Recommendations for drafting an application for a project note - document. Application for project development Example of a project application for a project
1. Customer or target audience
Who is this?
The customer and target audience means a specific person or group of people who are directly interested in your work. It is assumed that the project solves a specific problem of the customer or audience. For projects of one type, a customer is usually needed (for example, in the case of publishing or design projects), for projects of another type, a target audience (for example, for many events or educational projects).
Why is this needed?
That the project was not in vain! This confirms the urgency of the problem the project is aimed at solving.
How can I find people interested in my project?
Situation 1: The customer can contact the designer himself to solve a particular problem.
Situation 2: The designer himself is looking for a potential target audience / customer, i.e. people who might be interested in his project work.
How to prove that your project was created for someone?
If the project is created for target audience, focus group participants confirm the relevance of the problem that this project will solve and / or leave feedback after the project is implemented. If the project is created for the customer, it confirms the relevance.
2. Problem field (what problem does the project solve?)
Formulate a specific project problem and describe it:
What is the problem? Whom does it affect? What possible reasons? What could be the consequences? ...
You can prove or demonstrate the existence of a problem by referring to the target audience or customer, as well as to relevant and reliable data. So you justify the relevance of the project. Indicate in the application how you are going to do this.
Important for the future project: the product must solve the stated problem.Is the problem really solvable by the product? How to check it?
If you fill the chatbot with content so that people read it, then the chatbot should run. If you create a bill for the purpose of some changes, then the bill must be adopted, and the changes in real life should be noticeable and measurable. If you are working on a business plan, that business plan must be implemented in the business.
Otherwise, the problem is not solved.
3. Product image
Identify the most important product features that will solve the problem. Justify your decision. Consider the following criteria, or come up with your own:
- Functionality(What is the purpose of the product? What should the product contribute to, what should it do? How can it be used/supported?)
- Aesthetic aspect(For a material product, style, look, color, shape, size, texture, pattern, etc., for an event, any aesthetic characteristics, if applicable)
- Environmental aspect(Where and how will the product be used and how it may / may not affect the environment?)
- Security (How should security be considered?)
- Ergonomics (What anatomical / physiological features should be taken into account?)
- Cost (Cost limit, what does the cost consist of?)
4. Resources
List the resources needed to complete the project. Resources are all tangible and intangible objects that you will use to create a product.
For instance:
Human resources (time and other costs of people involved in the creation of your product);
Material resources (specific items needed to create a product),
Financial resources;
Your personal time;
Internet resources
At this point, it will be convenient to first classify the resources you will be using, and then list the required resources within each class.
5. What will I need to learn during the course of the project?
Briefly describe the knowledge and skills that will need to be acquired in the process of working on the project, necessary to solve the project problem.
6. Step by step planning
Make a list of tasks. Tasks are the “steps” that will move you step by step towards building the product.
Correlate tasks with time and resources (this is planning).
When filling out the application, use the first option for planning, i.e. just a list of tasks with deadlines and resources.
You can use other planning options (table, flowchart, Gantt chart) for your convenience when creating project reporting materials. Some examples:
Option 1: description of the steps
1. Task #1, timeline, resources
2. Task #2, timeline, resources
3. Task #3, timeline, resources
Option 2: table
| Task | Timing | Resources |
| 1. | ||
| 2. | ||
| 3. |
Option 3: Diagram/Block Diagram
Where can you get funds to start a business if you only have an idea? Get financial assistance from the state or special funds. To do this, apply for a grant. Consider how to increase the chances of its approval, what documents to prepare and the nuances that reduce the decision-making time.
Opportunity receive free funds attracts start-up businessmen to implement the business. but not all types of start-ups are eligible for grants To do this, they must meet certain criteria:
- Novelty. It's not about starting another business, but about the innovative nature of the idea.
However, there are also differences:
- Grant applications do not always pay attention to the commercial side. As a rule, the goal of the project is to achieve intangible benefits, and there may be no financial return at all.
