Technological pump operator of compressor units hazard net. Labor protection instructions for the compressor unit operator. Measures and means to ensure labor safety
The compressor operator is a specialist who ensures uninterrupted operation, maintains it, prepares it for starts and stops. In his work he is obliged to maintain the established technological rhythm.
With the help of automation equipment, measuring and control devices, protection and alarm systems, as well as blocking, the compressor unit operator inspects the equipment and determines the causes of breakdowns, after which they eliminate them.
Requirements
The job description of the compressor unit operator describes a list of duties for which the absence of contraindications is required. If an employee has health problems, then it is strictly forbidden to work on this installation.
The compressor operator must have vision that is resistant to fatigue. Sharp vision with normal color discrimination is one of the important criteria.
Good hearing, keen sense of smell, developed memory are qualities that must be at a high level.
Physically demanding work requires a lot of stamina. In case of health problems, as a result of which heavy physical activity and monotonous work are contraindicated, the employee must be dismissed.
The ability to work in a large team is an important personal skill, without which it is difficult to imagine the work of a mechanic.
Contraindications to work in this position are violations of the vestibular apparatus, hearing and visual impairments, a predisposition to colds.
Qualification Requirements
Difficult and responsible work for this employee. The compressor operator must have extensive knowledge in the field of chemistry, physics, electrical engineering. Knowledge of types and types is required to do the job efficiently.
Knowledge of the technological processes used in production is the key to successful work.
It is also necessary to know the principles of operation of the installation, the device of the compressor, electric motors, as well as the instruments with which measurements are taken.
Discharges
According to the reference book, there are 5 categories of compressor operators. For each, its own requirements for professional training are put forward, as well as the responsibilities that the employee must fulfill in this position are described.

In the ETKS classifier, machinists of the second, third, fourth, fifth and sixth categories are distinguished.
The highest is the second category, it is subject to the highest requirements in terms of experience and skills. The sixth, respectively, is the lowest.
The ranks of the compressor unit driver are assigned according to work experience. Responsibilities, as well as the level of remuneration, depend on the category.
Second rank
The operator of the compressor installation of the second category serves compressors with an operating pressure of up to 10 kgf / cm 2 (1 MPa). The flow rate of this unit is 5 m 3 / min.
Responsibilities include:
- starting, stopping and regulating compressors;
- monitoring the operation of auxiliary equipment, as well as the compressors themselves;
- lubrication of parts of mechanisms experiencing friction;
- prevention of malfunctions in the compressor;
- elimination of the arisen malfunctions;
- monitoring the operation of safety devices;
- repair of drive motors;
- filling oil into emergency tanks and service tanks, as well as pumping out oil;
- participation in the repair of compressor equipment.
Knowledge for the second category
The instruction of the compressor installation driver presupposes the availability of professional knowledge, without which the performance of direct duties will be impossible.

The employee must know:
- principles of turbocharger operation;
- the principle of operation of a reciprocating compressor;
- operation of steam engines and turbochargers;
- the principle of operation of electric motors;
- how to troubleshoot motors and compressors;
- methods of using instruments for measurements and control, as well as the purpose of each instrument;
- station piping diagram;
- working pressure and air temperature corresponding to each mode;
- the permissible temperature to which the operating unit of the unit can be heated;
- ways to eliminate overheating, as well as measures to prevent overheating;
- brands of oils used in the unit for lubrication of units.
Third rank
The compressor plant operator is trained not only at vocational schools or universities. There are advanced training courses, after which the student is issued a certificate of awarding him a higher grade.

Turbocompressors and stationary compressors with an operating pressure of up to 10 kgf / cm 2 (1 MPa), flow - above 5 m 3 / min. and up to 100 m 3 / min. Or installations with pressures above 10 kgf / cm 2 (1 MPa) and feed up to 5 m 3 / min. when working with non-hazardous gases driven by different motors.
For a specialist of the third category, duties are:
- regulation and start-up of compressors, engines and turbochargers;
- maintaining the required parameters of the compressor;
- switching between different units;
- prevention of emergency situations in the operation of the station;
- preparation of technical documentation for the operation of the serviced equipment;
- taking part in the repair of units and parts of the station.
Knowledge for the third grade
An employee with a third grade should know:
- reciprocating compressors, internal combustion engines, electric motors, steam engines and installations;
- technical characteristics of the described units and rules for their maintenance;
- arrangement of control and measuring equipment, maintenance rules and technical characteristics;
- installation piping diagram;
- the documentation required for the operation of the installation;
- fundamentals of thermodynamics, as well as electrical engineering;
- gas properties in compressor operation.
Fourth grade
The driver with the specified discharge serves turbocompressors and stationary compressors up to 10 kgf / cm 2 (1 MPa). The flow rate in these installations is more than 100 m 3 / min.
The work consists in:
- establishment and maintenance of an advantageous mode for compressor operation;
- monitoring the health of engines, devices, mechanisms;
- participation in the inspection and repair of equipment (according to the qualifications of a locksmith with the 3rd grade).
Knowledge for the fourth grade
To perform duties at a high level, he must know:
- design features, as well as the device of various types of compressors, internal combustion engines, turbochargers, electric motors, complex instruments for control and measurement, fittings and equipment, steam engines;
- layouts of pipelines, steam pipelines, tanks and fittings;
- diagrams according to which the automatic device for blocking the operation of the station is located;
- technical characteristics of the compressors to be serviced;
- electricity consumption rates for the normal operation of the station;
- consumption rates of materials for the production of gases or compressed air.
Fifth rank
The fifth-grade driver serves automated stations up to 100 m 3 / min.

His responsibilities are:
- switching over, as well as taking out the equipment for repair and into a standby state;
- regulation of technical processes;
- drawing up lists of defects, as well as lists for equipment repair;
- repair of station equipment (qualification of a locksmith of the 4th grade);
- repairing internal combustion engines and compressor units in the field and on-site conditions.
Knowledge for the fifth grade
A fifth-grade mechanic should know the internal structure well enough.

Required knowledge:
- kinematic diagrams of turbochargers, electric motors, steam engines, internal combustion engines;
- high pressure compressor devices;
- operating rules and characteristics of auxiliary equipment, steam engines, electric motors, turbocompressors;
- technological processes of the station;
- Compressor efficiency and applied structures and systems.
Sixth rank
The work of a sixth-grade machinist requires the greatest concentration, and knowledge must be supported not only by theory, but also by practice. Due to the fact that the serviced units have a large capacity, the employee must be able to carry out:
- watching over correct work equipment for the entire station;
- regulation of the process for the production of products of the station's work;
- preparation of defective statements;
- equipment repair (qualification of a locksmith of the 5th category).
Knowledge for the sixth grade
Knowledge is required:
- turbocharger design;
- kinematic diagrams;
- various power equipment: steam engines, electrical equipment, internal combustion engines;
- characteristics for the operation of power plants of compressors.
Work safety
Labor protection of the compressor unit operator is regulated by the current legislation of the Russian Federation. Labor legislation, as well as health and safety standards, establish the permissible operating limits for mechanics. The mode of work is consistent with the qualifications and is based on the health status of the employee.

Vacancies
In Moscow, the operator of compressor units receives from 80,000 rubles. An employee of this category is required for large manufacturing enterprises... To submit your resume for consideration, you need to monitor the labor market and track emerging vacancies.
SOLUTION
In the name of the Russian Federation
Pervomaisky District Court of the Tambov Region, composed of the presiding judge I.G. Tsuprik, with the participation of the plaintiff Davydkin M.I.<данные изъяты>"Inozemtseva O.B., the representative of the defendant of the State institution - the Office of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation in<данные изъяты>Zavrazhneva OA, with the secretary Alyokhina E.V. to the State Institution - Management of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation in<данные изъяты>on the inclusion in the length of service of the periods necessary for the appointment of an early labor old-age pension and on the appointment of an early labor old-age pension,
installed:
Davydkin M.I. filed a lawsuit against the State Institution - the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation in<данные изъяты>on the inclusion in the length of service of the periods necessary for the appointment of an early labor old-age pension and on the appointment of an early labor old-age pension, referring to the following circumstances. He was born DD.MM.YYYY. His total insurance work experience at DD.MM.YYYY was 38 years 11 months 7 days, of which special work experience at work with difficult working conditions, giving the right to assign an early retirement pension, is 26 years 4 months 11 days of work in a position a technological compressor operator, who is engaged in the maintenance of gas compressors (except for air) at the Pervomaisk Office of Main Gas Pipelines, a branch of LLC<данные изъяты>»), Including in the periods: from DD.MM.YYYY to DD.MM.YYYY (17 years 10 months 27 days); from DD.MM.YYYY to DD.MM.YYYY (5 years 3 months 29 days); from DD.MM.YYYY to DD.MM.YYYY (3 years 1 month 15 days). In the position of a technological compressors operator, employed in servicing gas compressors (except air) in LLC ", he works with DD.MM.YYYY to the present on the basis of order No. / k from DD.MM.YYYY. In the periods from April 21 to DD.MM.YYYY and from September 9 to DD.MM.YYYY in the direction of the employer, he was on refresher courses for the specified position. These periods are excluded from the specified special length of service required for the appointment early retirement old age. In accordance with subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 27 of the Federal Law "On Labor Pensions in the Russian Federation" No. 173-FZ of December 17, 2001, an old-age labor pension is assigned before reaching retirement age, for men upon reaching the age of 55, if they have worked in jobs with difficult working conditions for at least 12 years and 6 months and have an insurance record of 25 years. The list of positions with difficult working conditions that give the right to an early retirement pension is established by List No. 2 of industries, jobs, professions, positions and indicators that give the right to preferential pensions, approved by Resolution No. 10 of the Cabinet of Ministers of the USSR dated January 26, 1991. XXXIII "General Professions" of the same List No. 2, position 23200000-14257 provides for the position of a technological compressor operator, engaged in the maintenance of gas compresses (except for air). That is, if he has a special experience of at least 12 years and 6 months, an insurance experience of 25 years and reaching the age of 55, he is entitled to an early retirement pension. DD.MM.YYYY he applied to the State Institution - the Office of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation in<данные изъяты>with an application for the appointment of an early retirement pension, providing the necessary documents for its registration. In accordance with the Protocol of the Pension Fund from DD.MM.YYYY No. in the appointment of the specified pension he was denied. Of the above-mentioned periods of his work in LLC "in the position of a technological compressor operator engaged in servicing gas compressors (except for air), the defendant did not count him a single day in his special experience. The refusal to grant him an early pension was motivated by the absence, according to the defendant, in the disputed periods of his full employment during the working day as a technological compressor operator, engaged in servicing gas compressors (except for air). In particular, in the protocol the defendant refers to the letter of LLC according to which there are two shops on the territory of the gas compressor station: a turbo-driven and an electric-driven shop, from which the electric-driven shop is in a reserve state and works according to the telephone message for the start-up of gas-pumping units with an electric drive (EGPA), the operating time for this workshop for the period from DD.MM.YYYY to DD.MM.YYYY years was<данные изъяты>hours (at a monthly rate -<данные изъяты>hours); for discrepancies between the LLC certificate specifying the special nature of the work required for the early appointment of a pension and the data of its individual personal account (ILS ZL); on the book of orders, according to which he was annually provided with additional leaves for harmful conditions labor in the amount of 3 days, and according to the collective agreement for DD.MM.YYYY year, additional leave in the same number of days was provided for other professions; on the lists of persons retiring for DD.MM.YYYY years, in which the drivers of the electric drive shop are absent; on the attestation cards of the workplace for DD.MM.YYYY years, according to which the class of working conditions for the electric drive workshop was - "2" hazard class, and for the turbo drive workshop - "3.2". He completely disagrees with the defendant's decision to refuse to grant him an early retirement pension, and considers it unreasonable. Working in the aforementioned periods in LLC "as a technological compress operator, engaged in servicing gas compresses (except for air), he developed the necessary special work experience in difficult working conditions, which gives him the right to assign an early retirement pension. So, the certificate of LLC "from DD.MM.YYYY for №, specifying the special nature and working conditions necessary for the early appointment of a labor pension for old age, it is confirmed that in the period from DD.MM.YYYY on DD.MM.YYYY; from DD.MM.YYYY to DD.MM.YYYY; from DD.MM.YYYY to DD.MM.YYYY he worked in LLC "as a technological compressor operator, engaged in servicing gas compressors (except air) in special conditions labor. According to the clarifying certificate, in the periods from April 21 to DD.MM.YYYY and from September 9 to DD.MM.YYYY in the direction of the employer, he took advanced training courses for the specified position. The certificate also reflects that during the disputed period, he was not on parental leave, unpaid leave and student leaves, did not work for easy labor , did not participate in strikes, did not work part-time and did not combine work in other professions and positions. As indicated above by List No. 2, approved by Decree No. 10 of the Cabinet of Ministers of the USSR dated January 26, 1991, No. 10, the position he held in disputable periods as a technological compressor operator engaged in servicing gas compressors (except for air compressors) is provided for as a position with harmful and difficult working conditions , employment in which gives the right to an old-age pension on preferential terms provided for by subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 of article 27 of the Federal Law "On Labor Pensions in the Russian Federation" No. 173-FZ of December 17, 2001. According to clause 4 of the Rules for calculating periods of work, which gives the right to early assignment of an old-age retirement pension, approved by the Government of the Russian Federation of July 11, 2002 No. during a full working day, unless otherwise provided by these Rules or other regulatory legal acts, provided that insurance contributions are paid to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation for these periods. In accordance with clause 5 of the Clarification of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation of May 22, 1996 "On the procedure for applying the lists of industries, jobs, professions, positions and indicators, giving in accordance with Articles 12, 78 and 78.1 of the RSFSR Law" On state pensions in the RSFSR "(as amended and additions of October 1, 1999) full-time work means the performance of work in the working conditions provided for