtained that confirmed all theoretical calculations. All technical and engineering solutions were justified.

This made it possible in 10 years (1964) to launch the Beloyarsk NPP. Moreover, its capacity was 50 times greater than that of Obninskaya.
Where else are nuclear reactors used?
In parallel with the creation of the nuclear power plant, a group led by Kurchatov designed a nuclear reactor that could be installed on an icebreaker. This task was as important as providing electricity, without consuming gas and coal.
For the USSR, as well as for Russia, it was important to extend navigation in the seas that lie in the north for as long as possible. Nuclear icebreakers could provide year-round navigation in these territories.
Such developments were started in the 53rd year, and six years later the nuclear icebreaker "Lenin" was sent on its maiden voyage. He regularly served in the Arctic for 30 years.

The creation of a nuclear submarine was no less important. And she was launched in the 57th year. At the same time, this submarine carried out a cruise under the ice to the North Pole and returned to base. The name of this submarine was "Lenin Komsomol".
Impact of nuclear power plants on the environment
This question was of interest to people already when the first nuclear power plant in the world was built in the city of Obninsk. It is now known that the impact on the environment is carried out in three directions:
Thermal emissions;
Gas, which is also radioactive;
Liquid around the nuclear power plant.
Moreover, the release of radiation occurs even during normal operation of the reactors. Such constant influx of radioactive substances into the environment occurs under the control of the NPP personnel. They then spread in the air and ground, penetrating plants and organisms of animals and people.
It should be noted that not only the nuclear power plant is a source of radiation waste. Medicine, science, industry and agriculture also contribute to the total. All waste is supposed to be neutralized in a special way. And then they are to be buried.
 What you need to open a hookah lounge, and how to do it correctly
What you need to open a hookah lounge, and how to do it correctly How to start a business and choose donut equipment
How to start a business and choose donut equipment Opening a company in Montenegro Open a company in Montenegro
Opening a company in Montenegro Open a company in Montenegro The carpentry shop as a business
The carpentry shop as a business How to choose a business direction?
How to choose a business direction? Sample business plan of a dental office
Sample business plan of a dental office Five best business ideas that brought millions What business to open so as not to go bankrupt
Five best business ideas that brought millions What business to open so as not to go bankrupt