- Grants are "sponsored" help provided free of charge, and when submitting an application, it is not necessary to justify the possibility of returning borrowed funds.
- Of great importance are the "intangible" sections - purpose of the project, its significance. Compliance of this information with the essence of the grant program is the key to obtaining a subsidy.
Professionals should have correct (and positive) representation about the project, its realism and usefulness. Correct section design is important.
Sample of filling in the main points
Regardless of the foundation that offers sponsorship and documentation forms, any application contains a number of key sections. We provide brief guidelines for completing them.
- Implementation Work Plan- specifics. You describe all the steps and operations that will be performed on the way to the goals. Take it seriously, because mistakes or illogical calculations and conclusions will create a negative impression about you.
- Concrete Results- fixed indicators (qualitative or quantitative), upon reaching which you will declare the success of the project.
- Outcome Mechanism is also important. Show how the donor will monitor the success of the idea in which the funds are invested.
- Further funding and perspectives. Many non-commercial grant projects are "closed" upon reaching their goals and spending the budget.
- Financial plan How will you spend your grant money? This section should be as reasonable as possible, transparent and take into account all the nuances of taxation of the enterprise, legal and accounting subtleties.
How to apply and what other documents may be required
An organization applying for a grant is obliged to submit a package of documents to the foundation. Depending on the idea, the kit may vary, but the basic papers remain the same.
- Constituent documents Individual entrepreneur or LLC - registration certificates, charter, appointment orders, statistics codes and the like.
- Copies financial reporting for the last period (balance, ).
- Auditor's reports.
- Data of the main officials of the organization with brief information.
A big plus in the biography of the director or founder will be confirmed information about his achievements in the chosen field.
- Recommendations, letters of support. If the project is being implemented in social sphere, obtain the approval of the relevant funds and authorities. Attach their competent opinions with the contacts of the principals to the application.
- Documents for the right to use property, transport that will be involved - certificates of ownership, lease agreements.
It is not difficult to submit an application: it is enough to correctly draw up an idea and collect the necessary documents.
Applicants face difficulties in making an application. We have collected practical advice which will make things easier:
- Before starting the laborious work of writing a document, make sure that the goals of the selected fund match yours.
- At the stage of development and completion consult with the grantor. Most funds and public services have centers for working with applicants, where they provide serious information support and training free of charge.
So, even within the same system it is very different, and if you don’t know the nuances, you can make financial plan incorrect data.
- The total cost of implementation cannot be less than the amount of funds requested. For commercial organizations optimal if project budget for exceeds the amount of the subsidy - this is how you show that you are ready to invest your money. For non-commercial projects, implementation can be carried out within the scope of the grant.
- The main thing when receiving a subsidy - inspire confidence of the fund's specialists in the idea. The application must be logical, concise and perfectly structured, and the justifications must be convincing and without double interpretations.
- Experience in the chosen field- the first thing the grantor looks at. Having superficial knowledge about the object of application of forces, gleaned from the literature, do not count on a subsidy.
Conclusion
The first thing that specialists of state bodies and funds see when considering a project is an application. Whatever gift of persuasion an entrepreneur has, the impression is formed when studying it. If the document does not reflect real goals, does not disclose the implementation process, it may not reach the “face-to-face” defense.
Dear readers! If you have any questions or clarifications on the topic of the article, please leave a comment! We will try to cover the most relevant topics for you in the future. Looking forward to your ratings and opinions!
| Main stages of development | Timing | Cost of work (thousand rubles) | Result | Co-performers | The share of the work will comply. |
| Technical task | 20.09.12 | Report | |||
| Technical Proposal | 27.09.12 | Report | |||
| Analytical review | 11.10.12 | Report | |||
| Feasibility study | 11.10.12 | Report | |||
| Preliminary design | 08.11.12 | Report | |||
| Technical project | 22.11.12 | Documentation Drawings | |||
| General plan | 29.11.12 | Blueprints | |||
| Design documentation | 06.12.12 | Blueprints | |||
| Project handover | 20.12.12 | Presentation |
7. PROCEDURE FOR INTRODUCING CHANGES AND ADDITIONS
Changes and additions agreed with the Customer may be made to this specification.