by the Lists, at least 80 percent of the working time. At the same time, the specified time includes the time for performing preparatory and auxiliary work, and for workers performing work with the help of machines and mechanisms, also the time for performing repair work of a current nature and work of a current nature and work on the technical operation of equipment. The specified time may include the time of performance of work performed outside the workplace in order to ensure basic labor functions. It follows from the specified reference from the employer that during a full working day (except for periods of being on advanced training courses), he worked as a technological compressor operator, who was engaged in servicing gas compressors (except air) in special working conditions. Thus, the employer's clarifying certificate confirms that during the periods: from DD.MM.YYYY to DD.MM. YYYY; from DD.MM.YYYY to DD.MM.YYYY; from DD.MM.YYYY by DD.MM.YYYY he worked in this organization as a technological compressor operator, engaged in servicing gas compressors (except air) in the gas compressor service. Order No. / k from DD.MM.YYYY on his employment as a technological compressors operator did not indicate that he was hired in an electric drive shop, but indicated that he was accepted as a third-class technological compressor operator to the staff of the gas compressor service. The fact that he works in the electric drive workshop is indicated only in the clarifying certificate of the employer. At the same time, the structure of the LLC throughout all the controversial periods provided for a single gas compressor service serving various types of units, without dividing the maintenance areas of the main and auxiliary equipment and dividing the service into turbo-drive and electric-drive workshops, the division into workshops is conditional. V<данные изъяты>UMG has 3 electric drive workshops with 22 units in each and 1 turbo drive workshop, vk. XXX unit. Turbo-driven and electric-driven units drive gas compressors. He, as a technological compressor operator, during all controversial periods worked in electric and turbo-driven workshops without special order... Turbo-driven compressors are constantly in operation, while electric-driven ones are in standby. The reserve of electrically driven compressors does not imply a shutdown of the unit; the gas passes through the turbo-driven and electrically driven workshops. Electric-driven shops, like turbo-driven ones, are constantly under pressure. Its work is directly related to the work of the gas compressor unit (GCU). Information about the operating time for the electric drive workshop for the period from DD.MM.YYYY to years (<данные изъяты> hours), which the respondent refers to in the protocol, are taken into account only for the maintenance of the unit, and does not indicate that it is busy servicing gas compressors. The defendant, referring to the workplace certification cards for DD.MM.YYYY year, concludes that since, according to the workplace certification data for DD.MM.YYYY, the class of working conditions for the electric drive workshop was "2" hazard class, then there are no harmful working conditions in the electric drive workshop. This conclusion is untenable, since his position as a technological compressor operator engaged in servicing gas compressors (except air) is provided for by List No. 2, approved by Decree No. 10 of the USSR Cabinet of Ministers dated January 26, 1991, in Section XXXIII "General Professions", position 23200000 -14257 without indicating the degree of hazard. In addition, in accordance with paragraph 1 of the Ordinance of the Ministry of Social Protection of the Population of the RSFSR dated April 20, 1992 No. 1-28-U "On the Procedure for Applying the Law of the RSFSR" On State Pensions of the RSFSR "when assigning preferential pensions to employees, there is no need to demand from the heads of enterprises, organizations and data institutions on the results of certification of workplaces, conclusions of state examination bodies, sanitary-epidemiological stations and other bodies on the actual working conditions at workplaces. However, if the Lists for certain categories of workers, managers and specialists indicate indicators (conditions) under which they are granted pension benefits: hazard classes of harmful substances received or used, employment in hot work areas, mining in quarries and reserves with a depth of 150 m. and below, etc., then such information must be confirmed by a clarifying certificate with a link to the documents. In List No. 2, no additional conditions (for example, the degree of harm and danger) are indicated for the position of a technological compressor operator engaged in servicing gas compressors (except for air). Therefore, the results of certification, regarding the degree of harm, do not in any way affect the resolution of the issue of assigning him an early retirement pension. Line 110 of the certification cards of the technological compressor driver for 2006 indicates the preferential pension provision according to the specified List No. 2, section XXXIII "General professions", position 23200000-14257. In fact, during the controversial periods, he worked as a technological compressor operator engaged in servicing gas compressors (except for air) of the LLC gas compressor service. " The defendant's argument that, in accordance with the collective agreement for DD.MM.YYYY, additional vacations are provided to the compressor operators in the amount of three days, cannot be grounds for concluding that during these periods he did not work with harmful and difficult conditions labor employment, in which it gives the right to an old-age pension on preferential terms, and, accordingly, the grounds for refusing to grant him an early labor old-age pension. Thus, his total insurance work experience is 38 years 11 months 7 days, of which special work experience at work with difficult working conditions, which gives the right to assign an early retirement pension for work in LLC "as a technological compressor operator engaged in servicing gas compressors (except air) is 26 years 4 months 11 days, including periods: from DD.MM.YYYY to DD.MM.YYYY (17 years 10 months 27 days); from DD.MM.YYYY to DD.MM.YYYY (5 years 3 months 29 days); with DD.MM.YYYY by DD.MM.YYYY (3 years 1 month 15 days), which is the basis for assigning him an early retirement pension. Based on the foregoing and in accordance with subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 27 of the Federal Law "On Labor Pensions in the Russian Federation" No. 173-FZ of December 17, 2001, Resolution of the Cabinet of Ministers of the USSR No. 10 of January 26, 1991 on the approval of List No. 2, asks include him in the length of service, giving the right to an early retirement pension for old age, the periods of work in LLC "in the position of a technological compressor operator, employed in servicing gas compressors (except air): from DD.MM.YYYY to DD.MM.YYYY; with DD.MM.YYYY by DD.MM.YYYY, with DD.MM.YYYY by DD.MM.YYYY, and oblige the State Institution - the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation to<данные изъяты>assign him an early retirement pension with DD.MM.YYYY.
At the hearing the plaintiff Davydkin M.AND. He supported the claim, and also supplemented it with the requirements for the recovery of court costs from the defendant:<данные изъяты>rubles - payment for the services of a representative and<данные изъяты>rubles - payment of the state fee. He explained that the structure of the LLC throughout all the controversial periods provided for a single gas compressor service serving various types of units, without dividing the maintenance areas of the main and auxiliary equipment and dividing the service into turbo-driven and electric-driven workshops. Electric drive units are located in three rooms, 22 units each, 3 turbo drive units are located in one room. During his work, he serviced electric drive units that are constantly under pressure. Maintenance of units that are in reserve is more difficult than those that are constantly in operation. Service takes place daily. The principle of operation of the turbo-driven and electric-driven compressors is the same, the main and auxiliary equipment of the workshops is identical. The gas compressor is the same for both turbo-driven and electric-driven units. The working conditions in these workshops are the same in terms of harmfulness. He worked shifts and daily. He is a 6th grade machinist. Performed the following work: maintenance of individual process compressors, unit level control panels. Start-up and shutdown of gas-pumping units, control over the operation of technological equipment, regulation of the technological mode of operation of gas-pumping units. Production of operational switching in electrical installations with voltages up to 1000 volts in workshops with electrically driven gas pumping units. Identification and elimination of malfunctions in the operation of gas pumping units, repair of compressors, their drives, apparatuses, gas communication units and auxiliary equipment of workshops. Maintenance of repair forms. He was also engaged in work related to the maintenance of electric drive units. He worked full time and was not engaged in work not related to the maintenance of gas compressors. The workplace certification cards for the working conditions of a technological compressor operator indicate that he is entitled to preferential pension provision according to Schedule 2, section 33 of work, profession, positions and indicators giving the right to preferential pension provision, approved. By the decree of the Cabinet of Ministers of the USSR of January 26, 1991, No. 10. He signed the certification cards and had no doubt that he had the right to an early retirement pension.
The plaintiff's representative is lawyer E. B. Mikhina. the plaintiff's claims were supported and explained that the structure, staffing and staffing table LLC, throughout all the controversial periods, provided for a unified gas compressor service serving various types of gas compressor units (GCU), without dividing service areas for the main and auxiliary equipment, and the division of the service into turbo-drive and electric-drive workshops is conditional in order to determine the required number of drivers to work on gas compressors. These facts are also confirmed by the testimony of the witness FULL NAME6, working in LLC in the position of chief engineer. Certificate of LLC ”, specifying the special nature and working conditions necessary for early appointment to MI Davydkin. The old-age labor pension confirms that during the controversial periods he worked in LLC "as a technological compressor operator, who is engaged in servicing gas compressors (except for air ones). In his objections, the defendant considers that the case materials have not confirmed that during the disputable periods during the full working day (80% of the working time) the plaintiff was busy and performed work with harmful and difficult working conditions. As one of the arguments, the defendant indicates that the electric drive shop in which the plaintiff worked was in a state of reserve, and the operating time for this shop for the period from DD.MM.YYYY for years was<данные изъяты>hours (at a monthly rate -<данные изъяты>hours), and believes that maintenance of electric drive units is possible only when they are in working order. This argument of the defendant is untenable. Firstly, the defendant has no special knowledge in the field of the gas compressor service. Secondly, it is refuted by the testimony of the witness FULL NAME6, according to which in<данные изъяты> UMG has 3 electric drive workshops with 22 units in each and 1 turbo drive workshop, vk. XXX unit, division into workshops is conditional. Turbo-driven and electric-driven units drive gas compressors. Turbo-driven compressors are constantly in operation, while electric-driven ones are in standby. The reserve of electrically driven compressors does not imply a shutdown of the unit; the gas passes through the turbo-driven and electrically driven workshops. Electric-driven shops, like turbo-driven ones, are constantly under pressure. Maintenance of compressors in standby is more difficult than those that are constantly in operation, their maintenance is performed daily. The principles of operation of electric and turbo-driven compressors are the same, the main and auxiliary equipment of the shops is identical. The working conditions in these workshops are the same in terms of harmfulness. Witness FULL NAME6 also explained that the operating time for compressor shops with electric drive units is taken into account only for maintenance of the unit (accounting for its wear, etc.), but does not show the driver's employment in servicing gas compressors. Based on the indicated testimony of the witness, the defendant unreasonably concludes that the drivers of technological compressors employed in servicing electric drive units are not engaged in their maintenance, but in monitoring the operation of only auxiliary equipment. The testimony of the witness FULL NAME6 testifies to the technological process of the gas compressor service as a whole, the mechanism and operating conditions of the turbo-drive and electric drive units. The software line of the certification cards indicates preferential pension provision according to the specified List No. 2, section XXXIII "General professions", position 23200000-14257 position - technological compressor operators employed in servicing gas compressors (except air). List No. 2, approved by the Decree of the Cabinet of Ministers of the USSR No. 10 dated January 26, 1991, provides for the position of a technological compressor operator engaged in servicing gas compressors (except for air), but no additional conditions (for example, the degree of harm and danger) are specified or set depending on the workshop in which this work is carried out. Therefore, the results of these attestations do not in any way affect the resolution of the issue of assigning an early retirement pension to the plaintiff. In accordance with clause 5 of the Clarification of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation of May 22, 1996 “On the procedure for applying the lists of industries, jobs, professions, positions and indicators given in accordance with Articles 12, 78 and 78. 1 of the Law of the RSFSR "On state pensions in the RSFSR" (with amendments and additions dated October 1, 1999) full-time work means the performance of work in the working conditions provided for by the Lists, at least 80 percent of the working time. At the same time, the specified time includes the time for performing preparatory and auxiliary work, and for workers performing work with the help of machines and mechanisms, also the time for performing repair work of a current nature and work on the technical operation of equipment. The specified time may include the time of performance of work performed outside the workplace in order to ensure basic labor functions. The full employment of the plaintiff at work in the position of a technological compressor driver, servicing gas compressors during a full working day, that is, at least 80% of the working time, is confirmed by the specified certificate of LLC "from DD.MM.YYYY No. specifying the special nature and working conditions, necessary for the early appointment of an old-age labor pension. From which it follows that during all the disputable periods the plaintiff worked in this organization as a technological compressor operator engaged in servicing gas compressors (except air) in the gas compressor service. He considers it proven in court that during the disputable periods the plaintiff was employed during a full working day (80% of the working time) and performed work in accordance with his position - a technological compressor operator engaged in servicing gas compressors (except air). The arguments of the defendant that the employer did not timely submit information about the plaintiff's employment in special working conditions; that the plaintiff was not included in the list of persons retiring in DD.MM.YYYY year; that he and other operators of technological compressors for the period of work at the enterprise with DD.MM.YYYY were not paid for harmful working conditions, and the annual additional leave was provided in the amount of three calendar days, cannot be the basis for refusing the plaintiff to assign an early retirement pension old age, since this right is provided for in paragraphs. 