The division of labor in production is conducive. Social division of labor. Forms, essence and significance of the division of labor
The division of labor is the most important pattern of economic progress.
Differentiation means dividing, dividing the whole into different parts, forms and stages. Division of labor is differentiation, specialization labor activity, leading to the isolation and coexistence of its various types, the isolation of types of labor activity in society. The division of labor can be functional and territorial. There are such types of functional division of labor as social and technical.
The social division of labor is the differentiation in society of various social functions carried out certain groups people belonging to certain professional groups, and the allocation in this regard of various spheres of production and industries (general division of labor), which in turn are divided into sub-sectors (private division of labor). For example, such industries are distinguished National economy, as industry (heavy, light), agriculture (crop, livestock), transport (water, air, land), etc.
The social and technical division of labor finds expression in the professional division of labor. By acquiring a particular profession, an employee receives special knowledge for working in a certain field of activity, he does not perform all work in production, but specializes in those types of work that he does more efficiently than other workers, i.e. has a comparative advantage.
Territorial division of labor is regional, carried out between regions within the country, and international, carried out between different countries of the world.
The division of labor has evolved over the centuries as a result of progress productive forces and the complication of the organization of society. The factors of its deepening are scientific and technological progress, as well as the development of market relations. Scientific and technological progress leads to the emergence of new products and industries, and the expansion of markets facilitates exchange between producers of products and contributes to the satisfaction of their needs. In turn, the deepening of the division of labor is the most important factor in increasing labor productivity and improving product quality. The modern economy is highly specialized and relies on diversified mass production of various goods. However, the division of labor can also create some problems, including the monotony of performing routine tasks, technological unemployment arising in the absence of demand for certain professions, chronic unemployment that threatens the economy if it is not able to absorb the labor force released as a result of productivity growth.
The division of labor is carried out in the form of specialization. Specialization is a form of division of labor in which each economic entity concentrates its production efforts on one or more activities. It allows the economic system to use limited resources more efficiently and, as a result, to produce and consume more goods and services than in the absence of specialization.
The form of the social division of labor is the specialization of production, it reflects the process of concentration of production of certain types of products or parts of them in independent industries, industries and specialized enterprises. Specialized production is characterized by uniformity of products and technological processes, special equipment and personnel.
The main types of production specialization are
subject,
detailed (unit-by-unit) and
technological.
Subject specialization means the production of finished products (for example, automobile SHUDES, shoe factories, etc.), detailed specialization means the production of component parts (enterprises that produce parts and assemblies, for example, a motor plant, an auto-aggregate plant, etc.), technological - production semi-finished products (for example, foundries, forging and pressing plants in mechanical engineering).
The technical (unit) division of labor is the division of labor into a number of partial functions, operations within an enterprise or organization. It is characteristic of mass industrial production based on machine technology.
There are three main forms of social division of labor in order to develop production: individual, private and general. A single division of labor is expressed by the specialization of enterprises and their production units (workshops, sections). Specialization is understood as the concentration of production of a homogeneous (profile) product of labor. It exists in the form of: subject form, detailed form (units and parts of a product, details) and technological form (stages and methods of production).
The subject form of specialization is understood as the separation of the production of products of labor, ready for use and (or) exploitation (for example, the production of equipment, clothing, etc.).
The detailed (nodal) form of specialization is characterized by the allocation of production of parts of the finished product (assemblies, parts) intended either for completing the manufactured product, or as spare parts to replace worn out during repair, or as spare parts, tools and accessories attached to the finished product ...
The technological or staged form of specialization is the separation of individual phases (stages) of production as independent ones (for example, centralized foundry, press-forging, welding production).
By now, the types of specialization that have developed in practice in their three forms are classified, revealing more deeply the processes of differentiation of labor by kind, type, class, etc. not only at enterprises, but also in the regions, through a sequential transition from stage to stage.
It follows from this trend that the division of labor has reached a new level, the level of the private division of labor, which occupies an intermediate place between the individual and social division of labor.
So, the development of specialization of an economic region inevitably leads to the need to clarify the stages of development of specialization of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, other administrative units (regions, districts, cities), industrial and agro-industrial complexes.
The development of specialization of industries and types of activity leads to a consistent limitation of the diversity of the range of products, assemblies, parts, stages of production carried out in associations, at enterprises, in workshops and at sites.
For a long time, the production of products and parts used in various industries has been distinguished, the so-called intersectoral production (for example, the production of normalized parts, assemblies, fasteners).
Differentiation of production specialization according to the stages of classification of machines, units, parts and stages technological process leads to constructive and technological uniformity of product design (by types, classes, types, types, stages of production) with a variety of needs and demands.
Based on the characteristics of the essence and forms of specialization, its development in any direction can be considered economically justified if this achieves the possibility of using progressive technology, technology and organization of production, ensuring an increase in production efficiency.
Specialization is an endlessly developing process, and at each stage, at each time stage, it sets specific tasks and determines new methods and ways to solve them.
The specialization of production is inextricably linked with the concentration of production and cooperation. Cooperation is understood as the established long-term production and economic ties between business entities: regions, industries and directly enterprises that jointly manufacture certain products.
The enterprises participating in the cooperation are, as a rule, economically independent, therefore supplies are carried out on a contractual basis. Enterprises are mainly in direct production dependence, especially when cooperative ties are determined by the technological process of joint production of products, but they can also be in an indirect relationship, when cooperation is carried out only for the purpose of more complete capacity utilization and is not determined by the main technological processes (there are excess capacities).
The forms and directions of cooperation in terms of names and in essence coincide with the forms and directions of specialization, because in connection with the development of specialization, they arise. The narrower the specialization of the object, the greater the number of subcontractors and other enterprises involved in the manufacture of the final product.