This section completes the project development process by introducing the sequence of steps in developing a project description. The first type of work focuses on defining the goals and objectives of the project. The next one defines the logical links between the project objectives and the outputs of the activities. Next, the importance of setting information gathering metrics for the project is explored, and the work focuses on defining metrics for the purpose, objectives, and results of the project so that project progress can be assessed. The section concludes with a work plan and budget for the project based on a detailed list of activities and brief description strategic integrated plan (log frame).
INTRODUCTION
This section discusses the last step in the project development process, turning problem analysis and activity selection into a project description.
In the previous section, we made a description of the problem field, which guided us in the process of identifying a set of possible measures to eliminate / mitigate the causes of problems. These activities were then discussed in light of their impact, scope, feasibility and viability. As a result of these discussions, some activities may have been excluded from the project development process, while others may have been revised and improved. We are now ready to move on to drafting the project proposal.
Elements of a project proposal
Much is used for project proposals. various forms. People and organizations also use different words and phrases when talking about the same project elements. These differences in form and terminology can be confusing. But in almost all project descriptions there are common elements. They are listed below and are related to the terms that will be used in this section.
| Project description: basic elements | Terms used in this guide |
| Description of the long-term changes that the project will contribute to | Target |
| Description of changes in the problems that will contribute to the achievement of the project goal | Tasks |
| Description of the activities in the project and their expected results that will help in achieving the objectives of the project | Activities (activities, methods, steps in other sources) and their results |
| Description of the project development evaluation system and plan | Indicators Basic information Monitoring and evaluation plan |
| Description of project activities with distribution of responsibilities and deadlines | Project work plan |
| Description of project costs | Project's budget |
Structure of this section
Consistently, the process of project development to this point has moved from the analysis of problems to the selection of activities. This section follows the following sequence:
| Description of the changes the project aims to achieve | by specifying the purpose and objectives of the project |
| Description of specific activities to be carried out within the framework of the project | by specifying the activities in the project |
| Associating expected changes with project activities | by indicating the results of activities |
| Determining how to monitor and evaluate performance | using indicators for the goals, objectives and results of the project, as well as a discussion of the baseline information against which the implementation of the project is checked, and a description of the plan for monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of the project |
| Enumeration of stages of implementation of project activities with assigned responsibilities and deadlines | in the form of a project plan |
| Estimating Project Costs | as project budget |
PROJECT APPLICATION STRUCTURE
A project is a kind of bridge between an idea and its final implementation.
It is very important to see the difference between a project and a funding proposal.
First of all, the project is needed by the executor himself in order to accurately formulate the social problem that requires an immediate solution, to realize the difficulties facing him and to plan subsequent activities.
The application is created in order to convince donors that the problems you have noted really do exist and that you are the one who is able to solve them.
The proposal has a very clear vertical structure, the components of which are the title page, summary, introduction, and problem statement.
On the title page contains all the information necessary for the attention of the donor. As a rule, this is:
1. Name of the project.
2. Name of the applicant organization.
3. Legal status of the applicant organization.
4.Contact information including:
Legal address of the organization;
The physical address of the organization;
Phone, fax numbers; e-mail.
5. Surname, name, patronymic and Contact Information(tel./fax, e-mail):
Project Director;
project accountant;
The director of the applicant organization (if he is not in charge of the proposed project).
6. Territory where the project is being implemented.
7.Term of the project (duration, beginning and end).
8. Requested resources, the total cost of the project, the resources available in the organization for this project. The sequence of presentation of this information is most often suggested by the donor himself.