2 p. 1 art. 27 of the Federal Law "On Labor Pensions in the Russian Federation". In its objections to the claim, the defendant, referring to the Instruction on labor protection for the operator of technological compressors (electric drive workshop) No. 1-002 dated April 10, 2008, concludes that when the compressor workshop with electric drive units is in a state of reserve the driver's place is missing some dangerous and harmful production factors, and accordingly there are no harmful and difficult working conditions. This conclusion is untenable, since the defendant is not competent in determining the presence or absence of harmful production factors provided that the compressor electric drive units are in a hot standby state. The UPF's argument that the presented Davydkina M.AND. receipt of lawyer education No. from DD.MM.YYYY for the amount -<данные изъяты>rubles does not confirm that he paid the lawyer<данные изъяты>»Mikhina E.B. the indicated amount, and also that the content of the receipt does not allow to reliably determine in relation to which dispute the payment for the services of a lawyer was implied. By virtue of the provisions provided for in paragraph 1 of Art. 25 and clause 15 of Art. 22 of the Federal Law “On Advocacy and the Bar” No. 63-FZ of May 31, 2002, advocacy is carried out on the basis of an agreement between a lawyer and a client, agreements on the provision of legal assistance in a bar association are concluded between a lawyer and a client and are registered in the documents of the bar association. According to paragraph 6 of Art. 25 of the specified Federal Law, the remuneration paid to the lawyer by the client, and (or) compensation to the lawyer for the costs associated with the execution of the order, must be paid to the cashier of the relevant lawyer education or transferred to the current account of lawyer education in the manner and terms provided for by the agreement. In accordance with the protocol of the Non-Profit Organization “<данные изъяты>») From DD.MM.YYYY lawyer Mikhina E.B. with DD.MM.YYYY she was accepted as a member of this board with a place of work in<данные изъяты>branch. DD.MM.YYYY between Davydkin M.AND. and a lawyer<данные изъяты>»Mikhina E.B. an agreement was concluded on the mandate to provide him with legal assistance in the preparation of a statement of claim to the Pervomaisky District Court for the appointment of an early retirement pension and representation in this court. In accordance with this agreement on receipt No. from DD.MM.YYYY, on which there is an imprint of the branch, Davydkin M.AND. paid in cash to the cashier of the Pervomaisky branch of NO "<данные изъяты>»The specified amount. The specified amount was subsequently by the lawyer E. B. Mikhina. was deposited to the current account<данные изъяты>branch NO "<данные изъяты>», Located in the branch № Michurinsky branch № Savings FULL NAME4 RF. Thus, there is no reason to doubt that the plaintiff paid the above amount in<данные изъяты>branch of NO "<данные изъяты>»For the lawyer EB Mikhina. legal assistance in the preparation of a statement of claim to the Pervomaisky District Court for the appointment of an early retirement pension and representation of his interests in court. The arguments of the UPF regarding the inconsistency of the form of the specified receipt with the current legislation has nothing to do with the stated claim for the recovery of court costs, since the fact of payment for the services rendered to the lawyer<данные изъяты>»Mikhina E.B. confirmed by the specified receipt, and cannot be the basis for refusing to reimburse him legal costs. In addition, in accordance with Part 5 of Art. 53 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, the right of a lawyer to appear in court as a representative is certified by an order issued by the relevant lawyer education. Powers of attorney E. B. Mikhina when considering the case in the Pervomaisky District Court of the Tambov Region as a representative of Davydkin M.AND. were certified by order No. from DD.MM.YYYY, issued to the lawyer<данные изъяты>", Available in the materials of the civil case. Therefore, there was no need to attach to the plaintiff's application for reimbursement of court costs documents confirming the affiliation of the lawyer E.B. Mikhina. To<данные изъяты>branch of NO "<данные изъяты> ". According to Art. 48 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, citizens are entitled, and not obliged to conduct their affairs in court in person or through a representative, Davydkin M.AND. could conduct this case in court independently, without a representative. By virtue of the provisions of Part 1 and Part 4 of Art. 421 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a citizen independently determines the need to conclude an appropriate agreement (freedom to conclude an agreement), at the discretion of the parties to the agreement, its conditions are determined, including the amount and conditions for payment of remuneration to a lawyer for legal assistance provided. In accordance with Art. 48 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, citizens have the right to conduct their affairs in court personally or through a representative; personal participation in a citizen's case does not deprive him of the right to have a representative in this case. At the same time, the legislator does not associate this right with the complexity of the dispute, the presence of a citizen of special knowledge in the field of law. In this case, the plaintiff exercised his right to a conclusion with a lawyer E. B. Mikhina. contract from DD.MM.YYYY for the onerous provision of services for drawing up a statement of claim to the Pervomayskiy District Court on the appointment of an early retirement pension and representation of his interests in court. By virtue of the provisions of Part 1 and Part 2 of Art. 98, art. 100 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation to the party in favor of which the court decision was made, the court awards the other party to reimburse all costs incurred, including the costs of paying for the services of a representative. According to Art. 88 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, court costs consist of state fees and costs associated with the consideration of the case. In accordance with Art. 94 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, the costs associated with the consideration of the case include the costs of paying for the services of a representative. Consequently, the UPF's argument that the UPF should not be responsible for the implementation by M.I.Davydkin the right to conclude with a lawyer E. B. Mikhina. of the contract of assignment for the provision of paid legal services for the preparation of a statement of claim to the Pervomaisky District Court for the appointment of an early retirement pension and representation of his interests in court have no legal basis. By virtue of the provisions of Art. 6 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation on the administration of justice in civil cases on the basis of equality before the law and the court, in this case all organizations, regardless of their organizational and legal form, form of ownership and other circumstances, the UPF is obliged to compensate Davydkin M.I. all legal costs incurred by him related to the consideration of this case in court. The UPF's argument that the plaintiff's legal costs to be reimbursed exceed all reasonable limits is unfounded. By the Council of the Bar Association from DD. MM.YYYY a letter of recommendation on fee practice was approved<адрес>and<адрес>for the work of a lawyer. According to paragraphs 5, 10 of this letter to lawyers<адрес>it is recommended to charge at least<данные изъяты>rubles (unit of measurement - a document) for the preparation of complex statements requiring the study of the issue, the application of a significant number of legal acts, the application of technical and similar norms and rules and other documents, and<данные изъяты>rubles (unit of measurement - a day) for representation in civil cases in courts of general jurisdiction - first instance and appellate instance. The note to this letter of recommendation also states that the lawyer has the right to reduce or increase the recommended amount of payment, depending on the volume and complexity of the work, the length of time for its registration and other circumstances. It should be noted, however, that this letter of recommendation was approved in 2007. When concluding a commission agreement and determining the amount for representing the interests of M.I.Davydkin in the court of first instance of the Pervomaisky District Court, lawyer E.B. Mikhina. was guided by the amount of the amount for this type of legal assistance specified in the letter of recommendation. Thus, the amount paid by the plaintiff for the provision by the lawyer E. B. Mikhina. legal assistance to represent his interests in the court of first instance of the Pervomaisky District Court correspond to reasonable limits, and is subject to collection from the UPF in full.
The representative of the defendant of the State institution - the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation in<данные изъяты>Zavrazhneva O.A. she did not agree with the claims and explained. In accordance with subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 of Art. 27 of the Federal Law of December 17, 2001 No. 173-FZ "On labor pensions in the Russian Federation", an old-age labor pension is assigned to men upon reaching the age of 55, if they have worked in jobs with difficult working conditions for at least 12 years 6 months and have insurance experience of at least 25 years. Clause 2 of Article 27 of the Law provides that the Lists of relevant jobs, industries, professions, positions and specialties and institutions, taking into account which the labor pension is assigned, provided for in paragraph 1 of this article, as well as the rules for calculating the periods of work for the appointment of labor pensions, if necessary, are approved by the Government of the Russian Federation. Federation. In order to implement this provision of the law, the Government of the Russian Federation adopted a resolution of July 18, 2002 No. 537 "On lists of industries, jobs, professions and positions, taking into account which an old-age retirement pension is assigned ahead of schedule in accordance with article 27 of the Federal Law Federation ". In accordance with sub. "B" of clause 1 of the said resolution for the early assignment of an old-age retirement pension to workers employed in jobs with difficult working conditions, List No. 2 of industries, jobs, professions, positions and indicators with harmful and difficult working conditions, approved by the decree of the Cabinet of Ministers of the USSR from January 26, 1991 No. 10. Also, the Russian government adopted a resolution of July 11, 2002 No. 516 "On approval of the Rules for calculating periods of work, giving the right to early assignment of an old-age labor pension in accordance with Articles 27 and 28 of the Federal Law" On labor pensions in Russian Federation". Clause 4 of these Rules provides for such required condition to include periods of work in the seniority, giving the right to the appointment of an old-age retirement pension ahead of schedule, as the performance of such work, constantly throughout the full working day. The Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation in Clarification of May 22, 1996 No. 5 "On the procedure for the application of lists of industries, jobs, professions, positions and indicators giving, in accordance with Articles 12.78 and 78.1 of the RSFSR Law" On State Pensions in the RSFSR ", the right to an old-age pension in connection with special working conditions and retirement pension ”(approved by the Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation of May 22, 1996, No. 29), it is stated that full-time work means the performance of work at least 80 percent of the working time. In accordance with section XXXIII, position No. 23200000-14257 of the List No. 2 of industries, jobs, professions, positions and indicators with harmful and difficult working conditions, employment in which gives the right to a retirement pension (old age) on preferential terms, approved by the Resolution of the Cabinet Ministers of the USSR dated January 26, 1991 No. 10 (hereinafter List No. 2 dated January 26, 1991), the right to early appointment was granted to: Technological compressor operators engaged in servicing gas compressors (except for air ones). One of the necessary conditions for the appointment of such a pension is confirmation of the right to the appointment of such a pension by documents issued by the competent authorities containing reliable information about the applicant's work. In accordance with paragraph 1 of the instruction of the Ministry of Social Protection of the Population of the RSFSR dated April 20, 1992 No. 1-28-U "On the Procedure for Applying the Law of the RSFSR" On State Pensions in the RSFSR "when assigning preferential pensions to employees, there is no need to demand from the heads of enterprises, organizations and institutions data on the results of certification of workplaces, conclusions of state examination bodies, sanitary-epidemiological stations and other bodies on the actual working conditions at their workplaces. However, if the Lists for certain categories of workers, managers and specialists indicate indicators (conditions) under which they are granted pension benefits: hazard classes of harmful substances received or used, employment in hot work areas, mining in open pits and open-pit mines with a depth of 150 m and below, etc., then such information must be confirmed by a clarifying certificate with a link to the documents. According to the clarifying certificate No. issued by DD.MM.YYYY by the branch of LLC "<данные изъяты>»Davydkin M.I. worked by profession as a technological compressor operator, engaged in servicing gas compressors (except air) d. XXX, 5 of the electric drive shop of the gas compressor service DD.MM.YYYY (order No. / k from DD.MM.YYYY) by DD.MM.YYYY According to the documents presented by the branch of LLC "<данные изъяты>"And the documentary verification act No. from DD.MM.YYYY on the territory of the gas compressor service there are 2 shops: a turbo drive and an electric drive. The turbo-driven shop is in working order, the electric-driven shop is in a standby state and operates in accordance with the telephone message for the start-up of gas-pumping units with an electric drive (EGPA). Operating time in compressor shops with electric drives<данные изъяты>Pervomaisky UMG storage period for the dispatcher's logs is 5 years. There are discrepancies between the certificate specifying the special nature of work with the individual personal account of the insured person (ILS ZL), in this connection, the confirmation of the length of service is considered according to the primary documents of the accounting department and personnel documents. From DD.MM.YYYY year on extract from the individual personal account of the insured person, as well as on the form SZI-5K "Information on the pension rights of the insured person, the experience is indicated" on a general basis. " Full employment is not traced in these documents. So, according to the book of orders to Davydkin M.I. provided annually another vacation and additional leave for harmful working conditions in the amount of 3 days, but according to the collective agreement provided for DD.MM.YYYY gg. additional leave was also granted for other professions that do not belong to professions in the corresponding types of work. In the list of names of persons retiring from DD.MM.YYYY yy, there are no operators of the electric drive workshop. According to the attestation card of the workplace for DD.MM.YYYY for the electric drive workshop, the class of working conditions is "2" (permissible), and for the turbo drive workshop - "3.2" (harmful). The PFR office believes that the decision to refuse to grant an old-age retirement pension ahead of schedule to M.I. is legal and justified due to the lack of full employment of a technological compressor driver engaged in servicing gas compressors (except for air) of an electric drive workshop, in connection with which, the claims of M.I.Davydkin are not subject to satisfaction. In accordance with Part 1 of Art. 88 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, court costs consist of state fees and costs associated with the consideration of the case. Art. 94 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation does not include the costs of paying for the provision of services for the registration or drafting of the statement of claim to the costs associated with the consideration of the case. At the same time, by virtue of Art. 94 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, the costs associated with the consideration of the case also include the costs of paying for the services of representatives. In accordance with Part 1 of Art. 100 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation to the party in favor of which the court decision was made, at its written request, the court awards, on the other hand, the costs of payment for the services of a representative within reasonable limits. The FIU believes that the recoverable amount of costs associated with the consideration of the case exceeds all reasonable limits and is not reasonable. According to the applicant and confirms with copies of receipts attached to the application, the applicant to the lawyer E.B. Mikhina. paid<данные изъяты>rubles for drawing up a statement of claim and representation in the Pervomaisky District Court. These receipts bear an imprint of the stamp BUT “<данные изъяты> ". However, this form of receipt is not applied on the territory of the Russian Federation since December 1, 2008, due to the fact that the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of April 20, 1995 No. 16-00-30-33 "On the approval of the forms of strict reporting documents" force in accordance with the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 06.05.2008 No. 359. This circumstance is fully confirmed by the Letter of the Department of Tax and Customs Tariff Policy of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 26, 2009 No. 03-01-15 / 1-27. In addition, the application does not include documents confirming the affiliation of the lawyer to E. B. Mikhina. to the said organization, however, E.B. Mikhina is indicated as the cashier in the said receipts. Thus, these receipts, in the opinion of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, do not confirm the fact that the applicant's lawyer E.B. Mikhina. the indicated sums of money have been paid. In addition, Article 20 of the Federal Law of 31.05.2002 No. 63-FZ "On advocacy and the legal profession in the Russian Federation" (hereinafter - Federal Law No. 63-FZ) establishes that the forms of lawyers' formations are: a lawyer's office, a bar association, a lawyer office and legal advice. At the same time, these lawyers' formations, with the exception of the lawyer's office, are recognized as legal entities. Article 25 of Federal Law No. 63-FZ stipulates that advocacy is carried out on the basis of an agreement between a lawyer and a client, which is a civil contract concluded in a simple written form between the client and the lawyer (lawyers) to provide legal assistance to the client himself or to the person appointed by him. However, copies of the contract of order concluded between the lawyer E.B. Mikhina. and the applicant is not presented to the court and is not available in the case file. At the same time, by virtue of Art. 25 of Federal Law No. 63-FZ, an essential condition of the agreement concluded between the attorney and the client is the establishment of the procedure for the client to pay the attorney's remuneration and to compensate the attorney for expenses related to the execution of the client's order. At the same time, in accordance with clause 6 of Article 25 of Federal Law No. 63-FZ, the remuneration paid to the attorney by the client and (or) compensation to the attorney for expenses related to the execution of the order shall be obligatory entered into the cash desk of the relevant lawyer education or transferred to the current account of the lawyer education in the manner and the terms provided by the agreement. At the same time, lawyers 'formations, including lawyers' offices, do not fall within the scope of the Federal Law of 22. 