Therefore, the subject, detailed and technological forms of cooperation are distinguished. Among the directions, cooperation is distinguished between industries, associations, enterprises, economic and administrative regions, industrial complexes, etc.
Intra-district cooperation refers to production ties of enterprises located on the territory of one district. Interdistrict cooperation is understood as production ties of enterprises located in different regions.
Similarly, based on the sectoral affiliation of enterprises, intra-sectoral and inter-sectoral cooperation are distinguished.
The cumulative effect of specialization and cooperation is manifested in the concentration of production. The concentration of production based on the division of labor consists in the concentration of specialized (homogeneous) production both within the framework of technological systems, industrial enterprises, associations and industries, and within the regions.
Distinguish between absolute and relative concentration of production. The absolute characterizes the size of production units, and the relative characterizes the distribution of the volume of production of homogeneous products between production units different sizes.
Under the influence of social forms of the division of labor and the development of scientific and technological progress, four types of processes of concentration of production have developed: aggregate, technological, factory and organizational and economic forms.
Aggregate concentration is to increase the unit capacity of machines and equipment (units). For example, in the electric power industry, the unit capacity of turbines is increasing, in mechanical engineering, the production of multifunctional machine tools of the "Processing Center" type, program management, multifunctional computers, universal computer-aided design systems, powerful chemical equipment etc.
Technological concentration is the way to increase production capacity. Such concentration can develop intensively, on the basis of aggregate, and extensively, by increasing the number of units of the same type of equipment. An example of technological concentration are the capacities of specialized casting production - centroliths, spinning, weaving industries, continuous and mass production in machining and assembly, automated and automatic production in chemistry, light and food industries.
Factory concentration is carried out by increasing the size of enterprises and industries. It develops not only on the basis of aggregate and technological concentration, but also through mergers, combining several industries into one. These are, as a rule, specialized enterprises (for example, AvtoVAZ) and industrial plants, including different production one or more industries.
Organizational and economic concentration is the creation of associations of enterprises. A large number of various associations have been formed in the industries. All their modifications can be classified according to the following criteria: the nature of production activities; the scale of the activity; legal independence of the units that make up the association; forms of specialization and concentration.
By the nature of production activities, associations are subdivided into production; scientific; research and production; educational and scientific associations (UNO); research and production (NPO); scientific and technical (STO); educational-scientific-production (UNPO); agro-industrial associations (APO); industrial plants (PC), etc.
All-Union, republican, regional, sectoral, inter-sectoral and local associations differ in the scale and territory of their activity.
The association may include legally independent enterprises, enterprises deprived of independence, when only the parent enterprise acts legal entity, and enterprises of mixed ownership. When an association has a parent enterprise with legal rights, which is an association, all others act as production facilities, workshops that do not have legal rights, or as enterprises with limited legal independence provided to them by the association.
Since the main principle of creating an association is the concentration of production on the basis of specialization, then according to this criterion, they are mainly also divided into associations with subject, detailed and technological forms of specialization of work, types of activities, products manufactured in a certain territory.
Similar materials
| → |
| → |
| → |
| → |
| → |
Division of labor
Division of labor- the historically established process of isolation, modification, consolidation of certain types of labor activity, which takes place in social forms differentiation and implementation of various types of labor activities.
Distinguish:
General division of labor by branches of social production;
Private division of labor within industries;
A single division of labor within organizations according to technological, qualification and functional characteristics.
It is the reason for the increase in the overall labor productivity of an organized group of specialists (synergistic effect) due to:
- Developing skills and automatism of performing simple repetitive operations
- Reducing the time spent switching between different operations
The concept of the division of labor is quite fully described by Adam Smith in the first three chapters of his five-volume treatise "A Study on the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations."
Allocate social division of labor- the distribution of social functions among people in society - and the international division of labor.
Social division labor- This is the division of labor primarily into productive and managerial labor. (F. Engels "Anti-Dühringe" op., V. 20, p. 293)
The division of labor led to modern world to the presence of a huge variety different professions and industries. Earlier (in ancient times) people were forced to almost completely provide themselves with everything they needed, it was extremely ineffective, which led to a primitive way of life and comfort. Almost all the achievements of evolution, scientific and technological progress can be explained by the continuous introduction of the division of labor. Through the exchange of the results of labor, that is, trade, the division of labor becomes possible in society.
From the point of view of business engineering, division of labor is a functional decomposition of business processes. It is often possible to single out such a part of the functions in a separate form, which then becomes possible to entrust to automation or a machine. Thus, the division of labor continues to occur today and has a close relationship, for example, with automation processes. In the field of intellectual work, it is also possible and very useful to divide it.
The division of labor is the first link in the entire system of labor organization. The division of labor is the separation of various types of labor activity and the division labor process into parts, each of which is performed by a certain group of workers, united by common functional, professional or qualifications.
For example, the main method of work in accounting is the division of labor of specialists. We distribute the work of employees in accounting areas under the guidance of leading specialists and auditors, which allows us to achieve maximum efficiency of their work. Thus, we dynamically combine developments in the field of accounting automation and experience in the administration of accounting services.
see also
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
- Political Economy
- Masaryk, Tomas Garrigue
See what "Division of Labor" is in other dictionaries:
DIVISION OF LABOR- The term "R. T." used in societies. sciences in a different sense. Societies. R. t. Denotes the differentiation and coexistence in society as a whole of various social functions, types of activities performed by definition. troupes of people ... ... Philosophical Encyclopedia
Division of labor- (division of labor) The systematic (but not necessarily pre-planned or imposed) division of functions, tasks or activities. The Republic of Plato (Plato) mentions the functional division of labor: philosophers define laws, ... ... Political science. Dictionary.