A summary (abstract) is often referred to as " summary» project (no more than 1 page). This is a very important part. The experts will read the resume first, and it should be clear who you are, what the scope and cost of your project are. The summary repeats all parts of the full application (1-2 sentences for each part) and answers the questions: who will carry out the project; why and for what this project is needed; purpose and objectives of the project; planned activities in the project; project result; how the project will be implemented; duration of the project; the means necessary to carry it out.
Introduction(1-2 pages). This section is a presentation. It should contain information about the organization applying for the grant:
Story;
Implemented projects and achievements;
Availability of competent staff and cooperation with volunteers;
Availability of partners;
The level of communication with state and municipal authorities;
Compliance of previous experience with the problem being solved in this project;
And all the information that can give the donor confidence in your organization.
Formulation of the problem- this is an extremely important point of both the project and the project application, since the subsequent planning, and often the implementation, depends on its precise definition and formulation.
Psychologically, the problem is perceived as something annoying, disturbing, requiring urgent resolution. This is something that should have been, but for some reason is missing from society. Therefore, we objectively speak of it as something with a minus sign.
For example, we note that the number of street children has increased in our region. Is the situation we found a problem? It is rather a statement of the obvious fact. The problem lies deeper and is related to the fact that something important is missing in society, and as a result of this, the situation that lies on the surface worsens.
As a rule, the exact identification of a problem is preceded by a period of research and accumulation of information, which then, after appropriate processing, will form the basis of its formulation. In the attachment, you can provide documents confirming the results of the assessment. You must be sure yourself (to then convince donors) that the problem you have formulated can be completely or partially solved in a realistic time frame, with the resources available to you and the declared budget. As an exception to the rule, the problem may reflect the internal needs of the applicant organization if the requested funds are aimed at improving efficiency. own work. Lack of de-
neg can not be declared as a problem. What problem will the money be used to solve?
Usually, when posing a problem (in the absence of special donor requirements), the creators of the application and the project are required to clearly and convincingly explain what the need for the project is, describe the target group, the region of action, and, if possible, provide supporting statistics. Show how the existing problem relates to the objectives of the applicant organization. In general, this section of the application must meet the following criteria:
The problem is related to the goals and objectives of the applicant organization;
The objective situation is considered;
The problem is relevant, important and significant;
The existence of the problem is confirmed by statistics and research results;
The problem is formulated from the point of view of the target group and its needs, not the applicant;
Representatives of the target group are involved in solving the problem;
The problem is specific enough;
The problem is not replaced by methods for solving it.
Effective manager education(Project name)
Section 1. Project participants.
Information about Russian organization. Name and address of institutions participating in the project from the Russian side, telephone, fax, e-mail.
Project Manager. Surname, name, patronymic, position, scientific degree, academic title, a brief description of professional experience.
Project coordinator. Surname, name, patronymic, position, scientific degree, academic title, brief description of professional experience.
List of specialists-participants of the project. Surname, name, patronymic, position, scientific degree, academic title, brief description of professional experience.
Information about foreign partners.
Section 2 , Project proposal.
General information.
The project involves the development of a new approach to the theory and practice of education management, related to the training of an effective leader (manager) in a changing social and educational situation and an increase in the role of education in the modernization of Russia.
The relevance of the project is determined by:
strategic changes in the priorities of the development of education in Russia, formulated at the level of government documents on the modernization of education: the introduction of a new organizational and economic mechanism for the development of education, the requirement for the effectiveness of management in education, the formation of new economic and legal models for the activities of educational institutions;
· the need to overcome the contradiction that has developed between the development of a flexible variable multi-level system of educational institutions in large cities of Russia and the preservation of stereotypes in the organization and management of education;
· disorder in the training and certification of leading personnel of various types of institutions for the system of state and non-state education;
discrepancy between the style of activity and the level of communicative and business culture of a number of education leaders with the requirements of European practice and modern technologies management in education.