05.2003 No. 54-FZ "On the use of cash registers in the implementation of cash settlements and (or) settlements using payment cards", since the scope of cash registers is cash settlements in cases of sale of goods, performance of work or provision of services. The Ministry of Finance of Russia, which is authorized to approve the forms of strict reporting forms, did not approve any receipts for accepting cash from citizens as forms of strict reporting for lawyers' associations. Until now, there are no instructions or explanations of the Ministry of Finance of Russia about the possibility of lawyers' associations using such a form of strict accountability as a receipt indicating the purpose of the funds being contributed. Consequently, cash payments for the provision of legal assistance in lawyers' associations should be carried out through credit institutions through non-cash payments. This position is confirmed by the Letter of the Ministry of the Russian Federation for Taxes and Duties dated May 28, 2004, No. 33-0-11 / 357 "On the use of cash registers by lawyers and notaries"; Letter of the Federal Tax Service dated 20.09.2005, No. 04-2-03 / 130 "Activities of lawyers' associations". At the same time, it should be noted that according to the position of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, set out in the letter of the Department of Tax and Customs and Tariff Policy of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-01-15 / 4-116 dated April 20, 2007, “Lawyers' formations in order to implement paragraph 6 Article 25 of the Law on the Bar in the part of the obligatory payment of remuneration paid to the attorney by the client and (or) compensation to the attorney of expenses related to the execution of the order in the part of the obligatory payment of the remuneration paid to the attorney by the client, must draw up cash transactions in accordance with the procedure for conducting cash transactions in the Russian Federation, approved by the decision of the Council Directors of the Central Bank of Russia dated September 22, 1993 No. 40. According to paragraphs 12 and 13 of this Procedure cash is accepted at the cash desk according to incoming cash orders, and cash transactions are drawn up with standard interdepartmental forms of primary accounting documentation for enterprises and organizations, which are approved by the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation in agreement with the Central Bank of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. Forms of primary accounting documentation for accounting of cash transactions were approved in accordance with the established procedure by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated August 18, 1998 No. 88. Thus, the registration of cash transactions in lawyers' formations when accepting remuneration paid to a lawyer at the cashier's office of lawyer education and (or) compensation of expenses , related to the execution of the order, is carried out according to incoming cash orders (form "KO-1") with an indication of the purpose of the deposited funds and with the issuance of a receipt to the incoming cash order confirming the receipt of cash. " Considering all of the above, the PFR Office considers that the receipt attached to the application of M.I.Davydkin as a document confirming payment of the lawyer's services Mikhina E.B., cannot be recognized as admissible evidence, since the execution of such a receipt and the procedure for transferring the lawyer Mikhina E.B. cash, implied in the preparation of the specified receipt, does not comply with applicable law. In accordance with Art. 38 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, the parties in civil proceedings are the plaintiff and the defendant. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 48 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, citizens have the right to conduct their affairs in court personally or through representatives. Thus, the involvement of a representative in the case is a right and not an obligation of the plaintiff. Also, the norms of the Code of Civil Procedure provide for the scope of procedural rights available to persons participating in the case, including the plaintiff. Moreover, the norms of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation do not establish the circle of persons entitled to prepare the text of the statement of claim, to submit the statement of claim to the court. Based on the norms of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, such a right is possessed, first of all, by the plaintiff in a civil case. Consequently, the question of the possibility and necessity of the participation of a lawyer in court hearings as a representative is resolved by the plaintiff independently, in connection with the granting of such a right to him, and not by virtue of the obligations imposed on him by the norms of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation. In addition, deciding on the conclusion of an agreement on the provision of legal services and on payment of funds under such an agreement is the right of the plaintiff. As a general rule, the terms of the contract are determined at the discretion of the parties (clause 4 of article 421 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). These conditions include those that establish the amount and procedure for payment for the services of a representative. Considering the above, the PFR management believes that the other party cannot be held responsible for the plaintiff's exercise of such a right. The obligation of the court to recover the costs of payment for the services of a representative incurred by the person in favor of whom the judicial act was adopted from another person participating in the case, within reasonable limits, is one of the provisions provided for by law legal ways, directed against unreasonable overstatement of the amount of payment for the services of a representative, and thereby - on the implementation of the requirements of Article 17 (part 3) of the Constitution of the Russian Federation (Determination of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of December 21, 2004 No. 454-О, Determination of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of July 17, 2007 No. 382-O-O). Reasonable cost limits are an assessment category; there are no clear criteria for determining them in relation to certain categories of cases. In each specific case, the court is obliged to determine such limits, taking into account the circumstances of the case, the complexity and duration of the proceedings, the level of payment for the services of lawyers in the given locality to represent the interests of the principals in civil proceedings (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Central District of October 14, 2004 No. A54-875 / 04-С18; Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Central District of November 27, 2007, No. A36-871 / 2007). According to the established practice, when determining reasonable limits of expenses for payment of services of a representative, the following are taken into account: relevance of expenses to the case; the volume and complexity of the work performed; cost rates for business trips established by legal acts; the cost of economical transport services; the time that a qualified specialist could spend on the preparation of materials; the prevailing cost in a given region for similar services, taking into account the qualifications of the persons providing the services; available information of statistical authorities on prices in the market for legal services; the duration of the consideration of the case; other circumstances indicating the reasonableness of these costs. At the same time, when determining reasonable limits on the amount of expenses for the services of a representative of a person participating in the case, the courts may take into account other circumstances, including the behavior of the persons participating in the case, their attitude to procedural rights and obligations. The reasonableness of the costs of paying for the services of a representative must be justified by the party claiming reimbursement of these costs (Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation of February 7, 2006 No. 12088/05). In violation of the norms of Articles 56, 57 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, no documents were submitted confirming the tariff for the services provided in the form of filing a statement of claim and participation in court hearings of a lawyer, since evidence confirming the reasonableness of the costs of paying for the services of a representative must be provided by the party demanding reimbursement of these costs. It is not clear from the available documents what constitutes the amount to be recovered, which exceeds all reasonable limits. From the materials of this civil case, it follows that the work of the plaintiff's representative, in addition to participating in the court sessions, was to write a statement of claim. At the same time, with a sufficiently large volume of similar civil cases considered in the Pervomaisky District Court, lawyer E.B. Mikhina. is the only lawyer who has participated in all disputes of this nature without exception. Consequently, in view of the fact that the lawyer Mikhina E.B. She thoroughly studied both the subject of the dispute and the judicial practice in the region on similar disputes, her labor costs (time and effort to search for regulations, to draw up a statement of claim) could not be large. So the reasons for refusing to grant a pension, as well as the necessary references to regulatory legal acts and circumstances that are essential for resolving the dispute, were contained in full in the Protocol of the decision on the refusal to grant a pension. As evidence in the case, copies of the documents that were available in the pension file of M.I.Davydkin were attached to the statement of claim, all these documents were either issued directly to the applicant, or were already available from the applicant, and were not requested in order to prepare directly by the lawyer, additional evidence by the lawyer Mikhina E ... B. did not appear at the hearing. Consequently, the lawyer did not carry out work on the search for evidence in the case, as well as on the search for the normative acts necessary for the formation of a legal position. The statement of claim did not contain any arguments, calculations, or research. According to the Regulations on the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, approved by the Resolution of the Supreme Council of the Russian Federation dated 07.12.1991, No. 2122-1, the funds of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation are federal property, have a designated purpose, are strictly limited and are directed to the payment of state pensions. In accordance with Art. 16 of the Federal Law of 15.01.2001, No. 167-FZ "On compulsory pension insurance in the Russian Federation", the monetary funds of the pension fund are federal property, are not included in other budgets and are not subject to withdrawal. Budget funding is strictly targeted, that is, exclusively for the purposes provided for by law (Article 147 of the RF BC). In order to collect any payments from the territorial bodies of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, it is necessary that these expenses be provided for in a separate line in the expenditure side of the budget of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation. In the budget of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, such type of expenses as payment for the services of a representative by a court decision is not provided. Considering all of the above, the PFR Office believes that M.I.Davydkin the fact of payment to the lawyer E.B. Mikhina has not been proven. cash in the amount of 6,000 rubles, in addition, the amount of legal costs presented for recovery exceeds all reasonable limits, Davydkin M.AND. the validity of such an amount has not been confirmed, besides Davydkin M.AND. wants to reimburse court costs from the PFR budget, the funds of which are strictly targeted. Based on the foregoing, he asks to apply the principle of rationality and legality and refuse M.I.Davydkin. in meeting the requirements for the collection of court costs from the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation in full.
Representative of a third party of the branch of LLC<данные изъяты>»Inozemtseva O.B. the claim supported and explained that Davydkin M.AND. Since DD.MM.YYYY to the present time he has been working as a technological compressor operator, engaged in servicing gas compressors (except for air). According to the structure<данные изъяты>UMG gas compressor service is not divided into workshops, this division is conditional. Working conditions, hazard factors and job duties Technological compressor drivers working in both electric and turbo-driven workshops are the same. All work provided for by ECTS is mainly carried out with the unit stopped. All the work of the driver is related to the maintenance of the unit, including painting, snow removal, grass mowing, etc. Only an engineer can approach a working GPU. Harmful and dangerous working conditions consist not only in the fact that during the operation of the unit, increased noise and vibration are generated, but most importantly, the drivers are constantly in the zone of increased danger and only the drivers have access to this zone. Therefore, the operators of technological compressors have personal salaries that differ from other workers who are not employed in work with harmful and hazardous working conditions. According to the collective agreement, they are provided with an additional paid leave of 3 days. The machinists are busy at least 80% of their working time in servicing electric and turbo-drive units. They were not employed in other jobs, which is confirmed by a certificate specifying the nature of the work of labor. According to List No. 2, approved by Decree No. 10 of the Cabinet of Ministers of the USSR dated January 26, 1991, occupied by M.I.Davydkin. in disputable periods, the position of a technological compressor operator employed in servicing gas compressors (except for air) is provided for as a position with harmful and difficult working conditions, employment in which gives the right to an old-age pension on preferential terms provided for by subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 27 of the Federal Law "On labor pensions in the Russian Federation" No. 173-ФЗ dated December 17, 2001. In accordance with clause 1 of the instructions of the Ministry of Social Protection of the Population of the RSFSR of April 20, 1992 N 1-28-U "On the Procedure for Applying the Law of the RSFSR" On State Pensions in the RSFSR "when assigning preferential pensions to employees, there is no need to demand from the heads of enterprises, organizations and institutions data on the results of certification of workplaces, conclusions of state examination bodies, sanitary-epidemiological stations and other bodies on the actual working conditions at their workplaces. However, if the Lists for certain categories of workers, managers and specialists indicate indicators (conditions) under which they are granted pension benefits: hazard classes of harmful substances received or used, employment in hot work areas, mining in open pits and open-pit mines with a depth of 150 m and below, etc., then such information must be confirmed by a clarifying certificate with a link to the documents. List No. 2 provides for the position of a technological compressor operator engaged in servicing gas compressors (except air), no additional conditions are specified. Therefore, the certification results should not in any way affect the resolution of the issue of the appointment of an early retirement pension. For DD.MM.YYYY years, the employer submitted individual information to the Pension Fund without specifying employment in special working conditions, this is due to the incompetence of the employee who submitted this information, adjustments have now been submitted. I disagree with the arguments of the defendant, so in order to determine the right to an early retirement pension, it is only necessary to establish that the plaintiff worked in the position indicated in list No. 2, which is confirmed by his length of service and a certificate submitted to the Pension Fund.