DIVISION OF LABOR Modern encyclopedia
DIVISION OF LABOR- differentiation, specialization of labor activity, coexistence of its various types. Social division of labor, differentiation in society of various social functions performed by certain groups of people, and the allocation in connection with this ... ... Big Encyclopedic Dictionary
Division of labor- DIVISION OF LABOR, differentiation, specialization of labor activity, coexistence of its various types. Social division of labor, differentiation in society of various social functions performed by certain groups of people, and the allocation of ... Illustrated Encyclopedic Dictionary
DIVISION OF LABOR- (division of labor) The system by which specialization occurs in the production process. It has two advantages: firstly, workers specialize in those types of work in which they have a comparative advantage (comparative ... ... Economic Dictionary
Division of labor- (division of labor) Specialization of workers in the production process (or any other economic activity). Adam Smith (1723-1790), in his work The Wealth of Nations, described the division of labor as one of the greatest contributions to increasing ... ... Business glossary
Division of labor- division of labor functions between members of the working collective (link, brigade) in accordance with the division production process into the constituent processes and operations. [Adamchuk V. V., Romashov O. V., Sorokina M. E. Economics and sociology ... ... Encyclopedia of terms, definitions and explanations of building materials
division of labor- Delineation of the activities of people in the process of joint labor. [GOST 19605 74] Topics organization of labor, production ... Technical translator's guide
DIVISION OF LABOR- English. division of labor; German Arbeitsteilung. 1. A functionally integrated system of production roles and specializations within society. 2. According to E. Durkheim, a necessary condition for the material and intellectual development of society; a source… … Encyclopedia of Sociology
Books
- Justice in the national economy. Division of Labor, G. Schmoller. The readers are invited to a book by the famous German economist and historian Gustav Schmoller, devoted to the study of the problems of the national economy. In the first part of the book, the author tries to ...
The division of labor has become the basis of non-economics
Seemingly division of labor everyone knows, but since initially political economy and bourgeois neoclassical theory followed the path of comparative advantages, in economics the division of labor was considered only in terms of increasing productivity.
Therefore, when, at the beginning of our millennium, the Russian economist Oleg Vadimovich Grigoriev decided to use the degree of division of labor as a factor to compare economies different countries, he could not believe that no one had paid attention to it before him. When, in 2010, an object in the economy was opened, to which this factor of the division of labor could be applied, a domestic economic theory was born, called by Grigoriev the word neo-economics.
Division of labor clause rewritten 23.12.2017 as a narrative for the Theory of Economic History, which is the economic part of the science of NEOCONOMICS. Division of labor is ambiguous, since it can mean both the division of the time of day labor of one person into separate periods of production of different products, and be used in relation to the whole system of production, in which production was divided into separate operations, each of which is performed by a separate person.

2.3. Therefore, by itself this term (without clarification) Neo-Economics tries to use at a minimum, only where its specific meaning is clear from the context.
Readers who division of labor interests at a professional level - I recommend dictionary entries:
|
2.4. Contemporary view division of labor you can find in the book Oleg Grigoriev and the EPOCH OF GROWTH. Actually, in it all the problems of economics are considered from the angle of the factor of division of labor, but the scientific approach to the division of labor is explained in Chapter 1: ON DIVISION OF LABOR. 2.5. The first part of this article is occupied by the section PROBLEMS OF LABOR SEPARATION in the history of economic thought. Myself division of labor described in the articles: natural division of labor, history of the emergence of the economy, reproduction contour, the act of technological division of labor. |
THE PROBLEM OF LABOR SEPARATION
Division of Labor Wikipedia
3.1. The fact that modern economics considers division of labor too trivial and does not require any explanation - can be seen from the scarcity of the article division of labor on Wikipedia where i got the following definition of division of labor:
4.2. “The greatest progress in the development of the productive power of labor and a significant proportion of the art, skill and ingenuity with which it is directed and applied, were, apparently, a consequence of the division of labor "
4.3. This Smith clause: - « apparently ", Rather testified to the honesty of the great economist, who himself, apparently, did not consider himself an expert on the phenomenon of labor, therefore, to reinforce his statement -" The greatest progress ... was the result of the division of labor"- dedicated THREE chapters in the book WEALTH OF THE PEOPLES, as evidenced by their names:
- Chapter I "On the division of labor"
- Chapter II "On the cause causing the division of labor"
- Chapter III "The division of labor is limited by the size of the market"
5.3. The fact is that the subject of study of classical political economy was the national economy, therefore, when comparing, the first economists were struck by difference in natural resources from countries. When transferring the fact that countries have different natural advantages to Robinson's economic model- there was a thought that the emergence of a division of labor among people can be attributed to limited resources. They say that one subject has a certain set of natural resources, while the other has another, then, in order to produce something, they need to be exchanged. This idea was developed by David Ricardo, thanks to whom division of labor problems shifted into the plane of natural benefits. Moreover, the raw material factor to explain causes of social division of labor seemed clearer even to Karl Marx, therefore Marxist political economy considered division of labor fully resolved in David Ricardo's Theory of Comparative Advantage.
5.4. Understanding the division of labor could not fall into the focus of classical political economy, since the object of research was initially social ties that are formed under the influence of socio-economic phenomena, which especially prevailed in Marxist political economy, which became the pinnacle of the classics. Moreover, at present, the entire ideology of international organizations, including the World Trade Organization, is based on the ideas of Ricardo and Adam Smith about natural advantages. The WTO recommends that developing countries find some advantages in themselves, on the basis of which specialization should be carried out, which should certainly bring countries to a high position in the world division of labor.