At the same time, the existing experience in the work of innovative educational organizations and institutions (names) and their leaders, accumulated and summarized in the framework of certification and competitions during (period), forms the prerequisites for designing new approaches to the training of effective organizers of education, adapted to work in a changing social and educational situation.
Appeal to the experience of foreign colleagues due to the presence in (name of partner country) extensive organization practice educational activities in the conditions of various types of schools, experience both in a situation of decentralization and in the development of tendencies of centralization of management educational institutions.
For modern Russian system education management is interested in mechanisms to ensure stability and the traditionally high level of education of school graduates (name of partner country) in the context of reforms, in particular:
distribution of subsidies, models of financing educational institutions;
organization of a system of test control over the quality of education by management employees;
public participation in the management of educational institutions;
· typical professional problems and typical tasks that heads of educational institutions of different levels have to solve during the reform period.
The proposed project takes into account the experience of working with educational leaders gained in (period) within the framework of cooperation between Russia and (partner country) by projects (names) and programs (title).
The novelty of the project "Effective Manager of Education" is due to:
· orientation of its content to a fundamentally new state strategy for the development of the educational system of Russia;
· the use of hypermedia technologies and the possibilities of virtual computer space for the professional and personal development of the head of education;
transferring the criteria for assessing the effectiveness of the activities of the head (manager) of education in the European context;
working on the basis of innovative educational programs formed as a result of the integration of pedagogical achievements in the field of education management (names of cities, institutions);
Possible circle of partners in (the name of the country):
Ministry of Education and Employment;
· Association for Educational Research;
· Institute of Pedagogical Technologies;
· National Institute adult education;
Schools of various types in major cities (names).
Are common strategic goals.
Promoting the renewal of the corps of education administrators and managers (name of city, region) in accordance with the priorities of reforming education in Russia in the 21st century. in the context international experience.
Expansion of career opportunities for young teachers who are able to become effective leaders in the education system of large cities of modern Russia.
Objective of the project.
Determination of optimal management conditions for the implementation of competitive management in the educational situation of the metropolis.
Creation of a multi-level model of training and advanced training of an "effective manager of education" based on the integration of the experience of Russia and (indicate partner country).
target groups.
Educational institutions of the system of preschool, school and primary vocational education. Bodies of municipal and regional management of education. System higher education, suggesting socio-pedagogical and socio-economic specialization. The system of advanced training and retraining of specialists for the field of education. Scientific and methodological services of the district and city.
Implementation strategy. Leading ideas of the project:
· efficiency of management in education;
management of the quality of training an effective leader at all stages of continuous professional and pedagogical education;
integration of domestic and foreign experience training of the head of educational institutions and the organizer of education.
1. study of the problem of the effectiveness of the activities of the head of education at various levels of management. Development of a structural and functional model of effective management in a changing social and educational situation;
2. creation and testing of multilevel educational programs for the system of advanced training and retraining of personnel, focused on the formation of an effective education manager for various types of educational institutions based on modern experience Russia and the partner country;
3. organization of multi-level training of leading personnel in the system of advanced training and retraining in the following areas:
economic and legal framework activities of the head of education in the conditions state strategy modernization of education;
· innovative management in education and pedagogical science (in domestic and European practice);
communication and business culture modern leader educational institution;
· individual and group internships with effective organizers of education in Russia and the partner country;
4. design innovative technologies computer support for the professional growth of the head of education at all levels;
5. development and approbation of the implementation model professional competition management personnel of educational institutions;
6. improvement of the certification system for heads of educational institutions in (city, region).
Section 3 . Project implementation.
Project duration: (period).