Having heard the explanations of the parties, the testimony of the witness, having examined the materials of the case, the court considers that the claims are subject to satisfaction.
In accordance with paragraphs. 2 p. 1 art. 27 of the Federal Law "On Labor Pensions in the Russian Federation" No. 173-ФЗ dated December 17, 2001, an old-age labor pension is assigned before reaching retirement age for men upon reaching the age of 55, if they have worked in jobs with difficult working conditions for at least 12 years 6 months and have insurance experience of at least 25 years.
DD.MM.YYYY the plaintiff has reached 55 years of age.
His insurance experience is over 25 years.
These circumstances are not disputed by the defendant.
In List No. 2, approved by the Decree of the Cabinet of Ministers of the USSR dated January 26, 1991 No. 10 "On approval of lists of industries, jobs, professions, positions and indicators that give the right to preferential pension provision" in section XXXIII "General professions" position 23200000-14257 the position is envisaged: machinists of technological compressors employed in servicing gas compressors (except for air ones), which gives the right to a retirement pension (old age) on preferential terms.
According to the order of the head of LLC № / k from DD.MM.YYYY Davydkin M.AND. adopted with DD.MM.YYYY as a driver of technological compressors of the third category to the staff of workers of the gas compressor service.
According to the records in the work book of the plaintiff and the insert in the work book of the plaintiff: DD.MM.YYYY he was accepted by the driver of technological compressors in the 3rd category in the staff of the workers of the gas compressor service LLC, DD.MM.YYYY was assigned the 4th category of the driver of technological compressors, DD.MM.YYYY awarded the 5th rank of the operator of technological compressors, DD.MM.YYYY<данные изъяты>LPUMG was reorganized into<данные изъяты>, DD.MM.YYYY<данные изъяты>UMG was reorganized into a branch of LLC<данные изъяты>», DD.MM.YYYY was awarded the 6th category of technological compressor operator. By the decision of JSC<данные изъяты>"Member of LLC"<данные изъяты>"From DD.MM.YYYY No. LLC"<данные изъяты>in LLC "<данные изъяты>", Works up to the present time.
According to the certificate clarifying the special nature of work or working conditions necessary for the early appointment of an old-age retirement pension and confirming permanent employment in preferential work No. from DD.MM.YYYY of the branch of LLC "<данные изъяты>»Davydkin M.I. really worked full-time in an LLC with DD.MM.YYYY order No. / к from DD.MM.YYYY to the present as a technological compressor operator engaged in servicing gas compressors (except air) d. XXX, 5 electric drive shop of the gas compressor service in special working conditions, as provided by list No., position No. 23200000, section XXXIII. General Professions, Subdivision 23200000-14257. During the above period of work was on refresher courses: from DD.MM.YYYY to DD.MM.YYYY (order No. / o from DD.MM.YYYY); with DD.MM.YYYY by DD.MM.YYYY (order no. / about from DD.MM.YYYY). During this period Davydkin M.AND. was not on leave without pay; did not work in light physical labor; was not on student leave, did not participate in strikes, was not in custody, was not in correctional labor, has no absenteeism, was not on parental leave for the entire period of work; there was no distraction from preferential work. During this period Davydkin M.AND. did not work part-time, did not combine work, profession (the certificate was issued on the basis of: personal accounts for DD.MM.YYYY, personal card of the T-2 form, staffing for DD.MM.YYYY years, ETKS , orders for personnel for the period from DD.MM.YYYY year, technological processes).
According to the card of workplace certification for working conditions No. 10 of the operator of technological compressors M.I.Davydkina. " General information on the workplace "from 2001 in line 061 the assessment of working conditions is indicated: according to the degree of hazard and danger, it belongs to the 3rd class of working conditions, according to the degree of injury safety, the 2nd hazard class; in line 080 the surcharge to the tariff rate indicates work related to the maintenance and operation of gas compressors (except air) - surcharge 12%; line 100 indicates that the duration of additional leave (harmful working conditions) is 12 working days (the basis is the List of industries, workshops, professions and positions with harmful working conditions, work in which gives the right to additional leave and a shortened working day, approved by the USSR State Labor Committee and the Presidium of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions of October 25, 1974 No. 298 / P-22, instructions on the procedure for applying the List ..., approved by the Decree of the State Committee of Labor of the USSR and the Presidium of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions of November 21, 1975 No. 273 / P-20); line 110 indicates preferential pension provision: List No. 2, section XXXIII of jobs, professions, positions and indicators giving the right to preferential pensions was approved by Decree No. 10 of the USSR Cabinet of Ministers of January 26, 1991, type of production - general professions.
According to the certification card No. 2017 30101 00004 695 workplaces for the working conditions of the operator of technological compressors M.I.Davydkina. from DD.MM.YYYY “General information about workplaces (RM): in line 061 there is an assessment of working conditions: according to the degree of hazard and hazard 2.0 class of working conditions, according to the degree of injury safety hazard class 2; in term 100, the duration of the additional vacation is 6 days (the basis is list IX, clause 108b, page 154); in term 110, preferential pension provision is indicated List No. 2, type of production - XXXIII General professions, type of work - operators of technological compressors employed in servicing gas compressors (except air), position (thirteen-digit character) in the List of professions, positions 23200000-14257; line 120 indicates the recommended breaks (number, duration) up to 7% of the working time.
According to the certificate of the head of the branch<данные изъяты>UMG and the head of the GKS about the work carried out for the machinist of the t / c M. Davydkina. in the period: from November DD.MM.YYYY, he worked in the compressor shop with electric drive units. The certificate was issued on the basis of an entry in the "Logs of admission to work at the facilities of the compressor station, gas distribution station, linear part of the gas pipeline" from the period (DD.MM.YYYY-DD.MM.YYYY), (DD.MM.YYYY-DD.MM.YYYY) , (12.06-DD.MM.YYYY), (30.09-DD.MM.YYYY) and "Log of assignments of CC" Yamburg-Yelets 1,2 "from the period (10.01-DD.MM.YYYY); (DD.MM.YYYY-DD.MM.YYYY); (DD.MM.YYYY-DD.MM.YYYY); (29.05-DD.MM.YYYY).
According to the schedule of Measures to maintain the CC with EGPA (gas pumping units with electric drives) in the reserve approved by the chief engineer of the branch of LLC "<данные изъяты>»FULL NAME6 from DD.MM.YYYY annually, monthly, daily work is carried out to maintain KC with EGPA in reserve.
The duties of the operator of technological compressors working in electric and turbo-driven shops are the same (instructions on labor protection No. 1-002 for the driver of technological compressors of an electric-driven shop and No. 1-001 for the driver of technological compressors of a turbine-driven shop).
According to the Unified Tariff and Qualification Reference Book of Workers and Professions of Workers, Issue 36, section "Refining of oil, oil products, gas, shale, coal and maintenance of trunk pipelines" (approved by the decree of the State Committee for Labor of the USSR and the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions dated June 7, 1984 No. 171 / 10-109 ) paragraph 12b, the operator of technological compressors of the 6th category performs: Maintenance of compressor stations, control panels of the shop level, as well as general shop systems for cleaning and drying gas, oil supply, heat recovery at the compressor station. Production of operational switchings at the technological piping of compressor stations, regulation of the operating mode of the workshop as directed by the dispatching service. Removal of technological equipment for repair, participation in its delivery and acceptance from repair. Prevention, identification and elimination of malfunctions in the operation of technological equipment and its systems. Adjustment of compressors, their drives, apparatuses, auxiliary equipment of workshops, compressor stations. Production of operational switching in electrical installations with voltage over 1000 volts in workshops with electric drive gas pumping units. Supervising the work of less qualified machinists.
Witness FULL NAME6 explained that he works in the branch of LLC "<данные изъяты>"Chief engineer. Davydkin works as a technological compressor operator in the gas compressor service<данные изъяты>UMG. V<данные изъяты>UMG 3 electric drive workshops with 22 units in each and 1 turbo drive workshop, vk. XXX unit. Turbo-driven and electric-driven units drive gas compressors. According to the structure<данные изъяты> UMG gas compressor service is not divided into workshops, this division is conditional. Electric drive compressors are on standby. The reserve does not imply a shutdown, it is the operation of the unit. Gas passes through all workshops. Electric driven shops as well as turbo driven shops are constantly under pressure and at any time, if necessary, can be started up within 2 hours. Electric driven compressors are started once a month on schedule to check their technical condition. Compressors on standby are more difficult to maintain than compressors on a continuous basis. It takes more time and load to start the motorized compressor. The servicing of the electrically driven compressors takes place on a daily basis. The principle of operation of the turbo-driven and electric-driven compressors is the same, the main and auxiliary equipment of the workshops is identical. Each unit is divided into a motor and a pump. The working conditions in these workshops are the same in terms of harmfulness. Davydkin M.I. was busy at least 80% of the working time on the maintenance of electric drive units. He was not busy with other jobs. Davydkin M.I., as a driver of technological compressors of the 6th category, performed work in accordance with the Unified tariff and qualification reference book of work and professions of workers, issue 36, section "Refining of oil, oil products, gas, shale, coal and maintenance of trunk pipelines" (approved by the resolution of the State Committee for Labor USSR and the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions of June 7, 1984 No. 171 / 10-109) paragraph 12b Operator of technological compressors of the 6th category: Maintenance of compressor stations, shop level control panels, as well as general shop systems for gas purification and drying, oil supply, heat recovery at the compressor station ... Production of operational switchings at the technological piping of compressor stations, regulation of the operating mode of the workshop as directed by the dispatching service. Removal of technological equipment for repair, participation in its delivery and acceptance from repair. Prevention, identification and elimination of malfunctions in the operation of technological equipment and its systems. Adjustment of compressors, their drives, apparatuses, auxiliary equipment of workshops, compressor stations. Production of operational switching in electrical installations with voltage over 1000 volts in workshops with electric drive gas pumping units. Supervising the work of less qualified machinists. The task for the machinists is issued daily according to the journal of issuing tasks, a more complex task is given according to the permit. All work in the security zone is hazardous work, employees of other services cannot work in the security zone. In DD.MM.YYYY, the certification of drivers of technological compressors was carried out. According to the certification card this profession refers to preferential, has a second degree of harm. The operating time in compressor shops with electric drive units was<данные изъяты>hours for the period from DD.MM.YYYY years. Hours are the operation of the unit and are taken into account only for the maintenance of the unit. But it does not show the driver's employment in servicing gas compressors. The driver works not only with the compressor, but also performs other work related to the maintenance of the unit.
The above evidence confirms the plaintiff's arguments that during the periods indicated by him he worked as a technological compressor operator engaged in servicing gas compressors (except for air), that is, in a position with harmful and difficult working conditions, employment in which gives the right to early labor old-age pension.
The work of the plaintiff is directly related to the work of the gas compressor unit (GCU).
The arguments of the defendant that the plaintiff is not entitled to an early assignment of an old-age labor pension, since he worked as a technological compressor operator of an electric drive workshop, which was in a state of reserve, cannot serve as a basis for refusing to satisfy the claim.
The structure and staffing of the enterprise throughout all the disputable periods provided for a single gas compressor service serving various types of compressors, without dividing service areas for main and auxiliary equipment and dividing the service into turbo drive and electric drive shops, in which the plaintiff was employed as a technological compressor operator.
Refusing to grant an early retirement pension for old age, the defendant refers to the operating time in compressor shops with electric drive units, which amounted to<данные изъяты>hours for the period from DD.MM.YYYY years. According to the defendant, the monthly operating time rate should be<данные изъяты>hours. However, the defendant did not give reasons to confirm the monthly rate indicated by him. As the interviewee explained as a witness Chief Engineer branch of LLC<данные изъяты>»FULL NAME6, as well as a representative of a third party Inozemtseva OB, the specified operating time is a technical indicator of compressor shops and can not be an indicator of the employment of technological compressor drivers serving gas compressors.