5.5. Actually, an indistinct political economy definition of division of labor adopted neoclassical economic theory, which at the end of the 19th century was created as anti Marxism, since the theory of class struggle has gained great popularity. However, the hypothesis that neoclassicism could not be accepted not with the benefits of specialization, but with natural factors, for the reason that the subject of its study was not economics, but the individual.
5.6. Therefore, with the aim of refuting the Marxist theory of the class struggle, bourgeois political economy also took as a given that does not require explanation. By that time, the natural division of labor was familiar to everyone, without any explanation. Indeed, the natural division of labor was understood by everyone as a continuation of the sex-age division of labor, and even more - the division of activity inherent in many species of animals.
Division of labor
6.2. The process of deepening the division of labor he was not very interested in Marxist political economy and economics (micro-macro), which do not go beyond the time frame of capitalist relations and were noticeably politicized, since they opposed in their basic postulates about the finiteness of capitalism. All political economy emerged from the concept of surplus value, which the capitalist appropriates, which gave rise to the theory of class struggle, and economics, which appeared as the antipode of Marxism, today degenerated into a theory of the counter - what and how to put on the shelves in order to sell faster.
6.4. The depth of the division of labor, taken as a factor, immediately made it possible to study the interaction of reproduction contours and make forecasts of the results of the interaction of the economies of different countries, which act as a set of contours. Therefore, neo-economics has become a new level of economic knowledge.
6.5. Actually division of labor disclosed in thousands of articles, for example, in my natural division of labor, however, NEOCONOMICS as an economic science studies speculative theoretical or otherwise - abstract concepts. Therefore, this article can be read only for general educational purposes, and entrance to neo-economics starts with understanding new terms - speculative, like chain of division of labor in the production of goods, which is applied to a new speculative object in the economy called the reproductive circuit.
As a preparation, I recommend to the readers the book Fundamentals of Economics by M.A. Storchevoy. (edited by P.A. Vatnik.SPb .: Economic school, 1999.432s.)
According to the format of the article, further criticism of the Orthodox definitions of division of labor, for the standard of which I usually take an article from Wikipedia (division of labor Wikipedia), as a typical ore separation description, but I offer readers a much better division of labor article, the text of which I found on the page on the abstracts site bibliofond.ru.
Forms, essence and significance of the division of labor
- Introduction
- 1 Forms of work organization
- 1.1 Division of labor: concept and General characteristics
- 1.2 Forms of division of labor
- 2 Significance of the division of labor
- Conclusion
- Bibliography
Introduction
In production necessary funds of existence, people influence nature. Therefore, production is the relation of people to nature. However, acting on nature, they have a corresponding effect on each other, entering into a certain relationship. Those relations that are conditioned by the requirements of economic practice are usually called production, that is, economic relations. At the heart of any production process is work... Itself production can be characterized as a system of labor processes necessary for the production of this kind of material goods or services provided by individuals or organizations.
Even the most primitive labor of primitive man always proceeded with the support, interaction with other people. Therefore, this already concealed the social content of labor activity. All this suggests that the labor process and labor itself is an economic category, i.e. it always contains an element of economic, industrial relations. A person is a social being due to the fact that work makes him organically welded in relation to other people, not only of the present, but also of the past (when the experience of predecessors is adopted) and the future, when his results of labor will serve in the future. Economic theory examines the production and reproduction of material and other goods necessary for the life of the human race. Disclosure of these issues requires the identification of general or specific laws governing the production relations of people. Production relations include the relations of people in the process of production, exchange, distribution, consumption and accumulation of material goods. The entire set of these relations is unified system economic relations, within the framework of which the normal process of life of any economic system is possible. All material needs of society can be divided into two classes: in the production process, interaction takes place not only with the means of production, but also with their colleagues, colleagues in joint work and joint work has its economic significance, since it allows the exchange of not only activities, but also exchange of experience, skills, will to achieve the assigned tasks for the workers.
The labor of an individual worker, no matter how isolated he may seem, is a particle of the total social labor... This is facilitated not only by the production technology itself, but also by the constant not only human, but also industrial training of production participants, since the joint production and productive activity of people is carried out in the form cooperation and division of labor... This applies not only to the direct labor process, but also to the very organization of interaction. different forms property and types of economic systems. Itself consists in the specialization of the employee for the implementation of any work, operations, production of a separate product.
Forms of work organization
1.1. Division of labor:concept and general characteristics
At the heart of economic development lies the creation of nature itself - division of functions between people, based on gender, age, physical, physiological and other characteristics. The mechanism of economic cooperation assumes that some group or individual is focused on the performance of a strictly defined type of work, while others are engaged in other activities.
Definition of the division of labor
There are several definitions of division of labor... Here are just a few of them.
Division of labor- This is a historical process of isolation, consolidation, modification of certain types of activity, which takes place in social forms of differentiation and the implementation of various types of labor activity. Division of labor in society it is constantly changing, and the system of various types of labor activity itself is becoming more and more complex, since the process of labor itself is becoming more complex and deepening.
Division of labor(or specialization) is the principle of organizing production in the economy, according to which an individual is engaged in the production of a separate good. Thanks to the operation of this principle, with a limited amount of resources, people can receive much more benefits than if everyone would provide himself with everything he needs.
Division of Labor Wikipedia describes in the following words:
Division of labor- the historically established process of isolation, modification, consolidation of certain types of labor activity, which takes place in social forms of differentiation and the implementation of various types of labor activity.