Main stages
| Stages | Main directions and content of activities | Timing | |
| pre-project | Drawing up a project application, forming groups of participants, studying documents, conducting diagnostics | August 200* - March 200* | |
| Project implementation | I | Working visit to (partner country) project leaders. Development of a theoretical model of effective management in education based on the integrative experience of Russia and the partner country. Organizational work to create training center for leaders (managers) of education | April 200* - December 200* |
| II | Development of the content of educational programs of the educational and methodological complex "Effective Manager of Education". Organization of multilevel training in the system of advanced training and retraining of personnel using hypermedia technologies | January 200* - December 200* | |
| III | Development and approbation of the competition model for education leaders. Creation of scientific and methodological recommendations on the strategy of selection, training, certification, career advancement of the head (manager) of education | January 200* - April 200* | |
| Post-project | Dissemination of scientific and methodological results obtained during the implementation of the project in the practice of other large cities of Russia | Additional plan |
Calendar planning for the pre-project period (specify the period).
· August - drafting of the project proposal, submission to (name of the organization financing the project).
September - the formation of the Russian working group.
· October - participation in a working meeting organized by the founders of the project, defense of the project application.
· November - search for foreign partners (at the level of institutions and individuals).
· December - drawing up a program of joint activities in the field of expertise and project consulting.
· January-March - formation of a group of Russian experts and consultants.
Roles and responsibilities of project participants.
Russian side
Project leader: scientific support for the content of design and educational activities.
Project coordinator: selection and organization of interaction between project participants at all levels of the city's education management.
Methodist of computer support: creation of a software product, organization of training based on multimedia.
Technical Secretary: documentation of materials received during the project.
Contact person from the founders of the project: organization of interaction with the partner country and the founders of the project on all necessary issues.
Roles of foreign partners will be specified at the design stage.
Alleged functional responsibilities:
· counseling,
· examination,
· selection of a representative group of educational leaders of the partner country for professional interaction.
Section 4 Results (step by step).
Pre-project stage:
project application;
· formed groups: training participants, consultants, experts (Russian and foreign);
report on the interim results of search and organizational work.
· an analytical review of the experience and style of activity of successful (effective) heads of education in the partner country and (name of the city, region of Russia);
· a theoretical model of the activity of an effective manager of education in a large city.
An innovative model of training leaders (managers) of education, corresponding to the priorities public policy modernization of Russia;
· Educational-methodical complex of multi-level training "Effective education manager" (educational and training programs, diagnostic and test packages, computer product, etc.).
control algorithm career growth promising young organizers (managers) of education;
Regulations and regulations for the city competition of education leaders "Effective Education Manager";
Post-project stage:
· training and consulting center for education managers training;
· a database of the reserve of educational leaders (managers) who have undergone innovative training.
1st stage:
information messages in the media of the city and region;
information in (name of the magazine, newspaper) about the project;
creation of an information site of the project on the Internet.
· presentation of the educational program "Effective manager of education" for the pedagogical community;
organization of press conferences for media representatives.
· information about the city competition of leaders of education in the media.
· press conferences for the pedagogical community and journalists with the winners of the "Effective Manager of Education" contest.
Section 6 Evaluation procedures and performance indicators for project results.
The purpose of assessment is to determine:
· the adequacy of the proposed approach to the training and selection of the head (manager) of education in the modern socio-educational situation of a large city and European management practice;
degree of novelty and efficiency of the proposed models and algorithm;
· the possibility of extended use of the results obtained in the practice of modernizing the management of education in Russia (in the conditions of large cities).
A stepwise assessment is expected.
1st stage. External expert review theoretical model of the activity of an effective manager, created on the basis of the analysis of Russian and foreign experience. Internal expertise based on self-assessment of leaders from the experimental group of their activities in accordance with the structure of the theoretical model.
2nd stage. External examination of the quality of educational programs (criteria: innovation and manufacturability). Internal expertise: questioning of training participants (criteria: novelty, practical significance, comfort of training, prospects for use in personal practice, possibility of use in variable conditions).
-th stage. External expertise: a survey of the participants of the competition committee about the professional level of the contestants, heads of education (criteria corresponding to the structure efficient operation manager); expert evaluation of the overall results of the project by foreign experts (content analysis of reports and interview results). Internal expertise (self-reports of participants in project activities).