In accordance with clause 5 of the Clarification of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation of May 22, 1996 "On the procedure for applying the lists of industries, jobs, professions, positions and indicators, giving in accordance with Articles 12, 78 and 78.1 of the RSFSR Law" On state pensions in the RSFSR "(as amended and additions of October 1, 1999), full-time work means the performance of work in the working conditions provided for by the Lists, at least 80 percent of the working time. At the same time, the specified time includes the time for performing preparatory and auxiliary work, and for workers performing work with the help of machines and mechanisms, also the time for performing repair work of a current nature and work on the technical operation of equipment. The specified time may include the time of performance of work performed outside the workplace in order to ensure basic labor functions.
The plaintiff's employment in the position of a technological compressor operator serving gas compressors full-time, that is, at least 80% of the working time, is confirmed by the above evidence.
The arguments of the defendant that the employer did not timely submit information about the employment of the plaintiff in special working conditions, that wage the plaintiff, as an employee employed in jobs with harmful working conditions, should be established in an increased amount, that payment for harmful working conditions was not made constantly, cannot be the basis for refusing to assign an early labor old-age pension, since the plaintiff's right to an early old-age retirement pension is provided for in paragraphs. 2 p. 1 art. 27 of the Federal Law "On Labor Pensions in the Russian Federation" and cannot be limited by the specified circumstances.
The defendant claims that since, according to the data of attestation of workplaces for the working conditions of the operator of technological compressors of the electric drive workshop, the actual state of working conditions at the workplaces is classified according to the degree of hazard and danger. XXX-th class of working conditions (permissible), then harmful working conditions in the electric drive workshop of the branch of LLC<данные изъяты>absent.
The court cannot agree with such arguments, since the position of technological compressor operators engaged in the maintenance of gas compressors (except for air) is provided for by List No. 2, approved by the Resolution of the USSR Cabinet of Ministers dated January 26, 1991 No. 10 "On approval of lists of industries, works, professions , positions and indicators that give the right to preferential pension provision "in section XXXIII" General professions "position 23200000-14257 without indicating the degree of harm and danger.
The arguments of the defendant that when the compressor shop with the EGPU is in a reserve state, there are no dangerous and harmful production factors at the workplace of the operator of technological compressors, such as an increased noise level, moving machines and mechanisms, moved and lifted elements of equipment, high temperatures of the surfaces of units machines and mechanisms, the increased air temperature of the working area is not justified by anything.
In addition, as the defendant himself indicated in his objections, in accordance with paragraph 1 of the instructions of the Ministry of Social Protection of the Population of the RSFSR dated April 20, 1992 N 1-28-U "On the procedure for applying the Law of the RSFSR" On state pensions in the RSFSR "when assigning preferential pensions there is no need to demand from the heads of enterprises, organizations and institutions data on the results of certification of workplaces, conclusions of state examination bodies, sanitary-epidemiological stations and other bodies on the actual working conditions at their workplaces. However, if the Lists for certain categories of workers, managers and specialists indicate indicators (conditions) under which they are granted pension benefits: hazard classes of harmful substances received or used, employment in hot work areas, mining in open pits and open-pit mines with a depth of 150 m and below, etc., then such information must be confirmed by a clarifying certificate with a link to the documents. As indicated above in List No. 2, such indicators for the position of technological compressor operators engaged in servicing gas compressors (other than air ones) are not indicated.
Thus, the objections of the defendant do not refute the conclusions of the court that the plaintiff during the disputable periods worked in a position with harmful and difficult working conditions, employment in which gives the right to an old-age pension on preferential terms.
The plaintiff's right to preferential pension provision is confirmed by a set of conditions that give the right to early assignment of an old-age retirement pension: his labor activity proceeded in dangerous (difficult) working conditions; he held the position shown on List # 2; performed work in the specified position; execution of such work is at least 80% of the working time.
In addition, by the decision of the Pervomaisky District Court of the Tambov Region of December 21, 2009 at the suit of N.AND. Davydkin. to the State Institution - Office of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation for<данные изъяты>on the inclusion in the length of service of the periods necessary for the appointment of an early retirement pension and on the appointment of an early retirement pension, it was established that Davydkin N.AND. worked as a technological compressor operator engaged in servicing gas compressors in the branch of LLC<данные изъяты>»With harmful and difficult working conditions, employment in which gives the right to an old-age pension on preferential terms. Davydkin N.I. included in the special experience, giving the right to an early labor old-age pension in accordance with paragraphs. 2 p. 1 art. 27 of the Federal Law of December 17, 2001 No. 173-FZ "On labor pensions in the Russian Federation" the periods of his work as a technological compressor operator engaged in servicing gas compressors (except air): from DD.MM.YYYY year in the branch of LLC "<данные изъяты>". Davydkin N.I. and Davydkin M.I. worked in the same position during the same period and serviced electric drive units.
Therefore, the indicated periods of work of the plaintiff in the position of a technological compressor operator engaged in servicing gas compressors are subject to inclusion in the length of service, giving the right to an early retirement pension in accordance with paragraphs. 2 p. 1 art. 27 of the Federal Law of December 17, 2001 No. 173-FZ "On labor pensions in the Russian Federation".
According to Art. 19 of the Federal Law "On Labor Pensions in the Russian Federation", the labor pension is assigned from the date of applying for the specified pension. The day of applying for a labor pension is considered to be the day when the pension provider receives the corresponding application with all the necessary documents. The plaintiff, in the manner prescribed by law, applied to the GU-UPF RF in<данные изъяты>for the appointment of a pension DD.MM.YYYY and provided the necessary documents. DD.MM.YYYY the plaintiff has reached 55 years of age.
In accordance with Art. 98 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation to the party in favor of which the court decision was made, the court awards the other party to reimburse all legal costs incurred in the case.
According to Art. 100 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation to the party in favor of which the court decision was made, at its written request, the court awards on the other party the costs of paying for the services of a representative within reasonable limits.
The plaintiff paid his representative, lawyer E. Mikhina.<данные изъяты>rubles for drawing up a statement of claim, studying the materials of the case, participating in the consideration of the case, which is confirmed by the contract of assignment for representation from DD.MM.YYYY, receipt from DD.MM.YYYY No.
According to the "Letter of recommendation on fee practice, approved by the Council of the Bar Association<адрес>DD.MM.YYYY the amount of the fee for drawing up a complex application is not less than<данные изъяты>rubles, representation in civil courts in a court of 1 instance at least<данные изъяты>rubles for one day.
Taking into account the complexity of the case and the time of its consideration (three court sessions), the court considers that the amount spent by the plaintiff to pay for the services of a representative is proportionate and within reasonable limits.
The objections of the representative of the defendant regarding the unfoundedness of the claims of the plaintiff to collect payment for the services of the representative are refuted by the arguments of the representative of the plaintiff, attorney Mikhina EB, cited above.
Guided by Art. Art. 98, 100, 194, 198, 199 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, court
decided:
Count Davydkin M.I. in a special experience, giving the right to an early labor old-age pension in accordance with paragraphs. 2 p. 1 art. 27 of the Federal Law of December 17, 2001 No. 173-FZ "On labor pensions in the Russian Federation", the periods of his work in the branch of LLC "<данные изъяты>»In the position of a technological compressor operator engaged in servicing gas compressors (except air), total 26 years 4 months 11 days, including periods: from DD.MM.YYYY to DD.MM.YYYY (17 years 10 months 27 days); from DD.MM.YYYY to DD.MM.YYYY (5 years 3 months 29 days); from DD.MM.YYYY to DD.MM.YYYY (3 years 1 month 15 days).
Obligate the State Institution - Management of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation in<данные изъяты>appoint Davydkin M.I. early retirement pension in accordance with paragraphs. 2 p. 1 art. 27 of the Federal Law of December 17, 2001 No. 173-FZ "On labor pensions in the Russian Federation" from November 19, 2011.
Collect from a State institution - the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation<данные изъяты>in favor of M.I.Davydkin legal costs in the amount<данные изъяты>rubles, of which<данные изъяты>rubles payment for the services of a representative and<данные изъяты>rubles payment of the state fee.
The decision can be appealed to the Tambov Regional Court through the Pervomaisky District Court within one month from the date of adoption.
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted on http://www.allbest.ru//
INTRODUCTION
In the modern world, in all countries at any enterprise, the problem of improving working conditions is always relevant. The enormous importance of the working conditions of each employee for the enterprise as a whole can be explained by the fact that the level of a person's working capacity, the quality and efficiency of his work, physical and psychological health, as well as the attitude of the employee to his position and to the enterprise as a whole, directly depend on the state of the employee's workplace. ... In other words, it is beneficial for the company when its employees good conditions labor, since in this case productivity increases, and, accordingly, the number of products produced, the number of errors in the workplace decreases and there are fewer defects, the employee has time to rest, his body is less susceptible to disease, which means that the likelihood that a person will go on sick leave or earn money any occupational disease is much lower than in enterprises that do not care about the state of the workplace.
In our country, the problem of improving working conditions is especially acute. There are several reasons for this:
A significant part of the equipment and technology used in production does not meet modern international hygienic standards and safety requirements;
Most of the equipment at enterprises, especially at state ones, has long been physically and morally outdated, and the purchase of new and modern equipment requires significant costs;
Unfortunately, very often labor Relations the employer leaves much to be desired for his employee, the employer deliberately does not seek to improve the employee's conditions, and the employee is afraid to complain to the appropriate authorities.
The object of research in this work is various options and ways to improve working conditions at the enterprise, their significance for the employee and the enterprise as a whole.
The purpose of this work is to determine the main harmful production factors at the workplace of the compressor unit operator and to propose measures to improve these conditions.
To reveal the goal in the thesis:
Determined the harmful working conditions at the workplace of the compressor operator;
Proposed measures to improve the working conditions of the compressor operator;
Evaluated the effectiveness of the proposed methods to improve working conditions.
The structure of the thesis consists of an introduction, four chapters, a conclusion and literature.
CHAPTER 1. WATER SUPPLY AND SANITATION OF SETTLEMENTS
1.1 Modern problems of water supply and sanitation
In the modern world, water is becoming one of the most important resources, it can already influence the location of new zones Agriculture, industry, new settlements, etc. Water supply is becoming an increasingly important condition for solving socio-economic problems, forming the value of products manufactured by industry. Despite the fact that the problem of water supply to settlements is invisible, even now the water balance, i.e. the relationship between the demand for water and its availability in reservoirs is tense in many regions of our country.
Also, the distribution of water flow per year usually does not correspond to the distribution of demand for water resources, and the possibility of further regulation of this flow is difficult to fulfill. This can be explained by several conditions:
Often, topographic conditions do not allow the creation of capacious, more voluminous reservoirs, and the deliberate flooding of agricultural land, ecological and cultural sites or deposits of important minerals is unacceptable;
On the rivers, it is necessary to maintain guaranteed water availability in order to ensure the spawning of local fish species, to create watering areas for breeding and catching fish, to maintain conditions for the normal functioning of hydroelectric power plants and shipping in some areas.
In addition to what was said above, some of the water resources are used irrationally. For example, on many irrigation systems, a significant part of the water is lost during filtration, and water intake equipment is rarely equipped with systems for calculating the water intake, which also leads to unnecessary waste of water resources.
In industry, technological processes based on the use of a small amount of water, or no water at all, are beginning to be applied not quickly enough. A large volume of water is used to remove waste from various technical processes. In this case, it is more rational to switch to waste-free or low-waste production.
In the communal water supply of settlements, water losses are also present in large volumes. This is due to wear and tear and poor planning of water supply networks, the absence of water meters, although the latter is less and less common due to imperfect payment rates.
There are two types of water resources use - water use and water consumption. When using water, water is not consumed. In this case, it does some kind of work, for example, it is used in hydropower. Also, this type can include such types of work as the use of rivers and seas for navigation and timber rafting, fishing on an industrial scale.
With water consumption, as the name implies, part of the water is irretrievably taken from water resources. This includes the evaporation of water and its use for industrial purposes in the manufacture of various products and in agriculture. It is worth noting that some of the water that still returns to the reservoirs is polluted, and this is fraught with the blooming of rivers and lakes backwaters.
In practice, it is very difficult to separate water use and water consumption from each other. Therefore, with complex use, these varieties can be combined. The main water users are always settlements for which the water quality must be the highest. The next in terms of consumption are thermal and nuclear power plants, next to them on the same stage are enterprises with a continuous cycle of work. Irrigation of plants with water in large quantities is necessary only during the growing season, water transport in fact does not consume water, as well as fish farming. About 90 km 3 of fresh water is taken in the Russian Federation every year. One fourth of this amount is withdrawn forever (consumed, lost during transportation or when used in production).
Irrigated agriculture is an important part of agriculture, creating a guaranteed food supply. A significant part of vegetables, fruits, rice, etc. are grown in irrigated fields. Irrigation of these lands consumes about 10% of water per year. When solving the problem of using water resources, it is necessary to take into account that 40% of the used water is lost during filtration, discharge and evaporation. Therefore, it is necessary to introduce new methods of irrigation.