They also distinguish between the division of labor in a broad and a narrow sense (according to K. Marx).
Broad division of labor Is a system of different in their characteristics and simultaneously interacting with each other types of labor, production functions, occupations in general or their aggregates, as well as a system of social relations between them. The empirical diversity of occupations is considered by economic statistics, labor economics, sectoral economic sciences, demography, etc. The territorial, including international, division of labor is described by economic geography. To determine the ratio of various production functions from the point of view of their material result, K. Marx preferred to use the term “ distribution of labor».
Exists division of labor within society and division of labor within an enterprise... These two main types are interconnected and interdependent. Division of social production for his large families (such as agriculture, industry, etc.) K. Marx called general division of labor, the division of these types of production into types and subspecies (for example, industry into separate sectors) - by private division and, finally, within the enterprise - by a single division.
General, particular and unit division of labor- inseparable from the professional, specialization of workers. Division of labor is also used to denote the specialization of production within one country and between countries - international and territorial division of labor.
In a narrow sense, the division of labor- it social division of labor as a human activity in its social essence, which, in contrast to specialization, is a historically transient social relation. Labor specialization is division of labor on a subject that directly expresses the progress of the productive forces and contributes to it. The variety of such species corresponds to the degree of human assimilation of nature and grows along with its development. However, in class formations, specialization is carried out not as a specialization of integral activities, since it itself is influenced by social division of labor... The latter divides human activity into such partial functions and operations, each of which in itself no longer possesses the nature of activity and does not act as a way of reproduction by a person of his social relations, his culture, his spiritual wealth and himself as a person. These partial functions have no meaning or logic of their own; their necessity acts only as requirements imposed on them from the outside division of labor... This is the division of material and spiritual (mental and physical), performing and managing labor, practical and ideological functions, etc. Expression social division of labor is the selection as separate spheres of material production, science, art, etc., as well as their dismemberment.
Division of labor historically inevitably grows to class division.
Due to the fact that members of society began to specialize in the production of certain goods, society appeared profession – certain types activities related to the production of any good. The variety of benefits for which specialization took place created horizontal division of labor with the isolation of individual branches of production of related goods, in which further fragmentation into smaller, highly specialized manufacturing operations. Horizontal division of labor occurs with the emergence of a new type of product, but inside it naturally appears associated with the separation of the movement from the extraction of raw materials to final production and consumption into dedicated manufacturing operations.
Thus, an important element of labor organization is , i.e. separation of types of labor activity between employees, teams and other departments in the enterprise. This is the starting point for the organization of labor, which, based on the goals of production, consists in assigning to each employee and to each division of their duties, functions, types of work, technological operations. The solution to this issue should provide, along with the requirement for the most rational use of working time and the qualifications of the employee, such his specialization so that the content of work is preserved, its monotony is not allowed, and the harmonization of physical and mental stress is ensured.
1.2 Forms of division of labor
Distinguish the following forms of division of labor at enterprises:
- functional division of labor- depending on the nature of the functions performed by workers in production and their participation in the production process. On this basis, workers are divided into workers (main and auxiliary) and office workers. Employees are divided into managers (linear and functional), specialists (designers, technologists, suppliers) and technical executors... In turn, workers can make up functional groups main workers, service and support. Among the latter, there are groups of repair and transport workers, quality controllers, energy service workers, etc. Functional division of labor manifests itself in two directions: between the categories of workers included in the personnel of the enterprise, and between the main and auxiliary workers. The first means the allocation of such categories of workers as workers, managers, specialists and employees in the personnel of enterprises. A characteristic trend in the development of this type of division of labor is the increase in the proportion of specialists in the production personnel. Another direction of the functional division of labor is the division of workers into main and auxiliary. The first of them are directly involved in changing the shape and condition of the processed objects of labor, for example, workers in foundries, mechanical and assembly shops machine-building enterprises engaged in performing technological operations for the manufacture of basic products. The second do not directly participate in the implementation of the technological process, but create the necessary conditions for the smooth and efficient work of key workers. Classification of transactions appropriate division of labor between managers, specialists and employees (three interconnected groups): 1) organizational and administrative functions - their content is determined by the purpose of the operation and the role in the management process. Mainly performed by managers; 2) analytical and constructive functions are predominantly creative, contain elements of novelty and are performed by specialists; 3) information technology functions are repetitive and associated with the use of technical means... Performed by employees;
- technological division of labor- This is the dismemberment and isolation of the production process according to the subject or operational principle. It is caused by the development of scientific and technological progress and the deepening division of industries into sub-industries and micro-industries, specializing in the manufacture of technologically homogeneous products, the production of certain items, goods or services; types of technological division of labor are: subject and operational division of labor; in this case, the forms of manifestation of the division of people are: profession (focused on the final product) and specialty (limited to an intermediate product or service). Subject division of labor(detailed), i.e. specialization in the production of individual products, provides for the assignment of a complex of various operations to the worker, aimed at the manufacture of a certain type of product. Operational division labor- based on the assignment of a limited set of technological operations to specialized workplaces and is the basis for the formation of production lines. Technological division of labor classified by phases, types of work, products, assemblies, parts, technological operations. It determines the arrangement of workers in accordance with the production technology and largely influences the level of meaningfulness of labor. At narrow specialization monotony appears in the work, with too broad specialization, the likelihood of poor-quality work increases. The responsible task of the organizer of labor is to find the optimal level of the technological division of labor;
- - by specialties and professions. Reflects the production and technological side and the functional content of labor. As a result professional division of labor there is a process of separation of professions, and within them - the allocation of specialties. It is also interconnected with the social structure of society, since closely related to its social division. Based on this form of division of labor, the required number of workers in different professions is established. Profession- the type of activity of a person who owns certain theoretical knowledge and practical skills obtained as a result vocational training... Specialty - a kind of profession, specialization of an employee within the profession; (How does the concept Profession Wikipedia see the profession link)
- skill division of labor- within each professional group, associated with the unequal complexity of the work performed and, therefore, with different requirements for the qualification level of the employee, i.e. division of labor of performers depending on the complexity, accuracy and responsibility of the work performed in accordance with professional knowledge and work experience. Expression qualification division of labor serves the distribution of jobs and workers by category, employees - by positions. Regulated by tariff and qualification reference books. The qualification structure of the organization's personnel is formed from the qualification division of labor. Division of labor here it is carried out according to the level of qualifications of workers, based on the required qualifications of work.