For each stage, the results of the assessment are brought to the attention of all stakeholders, the main one for this stage. Evaluation information is stored and accumulated in electronic form.
Section 7 The logical frame of the project.
| Structure | Indicators | Measurements (indicators) | Assumptions and risks |
| General strategic goals | Renovation of the corps of city education administrators in accordance with the priorities of education reform in Russia and in the context of international experience. Expansion of career opportunities for young teachers who are able to become effective leaders in the education system of large cities of modern Russia | Indicators obtained in the course of scheduled certification of management personnel. The emergence of new scientific, methodological and educational structures and programs of the relevant profile | Support from the ministry (name), education committee, district administration. Psychological barriers and stereotypes management activities |
| Project Goals | The success of approbation of managerial conditions for the implementation of competitive management in the educational situation of the city. Functioning of a multi-level model of training and advanced training of an "effective manager" of education, created on the basis of the integration of the experience of Russia and the partner country | Formation of a contingent of young promising leaders of a new type of education who have undergone experimental training within the framework of the project | Administrative and organizational support from the city and district education authorities. Problems of changing the generation of heads of educational structures |
| 1. Structural and functional model of effective management in the changing social and educational situation of the city. 2. The presence of multilevel educational programs for the system of advanced training and retraining of personnel, focused on the formation of an effective education manager for various types of educational institutions. 3. Organization of multi-level training of leading personnel in the PC system and retraining in the following areas: - economic and legal foundations for the activities of the head of education in the context of the new state strategy for the modernization of education; - innovative management in education and pedagogical science; - communicative and business culture of the modern head of an educational institution; - individual and group internships with effective organizers of education in Russia and the partner country. 4. Innovative technologies of computer support for the professional growth of the head of education at all levels. 5. Model of holding a professional competition for the management personnel of educational institutions | Compliance with the strategic documents of the Government of the Russian Federation, the real social and educational situation, European experience | Support from foreign and Russian partners. Lack of budget funding for optimal implementation of the model | |
| I stage | Working visit to (partner country) project leaders. Theoretical model of effective management in education based on the integrative experience of Russia and the partner country. Completion of organizational work on the creation of a training center for leaders (managers) of education | Report quality. Results of external and internal expertise | All types of risks associated with innovative activities |
| II stage | Availability of educational programs of the educational and methodological complex "Effective Manager of Education". Organization of multilevel training in the system of advanced training and retraining of personnel using hypermedia technologies | - » - | - » - |
| Stage III | Model of the competition of leaders of education of the city. Scientific and methodological recommendations on the strategy of selection, preparation of certification, career advancement of the head (manager) of education | - » - | - » - |
Section 8 Budget.
| No. p / p | Direction and content of activity | Amount of expenses |
| Work of foreign experts in Russia: (1 person for 5 days) - air tickets; - travel expenses; - hotel; - travel; - payment of expert consultants | for each direction, the amount of expenses is indicated (in c.u.) | |
| Work of Russian experts (consultants): 5 people (targeted consulting) | - » - | |
| Computer technology and office equipment: Personal Computer and printer; Email(modem, Internet); Fax; payment for the content of the site on the Internet | - » - | |
| Consumables: for the operation of communication tools, the preparation of documentation and training materials | - » - | |
| Training: expenses for the preparation and conduct of training courses | - » - | |
| Payment of the working group: - program management; - program coordinator; - computer support methodologist | - » - | |
| Working trip to (the name of the country) Russian participants of the working group (4 people): - air tickets; - travel expenses, accommodation and travel | - » - | |
| Internship (in the country) winners of the competition of education leaders (2 people) | - » - | |
| Publication of design materials | - » - | |
| Program presentation | - » - | |
| Force majeure (3% of the total amount) | - » - |
Financing the planned training of educational leaders carried out within the budget of the city in accordance with the plan-order (name of the institution-customer). Innovative forms of training are additionally supported from extrabudgetary funds of district departments of education and individual educational institutions. Under the proposed theme of the project, it is possible to attract sponsorship funds.