Waste water from the sewerage system contains a huge amount of organic and inorganic substances in various states. The concentration of all this more often than usual exceeds the maximum permissible concentration, and these effluents have to be diluted with clean water before being discharged into the reservoir. remote compressor operator
The development of many regions of the country in the economic direction depends on the use of small rivers, which sometimes are the only source of water in a settlement. Intensive drainage in small rivers can harm not only these small settlements, but also harm the river basin in general, and therefore a much larger area.
To solve all these problems, you need to implement:
New water-saving technological processes that do not require a lot of water when executed;
New methods for the purification of sewage water;
Closed original water management systems, equipped with everything necessary for waste disposal.
At present, a development path is outlined in the economy of water consumption. But it should be borne in mind that in areas where there is a shortage of water resources (this applies more to the southern regions of the country), it is more rational to use water-saving technologies, create water supply networks for technical needs, where it is possible to reuse water of average quality, create services for the protection of natural water use and protection waters from pollution. All these solutions are in most cases more economical and environmentally friendly than the territorial distribution of water.
Now, to protect the water economy in the country, there is a metering of water consumption from river basins, based on the bases of automatic collection of information and the use of geostationary satellites. Therefore, the tasks of providing territories with water are solved in an integrated manner, taking into account the regulation of surface and ground waters, as well as protecting it from pollution and depletion.
1.2 Definition of the water supply and sewerage system of the settlement
Modern water supply networks for cities and towns are a complex system that receives water from a reservoir and purifies it, and then distributes it to consumers. The most common are multifunctional systems, they supply both drinking water and water for household needs and fire water supply.
On average, water consumption throughout the year can be divided into:
Household and drinking expenses of people - 56% (cooking food and drinking water - 30%; washing - 10%; using the bathroom, shower - 30%; using the toilet - 30%);
The needs of public buildings - 17%;
Industrial needs - 17%;
The needs of fire organizations - 3%;
Urban needs (irrigation of flower beds, green spaces, operation of city fountains, etc.) - 1%;
Other needs - 6%.
Figure 1.1 - Distribution of annual water consumption
The composition of drinking water for any water sources, methods of purification and features of the water supply network must be safe and comply with the standards of GOST R 51232-98 “Drinking water. General requirements for the organization and methods of quality control ”and SanPiN 2.1.5.980-00“ Hygienic requirements for the protection of surface waters ”.
To reduce the non-production costs of water resources, i.e. different leaks, you can adjust the water pressure depending on the number of floors in the building. The average daily amount of water consumed helps to determine the water consumption at any time of the year.
Accordingly, water supply facilities are calculated depending on the water consumption, taking into account the possible development and increase of the settlement. For this, additional areas are reserved for the construction of new water supply systems. When selecting pumping and compressor equipment, it is necessary to be guided by possible short-term periods of maximum water supply, for example, in the evening, water consumption is greater than in the afternoon or morning, people cook and take a shower after work, and water consumption also greatly increases in summer dry weather, this is due to the same as with increased consumption of drinking water by the population, and irrigation of agricultural land.
Drainage networks have been created to remove wastewater outside the boundaries of settlements and enterprises. Wastewater is water, altered by human activity and contaminated with organic and mineral substances. They are liquid waste that appears as a result of industrial and domestic activities of people, as well as waste of sediments removed from the territory. In the city, they most often end up at treatment facilities, and after that they are discharged into water bodies or other specially designated places.
Based on this, wastewater can be divided into:
Waste water from settlements (a mixture of domestic and industrial waste water);
Rainwater wastewater (formed as a result of atmospheric precipitation);
Industrial waste water (generated from technological operations in production);
Waste water from irrigation systems (drainage systems).
Sewage wastewater serves as a medium for the development of microorganisms, including those that are causative agents of various diseases. Also, various toxic substances that can poison living organisms or cause the death of plants are not uncommon in wastewater. Water discharged from production always contains pollution different types and concentrations.
To drain precipitation runoff, it is important to analyze their amount and know at what time of the year the sewerage load will be large. Taking into account this analysis, it is necessary to take care of the good condition of the storm sewer in advance, monitor the condition of drains and gratings, and in the spring period of snow melting, involve vehicles to remove snow from the most problematic areas.
Sanitary requirements dictate the need to install high-quality and modern drainage systems to improve the living conditions of the population and ensure the proper operation of production facilities of various nature. Drainage systems are a complex of structures, buildings and pipelines intended for collection, transportation, removal of pollutants, bacteria from wastewater, and subsequent discharge into designated water bodies.
Drainage systems consist of several parts: drainage systems inside buildings and structures, drainage networks inside the quarter and inside the street, external drainage networks, tanks, pump and compressor stations, treatment facilities, water discharge systems, these include emergency exhaust systems, storm water inlets, storm drains etc.
Due to the difference in the composition of pollutants from rainfall, industrial and domestic wastewater, different methods of purification have been developed, and there is also a need for separate drainage of water. Drainage systems can be divided into three main types: general alloy, divided and combined. In turn, these three categories can also be divided.
The common sewage system has one common network, which is used to drain all types of wastewater. These are, respectively, and rainwater and all types of industrial and residential wastewater. This system is still the most widespread in our country, because it is the easiest to design and requires less funds to build, upgrade and maintain it in the desired condition. The disadvantages of the system may be that the drains are not sufficiently cleaned before being discharged into the reservoir, because the amount of pollutants is very diverse.
A complete split system consists of several separate piping networks, each of which is used for a specific type of effluent and feed to a suitable treatment system. Also, with this type of drainage, it is possible to reuse water, for example, a rainwater drainage system, after passing through a certain treatment, can be brought into production facilities and, on occasion, use such water instead of clean water.
An incomplete split system has only a separate sewerage network for the disposal of industrial and household waste. The drainage of rainwater goes along the surface, i.e. by cuvettes, channels, etc. This system is used only in sparsely populated areas, because arrangement of sewage canals in large settlements is often complicated by the already established network highways, although in this case, at present, during the modernization of roads and highways, storm canals are being built on the sides.
A semi-divided drainage system can be distinguished by the following feature: it has two water drainage networks, industrial and household and rainwater. These networks can intersect with each other and are equipped with separation chambers. Depending on the load on the first or second network, these chambers can be opened and closed, thus redirecting wastewater flows. The disadvantage of the system is the complexity of its management. Opening and closing the separation chambers in any case takes time, and the weather forecast is not always correct, so it is difficult to open or close the necessary chambers in advance.
A combined system is a sewerage network, in which both combined and separate systems can be located on its various parts. This happens most often during the reconstruction and completion of the sewerage system as a result of the expansion of the settlement or the opening of new enterprises. In other words, in the old part of the settlement there will be an all-alloy network, and the new one is already separate. It is also possible that the combined-alloy network is left for industrial or domestic needs, while a new network is being built in parallel, for example, a rain network.
Each of the listed sewerage systems has pluses and minuses, therefore, when designing a sewerage network, one should strive to ensure the most favorable sanitary condition of the settlement from which water will be discharged, and the reservoir into which the discharge is made, and also try to determine the minimum spent funds for construction and maintenance of this system.
Figure 1.2 shows a schematic water supply and sewerage system, which clearly shows the cycle of used water resources using the example of a residential building.
Figure 1.2 - Scheme of water supply and drainage of a residential building
But despite the presence of several types and subspecies of drainage systems, it is worth noting that in any of them compressor and pumping units and stations are used. They can be of different types, designs, but any of them requires a person who will monitor the correct and uninterrupted operation of the unit, as well as adjust various parameters.
Thus, the profession of a compressor unit operator is in great demand on the labor market today. Many enterprises and firms require highly qualified specialists in this field. The work of a compressor unit operator is an activity using the knowledge gained in the preparation process about the design of reciprocating compressors and turbocompressors, internal combustion engines, steam engines and electric motors, their technical characteristics and maintenance rules, turbine pipelines, instrumentation, gas properties.
Sometimes in the drainage system it happens that the compressor installation operator performs the duties of the pumping station operator, if the qualifications and experience of the worker allow it. In this case, compressor and pumping units are conveniently located in the same building or workshop. In this case, the driver must additionally know not only the principles of operation of the pumps. different designs, and drives to them, but also communication schemes, permissible loads on them in the process of operation, methods for eliminating problems that arise and emergency situations, as well as have certain knowledge of the physicochemical properties of pumped liquids, know the classification and brands of oils used for equipment.
In order to get a job as a compressor operator, you do not need to have a higher professional education in this specialty. To work in this chosen profession, it is enough to have a diploma of secondary vocational education received at a college or technical school, or, for example, it is enough to complete special training courses.
1.3 Hazardous and harmful production factors at the workplace of the compressor operator
According to the normative document "Rules for labor protection during the operation of municipal water supply and sewerage facilities" (approved by the Order of the Ministry of Land Construction of the Russian Federation of 09.22.1998 N 93):
“When operating structures and networks of water supply and sewerage facilities, it is necessary to take into account the presence and possibility of exposure to the following hazardous and harmful production factors:
Moving elements of equipment (pumping, power, mechanized grids, winches, scrapers, sprinklers, mechanical mixers and other mechanisms);
Flying objects (when crushing wastes removed from gratings in crushers), flying parts (when knocking out plugs in tested pipelines, when processing and chipping concrete pipes and fittings, etc.);
Falling objects and tools (when working in water and sewer wells, at treatment facilities and networks, indoors, etc.);
Formation of explosive gas mixtures (in wells, chambers on networks, in digester rooms and in other rooms and structures);
A dangerous voltage level in an electrical circuit, the closure of which can pass through the human body;
Reduced air temperature in industrial premises and structures;
High air humidity (in pumping stations, in the premises of filters, sedimentation tanks, etc.);
Increased level of ultraviolet (germicidal installations) and infrared (deworming) radiation;
Increased noise and vibration levels (in the engine rooms of pumping and blowing stations and other rooms and structures where technological equipment is installed);
Insufficient illumination of the working area (in wells, chambers, channels, etc.);
Gaseous substances of general toxic and other harmful effects in wells, chambers, canals, treatment facilities (hydrogen sulfide, methane, gasoline vapor, ether, carbon dioxide, ozone, etc.);
Gases emitted as a result of leakage from cylinders, barrels, tanks (ammonia, chlorine and other compressed, liquefied and dissolved gases);
Flammable impurities that have got into wastewater (gasoline, oil, etc.), as well as dissolved gaseous substances that can form explosive mixtures in sewer networks and structures;
Increased dustiness of the air in the working area with dust-forming reagents (aluminum sulfate, ferric chloride, quicklime bleach, soda, caustic soda, Activated carbon, fluorine-containing reagents, etc.);
Mercury vapors (when working with devices with mercury filling);
Pathogenic microorganisms in waste and natural waters. "
One of the workers involved in the operation of the water supply and sewerage system is the compressor operator. According to the "Unified Tariff and Qualification Reference Book of Work and Occupations of Workers", the compressor unit operator has 5 categories. Depending on the discharge, he must service stationary compressors and turbochargers, start, regulate and stop compressors, monitor the operation of compressors and auxiliary equipment, lubricate the rubbing parts of compressor mechanisms, prevent and eliminate malfunctions in the operation of compressors, monitor the operation of their safety devices, service drive motors , maintain the required operating parameters of the compressors, detect and prevent abnormalities in the operation of the compressor station, maintain reporting and technical documentation on the operation of the serviced compressors, machines and mechanisms, participate in the repair of the compressor station equipment.
Also, the compressor operator must know the principle of operation of reciprocating compressors, turbochargers, steam engines and electric motors; methods of preventing and eliminating malfunctions in the operation of compressors and motors; purpose and methods of application of instrumentation and control automation; compressor station piping diagrams; working pressure by degrees and the corresponding air temperature; permissible heating temperature of units of serviced units, measures to prevent and eliminate overheating; grades and brands of oils used to lubricate mechanisms.
Analyzing the duties and the usual working environment of a compressor installation operator, several points can be distinguished from the list of hazardous and harmful production factors of workers in the water supply and sewerage system. First of all, one can note such a common thing as a dangerous voltage level in an electrical circuit. Most modern professions are faced with this dangerous factor. Electric current has long become an integral part of our life, it is difficult to imagine without it modern world... But, unfortunately, despite the well-known and well-established rules for handling electric current and electrical appliances, electrical injuries are often found in many enterprises.
Electrical traumatism is characterized by the following features: a protective reaction of the body appears only after a person comes under voltage, that is, when an electric current is already flowing through his body; electric current acts not only in the places of contact with the human body and on the path of passage through the body, but also causes a reflex action, manifested in the disruption of the normal activity of the cardiovascular and nervous system, respiration, etc. live parts, and in case of shock voltage of a touch or step, through an electric arc. There are several reasons for electric shock to a person: touching non-insulated live parts; to metal parts of the equipment that are energized due to damage to the insulation; to non-metallic objects that are energized; shock voltage step and through the arc.
The electric current flowing through the human body affects it thermally, electrolytically and biologically. The thermal effect is characterized by tissue heating, up to burns; electrolytic - by the decomposition of organic fluids, including blood; the biological effect of electric current is manifested in the violation of bioelectric processes and is accompanied by irritation and excitation of living tissues and muscle contraction.