There are also three forms social division of labor:
- characterized by the isolation of large kinds (spheres) of activity, which differ from each other in the form of the product (agriculture, industry, etc.);
- private division of labor- this is the process of separating individual industries within the framework of large types of production, divided into types and subspecies (construction, metallurgy, machine-tool construction, animal husbandry);
- unit division of labor characterizes the separation of production of individual constituent components of finished products, as well as the separation of individual technological operations, i.e. separation of various types of work within an organization, an enterprise, within its certain structural divisions (workshop, site, department, management, team), as well as the distribution of work between individual employees.
2 . The essence and significance of the division of labor
For dealing with division of labor use the concepts " division of labor" and " division of labor".The boundaries of the division of labor- the lower and upper limits, below and above which the division of labor is unacceptable. Division of labor- the accepted calculated or actually achieved value that characterizes the state of the division of labor.
In the division and cooperation of labor, the question is resolved: who and what will do, how and with whom will interact. For the organization of highly productive work, it is also necessary to solve the following question: how, how the work should be done.
For example, consider a branch of industry in which the division of labor was very often noted, namely production of pins... A worker who was not trained in this production (the division of labor made the latter a special profession) and who does not know how to handle the machines used in it (the impetus for the invention of the latter was probably also given by this division of labor), perhaps, with all his diligence make one pin a day and, anyway, won't make twenty pins. But with the organization that this production now has, it itself as a whole not only represents a special profession, but is also subdivided into a number of specialties, each of which, in turn, is a separate special occupation. One worker pulls the wire, another straightens it, the third cuts it off, the fourth sharpens the end, the fifth grinds one end to insert the head; the manufacture of the head itself requires two or three independent operations; its nozzle constitutes a special operation, polishing a pin is another; an independent operation is even wrapping ready-made pins in bags. Thus, the complex labor of making pins is divided into about eighteen independent operations, which in some manufactures are all performed by different workers, while in others the same worker often performs two or three operations.
In every other craft and manufacture consequences of the division of labor are similar to those described in this production, although in many of them labor cannot be so divided and reduced to such simple operations. but in any craft, no matter how large it is introduced, it causes a corresponding increase in labor productivity. Apparently, the separation of various professions and occupations from each other was caused by this advantage. At the same time, such a distinction usually goes further in countries that have reached a higher stage of industrial development: what in the wild state of society is the work of one person, in a more developed society is performed by several. In any developed society, the farmer is usually engaged only in farming; the owner of a manufactory is occupied only with his manufacture. The labor required to produce some finished object is also almost always distributed among a large number of people. How many different professions are employed in each branch of the production of linen or cloth, from those who raise flax and sheep, delivering wool, and ending with those who are engaged in bleaching and glossing linen or dyeing and finishing cloth.
True, agriculture by its very nature (as an exception, which has seasonality from climatic conditions) does not allow for such a diverse division of labor, or such a complete separation of various works from each other, as is possible in manufacture.
It is impossible to completely separate the occupation of the pastoralist from the occupation of the plowman, as is usually the case with the professions of carpenter and blacksmith.
The spinner and weaver are almost always two different faces, while the worker who plows, harrows, sows and reaps is often the same person. In view of the fact that these different types of work must be performed at different times of the year, it is impossible for each of them to be constantly occupied by a separate worker throughout the year. The impossibility of such a complete separation of all the different types of labor practiced in agriculture is, perhaps, the reason that the increase in labor productivity in this area does not always correspond to its growth in industry.
Such a significant increase in the amount of work that can be done as a result division of labor the same number of workers depends on three different conditions: first, from increased dexterity every single worker; Secondly, from saving time, which is usually lost in the transition from one type of labor to another; third, from the invention of a large number of machines that facilitate and reduce labor and allow one person to do the work of several.
This is achieved by establishing rational methods and techniques of labor. Of course, the way work is done is largely determined by technology, but each technological operation can be performed in different ways: with more or less number of movements, more or less skillfully, with the expenditure of different amounts of time and physiological energy. Establishing a way the most economical performing every action, technique, operation, every work is a responsible task of the organizer of labor. It involves the analysis and development of all parts of the work process, including all calculations and construction, and coordination of movements, the choice of a comfortable working posture, the way of using the tool and controlling machines and mechanisms, time for rest, downtime, etc.
It should be noted that , meaning the simultaneous coexistence of different types of labor activity, plays important role in the development of the organization of production and labor:
- first, the division of labor is a necessary prerequisite for the production process and a condition for increasing labor productivity;
- Secondly,
- third,
But as a process of specialization of workers cannot be regarded only as a narrowing of the sphere of human activity by performing increasingly limited functions and production operations.