To the sources indirect financing can be attributed:
budgetary payment of employees of city institutions, at the expense of which it is planned to develop educational programs, software products for computer support, innovative technologies;
· Provision by educational institutions of the city of space and educational equipment for training leaders;
· Expenses of the education committee and regional departments of education for organizing a competition for education leaders.
Total amount:
Annex 8. About the Russian-American project "Development of the creative thinking of visual arts»
(FOOTNOTE: This project, started in 1993 with financial support International Foundation "Cultural Initiative", was carried out by an interdepartmental working group among the international programs of the St. Petersburg state university teaching skills.)
The project developed innovative program of aesthetic development of schoolchildren. The team of authors, including developers, consultants, experts, included employees of the University of Pedagogical Excellence, the State Russian Museum (Department of Socio-Psychological Research), the State Hermitage Museum (School Center), as well as a group of experimental teachers who directly tested and corrected the course.
The first (pilot) stage of work with the American program VTC ("Visual Thinking Program") was held in 1993 in five schools in St. Petersburg. The study proved not only the viability of the program in Russian conditions, but also expediency of its use at the earliest stages of schooling.(In the United States, the two-year program was taught only in grades IV-V.) significant change methods of training teachers - teachers of the course.
At the second stage (1994-1995) the program and educational-methodical complex were adapted to Russian conditions. The St. Petersburg model of the program "Visual Thinking Strategy" was created. The experiment involved 11 schools and one kindergarten in St. Petersburg. The new group of teachers was trained by American and Russian experts jointly.
The Russian side independently started development of an intersessional training of teachers who teach the program, which proved to be crucial for the continuity of professional growth, without which the program could not be viable. Such work was not provided for by the American version of the training.
In the course of work it became obvious the possibility of creating an independent educational subject, which would start with preparatory group kindergarten and continued in I - 3rd grade schools.
Activities in the third phase (1995-1996) were carried out Russian specialists. (The American side provided one-time consultations.) For the first time, Russian developers independently acted as trainers. The experiment expanded even more, it was attended by: 33 experimental teachers from 16 schools and six kindergartens; 63 study groups, 874 children.
The participants of the project set themselves the goal of creating in the project mode a program of a completely new training course"Image and Thought", aimed at the aesthetic development of children based on knowledge of the stages of this development and the use of the strategy of visual and creative thinking. The work was based on collective forms of discussion of works of art in the school audience, as well as in the conditions of a museum exposition. The main task of the new project was the theoretical substantiation and practical testing of the course "Image and Thought". This involved: the development, examination and implementation of the course program in the mass practice of kindergartens and primary school; creation and publication of the program and teaching materials; development of a system for training teachers to work under the program in the advanced training system; verification of a comprehensive system for evaluating the effectiveness of the program.

 The success story of a famous tailoring magazine
The success story of a famous tailoring magazine Thesis plan abstract. How are abstracts written? What are abstracts and how not to make mistakes when writing them? Conference report
Thesis plan abstract. How are abstracts written? What are abstracts and how not to make mistakes when writing them? Conference report What is "gold" and "blue" watches in photography
What is "gold" and "blue" watches in photography How to make money with advertising on a car and what you need for this Examples of detailed, information-rich advertising
How to make money with advertising on a car and what you need for this Examples of detailed, information-rich advertising Quadratic and cubic functions
Quadratic and cubic functions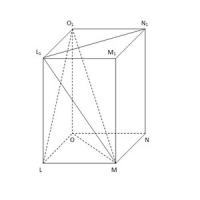 How to make a paper prism
How to make a paper prism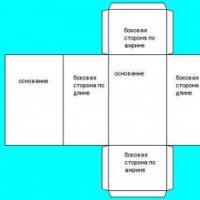 Everything you need to know about the prism for passing the exam in mathematics (2020)
Everything you need to know about the prism for passing the exam in mathematics (2020)