Division of labor is a multilateral, complex process that, changing its forms, reflects the action of the objective law of change in labor: the socio-economic law of social production, expressing objective, significant, continuously increasing and expanding connections between revolutionary changes in the technical basis of production, on the one hand, and functions workers and social combinations of the labor process - on the other. The accelerating mobility of labor functions is an indisputable requirement of this law. In the context of requirements it comes about universality work force, her flexibility, versatility, adaptability as a condition of her ability to change labor. The main reasons for the need for a change in labor are revolutions in the technical basis of production. First, changing the technique, technology and organization of production, they lead to the disappearance of some professions and the emergence of new ones associated with the use of technology of a higher level. Second, by creating more progressive branches of production, revolutions in the technical basis sharply change the proportions in the balance of the labor force, which leads to a change in its professional and qualification structure. If at the first stages of the development of large-scale industry during the labor activity of one generation, changes in the professional structure were hardly perceptible in order to discern a tendency towards a change in labor, then at the present stage one generation needs to change profession two or three or more times. The nature of large-scale industry is constantly revolutionizing inside society and continuously throws masses of capital and masses of workers from one industry to another. Therefore, the nature of large-scale industry determines the change in labor, the movement of functions, the all-round mobility of the worker.
Revolutionizing the division of labor entails radical changes in its content, and the latter creates the preconditions for the emergence of new sectors of the economy and new professions. The change of labor can be carried out in time, in space, as well as in time and space at the same time. When considering the change in labor in time, it is necessary to distinguish between a complete switch from one type of work to another, carried out in large intervals of time, and the alternation of various types of activity. The change of labor in space is associated with the management of complexes automatic systems, including a variety of types of work. In domestic production, it manifests itself in three main forms: a change in labor within the boundaries of a given profession; transition from one type of work to another; combination of basic work with various activities on a voluntary basis. The variety of forms of manifestation of the law directly depends on the degree of development of scientific and technological progress.
It is important to note that when division of labor in enterprises should take into account not only the growth of labor productivity, but also the conditions for the all-round development of workers, the elimination negative influence working environment on the human body and increasing the attractiveness of labor. Division of labor largely depends on the specific operating conditions of the enterprise: belonging to the industry, type and scale of production, the level of mechanization, automation, the volume of production and the specifics of products, etc.
Significance of the division of labor is an:
- a necessary prerequisite for the production process and a condition for increasing labor productivity;
- allows you to organize sequential and simultaneous processing of the subject of labor in all phases of production;
- promotes the specialization of production processes and the improvement of the labor skills of the workers involved in them.
The division of labor is a production operation., which is understood as a part of the labor process performed by one or a group of workers at one workplace, over one object of labor. A change in at least one of these signs means the completion of one operation and the beginning of another. Manufacturing operation, in turn, consists of techniques, labor actions and movements.
Labor movement represents a single movement of the hands, legs, body of the worker in the process of labor (for example, reach out to the workpiece).
Labor action- this is a set of labor movements performed continuously and having a particular purpose (for example, the labor action "take the workpiece" is made up of consistently and continuously performed movements "reach out to the workpiece", "grip it with your fingers").
Labor reception- This is a set of labor actions, united by one purpose and representing a complete elementary work.
The boundaries of the division of labor(ignoring them can negatively affect the organization and results of production) obviously coincide with the beginning and the end labor admission in a production operation:
- should not lead to a decrease in the efficiency of using working time and equipment;
- it should not be accompanied by impersonality and irresponsibility in the organization of production;
- should not be overly fractional, so as not to complicate the design and organization of production processes and labor rationing, as well as not to reduce the qualifications of workers, not to deprive work of meaningfulness, not to make it monotonous and tedious.
Monotony of work is a very serious negative factor that manifests itself in deepening division of labor in production.
The means against monotony can be the periodic change of jobs, the elimination of the monotony of labor movements, the introduction of variable rhythms of work, regulated breaks for active rest, etc.
Division of labor tasks:
- growth in labor productivity;
- comprehensive development of employees;
- elimination of the negative impact of the industrial environment on the human body;
- increasing the attractiveness of labor.
Division of labor largely depends on the specific conditions of the enterprise: belonging to the industry, type and scale of production, the level of mechanization, automation, the volume of output and the specifics of products, etc. The degree of division of labor depends on the number of production operations required for the production of goods using a specific technology.
Conclusion
Exactly caused the separation from each other of various professions and occupations, which contributed primarily to an increase in productivity and the higher the stage of industrial development of the country, the further this separation goes. What in the wild state of society is the work of one person, then in a more developed state it is performed by several. Labor Needed to Produce Some Finished Item always distributed among a large number of people.
Division of labor speaking in different types and the forms of its manifestation, is a defining prerequisite for the development of commodity production and market relations, since the concentration of labor efforts on the production of a narrow range of products or on certain types of it forces commodity producers to enter into relations of exchange in order to obtain the goods they lack.
Bibliography
- Bychin B.V., Malinin S.V., Shubenkova E.V., Organization and regulation of labor. Textbook for universities - Moscow, 2003
- Razorvin I.V., Mitin A.N., LABOR ECONOMY, Educational-methodical complex, - Yekaterinburg, 2003
- Karl Kautsky. "The economic doctrine of Karl Marx" - Moscow, 2007
- A. Smith "Research on the nature and causes of the wealth of peoples", Moscow, 1999
- Yandex dictionary http://slovari.yandex.ru/
- 6. World Economic Forum http://business.polbu.ru/fomichev_inttrading/ch10_xiv.html
Actually in Marxism division of labor(see Division of Labor The Great Soviet Encyclopedia) is revealed more declaratively as the reason for technological progress, while the main emphasis is on productivity. Itself division of labor not difficult and studied in detail, but I draw the attention of readers to the fact, what depth of division of labor or as it is named in the article - division of labor- has never been used by anyone to characterize the economy.
Exactly division of labor made it possible to understand economic history as the interaction of the contours of different units of humanity, so that today neo-economics can predict the result of the interaction of the economies of different countries. Therefore, many problems of the modern economy, unsolvable in political economy and economics (simply due to the lack of a research apparatus in them), have become available for scientific study in NEOCONOMICS.
why does division of labor and specialization increase labor productivity? and got the best answer
Answer from Nikolay Golubtsov [guru]
The simpler the work, the easier it is to teach, the easier it is to control, the easier it is to increase the speed of work.
Answer from Ѐilgrim[guru]
So says NOT.
Answer from Nikolay Mavrin[guru]
Objective given.
Answer from Iimur Ivanov[guru]
It depends on what kind. It depends on how, in a complex, this work is provided and organized. If there are enough narrow specialists to carry out each cycle of the production process, then of course it helps. If, for example, you have a private enterprise in which only a janitor who sweeps the porch and another person who is able to very skillfully perform only one production operation is employed, and 50 is required, then of course not ... does not contribute.
Answer from N_esta[newbie]
"" Specialization in the production process. A set of jobs can usually be completed cheaper with a large number of people each performing a small number of specialized tasks than one person trying to complete the entire job. The idea that specialization lowers costs and thus the consumer pays the price is embedded in the principle of comparative advantage. The division of labor is the basic principle behind the assembly line in systems mass production. ""
Answer from NO[guru]
An innate property of all living things and Man, including the desire to reduce the costs of his activity to achieve any goal. When repeating similar conditions for achieving similar or identical goals, learning how to achieve a goal means choosing the least costly way. And labor productivity is the amount of costs (no matter what - calories. Time) to obtain a goal - a product.
Answer from Andrey Kuznetsov[expert]
It is more convenient, easier and more understandable for a person to work this way.
Primitive communal model of economic development: the main stages of formation and features.
Signs:
Low level of development of productive forces and their slow improvement
Collective appropriation of natural resources and production results
Equal distribution, social equality
Lack of private property, exploitation, classes and state
Low rates of development of society.
Stages:
Paleolithic (ancient Stone Age) - 3 million - 12 thousand years BC
Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) - 12 - 8 thousand years BC
Neolithic (New Stone Age) - 8 - 3 thousand years BC
1st Early Paleolithic (up to 100 thousand years BC). Pithecanthropus, Sinanthropus, Neanderthals - gathering, fishing and driven hunting.
2-Middle Paleolithic (ended 40 thousand years ago). Cro-Magnon man along with Neanderthals. Articulate speech. Making fire. Stone technology.
3-late Paleolithic (completed in the XII millennium BC). Matriarchy. Public prohibitions. Simple appropriative economy - hunting, fishing and gathering. The level of stone technology has increased. Labor as a simple cooperation without division. Everything is collectively owned. Labor distribution of production. Exchange between communities.
4-Mesolithic (XII-VIII millennium BC). Individual hunting. Improvement of weapons, the appearance of a bow. New techniques in fishing. Lightening the weight and reducing the volume of stone tools. An appropriating farm of lower hunters, gatherers and fishermen. The principle of collectivization. Use of boats. Development of new lands. Several of the closest clans began to unite into a tribe. Patriarchy.
5th Neolithic (VIII-IV millennium BC). The first social division of labor into agricultural and cattle breeding. Then the second social division of labor - the separation of craft from Agriculture- individualization of labor, the emergence and development of private property. The first craft is pottery. "Neolithic revolution" - the emergence new technology, forms of production and way of life, the development of new territories and their effective use. The origin of exchange - because surplus agricultural and handicraft industries appeared. The transition to a sedentary lifestyle.
6-Eneolithic (4-3 thousand BC). The appearance of metal - copper, gold, bronze. Irrigated and plow farming system, increasing property inequality.
The first and second social division of labor: causes, essence and consequences.
First division of labor:
Prerequisites:
The emergence and spread of agriculture in fertile regions, then the domestication of animals, which often gave more income than agriculture. Some tribes even completely switched to cattle breeding.
Essence:
In the general mass of primitive tribes, 2 groups were distinguished: cattle-breeding and agricultural.
Consequences:
1.transition to a sedentary lifestyle
2. growth of labor productivity
3.the possibility of accumulating stocks (wealth)
4.the origin of trade (exchange in kind)
5. development of religion, art.
Second division of labor:
Causes:
The emergence of free time due to the growth of labor productivity (less time and energy consumption was required to get food), the emergence and development of crafts.
Essence:
Distinguishing handicrafts from agriculture.
Consequences:
1.individualization of labor
2. development of private property
RESULT:
Transition to a producing economy:
Variety of products to exchange
Expanded exchange system
The need to enter a universal equivalent.







 From a student of a FZU school to a director and a minister (Hero of Socialist Labor V
From a student of a FZU school to a director and a minister (Hero of Socialist Labor V Law on public organizations of the Russian Federation
Law on public organizations of the Russian Federation Votkinsk machine-building plant: history, products, address Votkinsk machine-building plant
Votkinsk machine-building plant: history, products, address Votkinsk machine-building plant Founder's decision to appoint a director of sample ltd
Founder's decision to appoint a director of sample ltd Sample notification of the start of business
Sample notification of the start of business What is a journal-order accounting system in accounting
What is a journal-order accounting system in accounting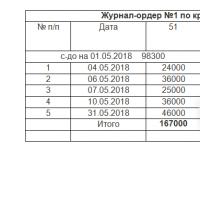 Journal-order: sample filling
Journal-order: sample filling