There are two types of electric shock to the body: electrical injury and electrical shock. Electrical injuries are local injuries to tissues and organs: electrical burns, electrical signs and electrometallization of the skin. In addition, electrical injuries include mechanical injuries as a result of involuntary convulsive muscle contractions during the flow of current (ruptures of the skin, blood vessels and nerves, dislocation of joints, bone fractures), as well as electrophthalmia - inflammation of the eyes as a result of the action of ultraviolet rays of an electric arc. An electric shock is the excitation of living tissues with an electric current, accompanied by an involuntary convulsive muscle contraction. According to the outcome, electric shocks are conventionally divided into five groups: without loss of consciousness; with loss of consciousness, but without disturbance of cardiac activity and breathing; with loss of consciousness and impaired cardiac activity or breathing; clinical death and electric shock.
The outcome of an electric shock also depends on the duration of the current flowing through a person. With an increase in the duration of a person's stay under voltage, this danger increases. The individual characteristics of the human body significantly affect the outcome of an electrical injury. For example, a non-releasing current for some people may be a threshold perceptible for others. The nature of the action of the current of the same strength depends on the mass of a person and his physical development. It was found that for women the threshold current values are approximately 1.5 times lower than for men.
The degree of action of the current depends on the state of the nervous system and the whole organism. So, in a state of excitement of the nervous system, depression, illness (especially diseases of the skin, cardiovascular system, nervous system, etc.) and intoxication, people are more sensitive to the current flowing through them. The "attention factor" also plays a significant role. If a person is prepared for an electric shock, then the degree of danger is sharply reduced, while an unexpected shock leads to more serious consequences.
The path of the current through the human body significantly affects the outcome of the lesion. The danger of injury is especially great if the current, passing through the vital organs - the heart, lungs, brain - acts directly on these organs. If the current does not pass through these organs, then its effect on them is only reflex and the likelihood of injury is less. The most common paths of current through a person, the so-called "current loops", have been established. In most cases, a circuit of current through a person occurs along the path of the right arm - legs. However, the loss of working capacity for more than three working days is caused by the flow of current along the hand - arm path - 40%, the right arm - legs current path - 20%, left arm - legs - 17%, other paths are less common.
Distinguish between individual and general means of protection against electric shock. Personal protective equipment includes rubber dielectric gloves, galoshes, rugs, insulating coasters, plumbing tools with wooden handles, etc. Common protective equipment against electric shock include protective grounding, neutralization and shutdown.
Protective grounding provides reliable electrical contact between electrical equipment and earth. Protective grounding is used instead of protective grounding in electrical systems with voltages up to 1000 V, in networks with grounding neutral.
Protective grounding is a connection of the body of electrical equipment with repeated grounding by a neutral wire. If the insulation is damaged, the body of the electrical equipment is energized. As a result of a breakdown, a short circuit occurs between the phase and neutral wires. A large current flows through the fuse, which can cause the fuse to blow or trip the circuit breaker. The equipment will be disabled and safe to touch.
A protective shutdown is the most perfect method of protection, which successfully operates at any voltage in the network. When the electrical equipment is closed to the case, a special automatic installation is triggered, in which, when a voltage appears at the terminals of the electromagnetic coil, the switches are instantly triggered. This is how the damaged section of the circuit is disconnected.
It is also worth noting that at enterprises, before admitting an employee, in our case a compressor installation driver, to the workplace, he must be instructed in electrical safety and sign in the appropriate magazine. Instructions on electrical safety for non-electrical personnel of the enterprise MUP "Eletsvodokanal" are given in the third chapter.
The following dangerous and harmful production factors will be present in those operators of compressor installations who, as noted in the previous paragraph, temporarily due to the illness of one operator or on an ongoing basis, if qualifications allow, also combine the duties of an operator of pumping installations. These include the danger of moving elements of pumping equipment and high humidity in the room of the pumping station.
In the first case, the driver may be threatened by the moving elements of the mechanisms. To avoid injury, all mechanisms must have a strong metal fence that reliably closes access from all sides to moving parts. Open the doors of the guards or remove the guards after a complete stop of the equipment or mechanism. The start-up of the equipment is allowed only after installation in place and reliable fastening of all removable parts of the fence. Figure 1.4 shows the protective covers on the pumping equipment. They are specially painted red, as this attracts attention and indicates the presence of a hazard in a certain part of the machine. A white arrow on red paint shows the direction in which the casing opens to access the mechanism. There is a control panel on the wall opposite each pump; actions run again.
In the second case, due to the presence of pumping equipment, continuously 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, pumping liquid, there may be high humidity in the pump room. This is fraught for two reasons. Firstly, it is dangerous for the well-being and health of a person. In the air, excessively saturated with water vapor, it is difficult for moisture to evaporate from the surface of the skin and lungs, which can dramatically worsen the condition and reduce a person's performance. At a temperature in the production room of 26 ° C and above and at work of moderate to severe, evaporation of sweat plays an important role in the heat transfer of the body. It is the evaporation of sweat, because the sweat that only flows down from the body does not bring relief to the body, does not take away heat from it.
The first signs of excessive heat: a feeling of stuffiness and heaviness, deterioration of health, decreased performance. The constant presence of a person in rooms with high humidity leads to a decrease in the body's resistance to infectious and colds, as well as to more serious consequences: kidney disease, tuberculosis, rheumatism, etc. Not only the human body suffers from high humidity, but also the interior of the premises. In damp places, fungus and mold develop, releasing a large number of spores into the atmosphere of the room, contaminating the air we breathe. The danger of high humidity lies in the slow speed of the reactions. For many years, one may not notice the reasons for the deterioration in health, well-being and the appearance of various diseases.
The second reason for the danger of high humidity in the room is the same electric current. The increased humidity of the ambient air, together with the surrounding electrical equipment, is very dangerous. So poorly insulated parts with dangerous voltages can cause electrical injury even without direct contact with them, you just need to come up or bring your hand and you can get an electric shock. Figure 1.4 shows the ground cables from each pump. Their condition, or rather external condition their isolation, this is the first thing the operator of the compressor or pumping unit should pay attention to when inspecting the pumping equipment, and he should pay attention to them even before he directly approaches them.
Now let's move on to the main harmful factor in the profession of a compressor installation operator. Compressor units today are one of those types of equipment in factories that generate noise and vibration. Compressor plants in municipal services are mainly referred to as equipment with a continuous cycle. The main operating units are stopped only when the maintenance of a particular compressor unit takes place, for example, an oil change or replacement of a worn out part, as well as when a compressor unit breakdown occurs, or when the electrical networks on a line are serviced. During this period of time, spare compressor units are always started. Pumping units also generate noise and vibration. Taken together, noise from all installations can reach levels that are hazardous to hearing.
Vibration and noise are mechanical vibrations that propagate in gaseous and solid media. They differ in vibration frequency. Mechanical vibrations that move through dense media with a vibration frequency of up to 16 Hz are perceived by a person as a shock, which is commonly called vibration. Oscillatory movements transmitted through the air with a frequency of 20 to 16000 Hz are perceived by the auditory organ as sound. Oscillatory movements above 16000 Hz refer to ultrasound and are not perceived by the human senses.
To measure the characteristics of noise and vibration in production, there are special instruments - noise meters, noise frequency analyzers and vibrographs. Until recently, it was generally accepted that noise has a negative effect only on the organs of hearing. It has now been established that people working in noise conditions get tired more quickly and complain of headaches. When the body is exposed to noise, a number of functional changes can occur on the part of various internal organs and systems: blood pressure rises, heart rate increases or slows down, various diseases of the nervous system (neurasthenia, neuroses, sensory disturbances) can occur. Intense noise has a negative effect on the entire human body. Attention is weakened, labor productivity decreases. Vibration, like noise, has a harmful effect on the body and primarily causes a disease of the peripheral nervous system, the so-called vibration disease.
Analyzing various sources of information, there are several main measures to combat vibration and noise:
Replacement of noisy processes with silent or less noisy ones, or modernization of already installed equipment;
Shelter for sources of noise and vibration, i.e. installation of protective screens, etc .;
Removal of workers from the area of exposure to noise and vibration, for example, arrangement of a sound and vibration-proof operator's cabin;
Use of personal protective equipment such as earmuffs, earbuds, etc.
In our case, the last two measures from this list can be applied at the workplace of the compressor operator. First of all, the driver with an increased noise level must use individual means protection. Depending on the amount of time spent in the area of increased noise, and the actual value of exceeding the maximum permissible level, it can be either elementary earbuds or headphones, or more complex and expensive headsets.
Secondly, an employee of the water supply and sewerage system, servicing compressor and pumping installations, can install a soundproof cabin or room. Equipment control panels and a monitor for monitoring the units can be brought out here. This will minimize the driver's stay in a noisy area, for example, if before the installation of such a cab the driver was obliged to make a round and inspect the equipment every hour, now two or three rounds per shift are enough.
Further in our work, we will consider what harmful and hazardous production factors are at a particular enterprise MUP "" the driver of the compressor installation, combining the duties of the driver of the pumping unit. After that, we will provide specific measures to improve working conditions and analyze their effectiveness and economic benefits.
CHAPTER 2. CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENTERPRISE
2.1 Description of the structural unit "" and the workplace of the compressor unit operator
The purpose of the sewerage system is to improve settlements, residential, public, industrial buildings, to provide the necessary sanitary conditions and a high level of convenience for work, life and recreation of the population. points or industrial enterprises contaminated wastewater, as well as for treatment and disposal before disposal or discharges into a water body.
CHAPTER 3. LABOR PROTECTION IN THE WORKPLACE OF THE MACHINER OF THE COMPRESSOR UNIT MUP ""
3.1 General Provisions operating instructions for the compressor unit operator
The operator of the compressor plant of the city sewage treatment plant (SES) belongs to the category of workers and is subordinate to the foreman, the technologist of the SES.
The operator of the GOS compressor unit is hired and dismissed by order of the director of the enterprise in the manner prescribed by the current labor legislation of the Russian Federation.
During the period of temporary absence of the compressor installation driver (vacation, illness, etc.), another worker replaces him by order of the director of the enterprise.
Persons at least 18 years of age are allowed to work, after:
Passing a preliminary medical examination;
Introductory briefing on labor protection;
Initial briefing on labor protection at the workplace;
Training and internship according to the type of work performed;
Testing of knowledge, labor protection requirements by the examination committee and obtaining a certificate for the right to work independently.
During. production activities periodically undergo medical examinations, training and instructions, testing of knowledge on labor protection.
The work of the compressor unit operator is carried out in shifts, according to the approved schedule.
The driver of the GOS compressor unit of the 3rd category must know:
Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering, Thermodynamics, Hydraulics and Mechanics;
Gas properties manifested during the operation of compressors;
Rules for the operation and repair of serviced equipment;
The device and design features of various types of auxiliary mechanisms, instrumentation;
Scheme of pressure pipelines of industrial water;
The principle of operation of centrifugal, piston pumps and other equipment of pumping units;
Physical and chemical properties of water;
Characteristics of pumps and drives to them;
Permissible pump loads during operation;
Diagrams of communication of pumping units, location of valves and safety devices;
Rules for the maintenance and switching of pipelines;
Applied grades and brands of oils;
Lubrication system of installations;
The principle of operation of the serviced electrical equipment;
Methods for troubleshooting equipment operation and eliminating accidents;
Purpose and use of instrumentation;
Labor protection rules, safety measures, industrial sanitation and fire safety.
3.2 Labor protection instructions for the compressor unit operator
3.2.1 General safety requirements
Persons who are at least 18 years of age are allowed to work as a compressor installation driver who have completed an introductory instruction on labor protection, initial instruction on labor protection at the workplace, medical checkup and on-the-job training. Subsequently, instructions on labor protection at the workplace are repeated every 3 months. Within a period not later than 3 months from the date of employment, the driver must undergo training and pass exams for knowledge of labor protection requirements. Subsequently, training and exams are held annually.
The driver must work in overalls and, if necessary, in protective equipment. Overalls are issued in accordance with the Standard industry regulations free distribution of overalls. Switch on and off the units with dielectric gloves, standing on a dielectric mat.
List of hazardous and harmful production factors:
Moving elements of equipment (pumping, power, powered grids, winches, scrapers, sprinklers, mechanical mixers and other mechanisms);
Falling objects and tools (when working on sewage treatment plants and networks, indoors, etc.);
Formation of explosive gas mixtures (in wells, chambers on networks, pumping stations, and in other rooms and structures);
Dangerous voltage level in an electrical circuit, the closure of which can occur through the human body;
Reduced air temperature in industrial premises and structures;
High air humidity;
Increased level of noise and vibrations (in the engine rooms of pumping and blowing stations and in other rooms and structures where technological equipment is installed);
Pathogenic microorganisms in waste and natural waters (bacteria, viruses, protozoa);
Helminth eggs in sewage.
The driver must know the structure of the compressor unit and strictly follow the rules of its operation.
The driver must know the structure and rules of technical operation of control devices, know the location of pipelines and valves on them within the building and the territory of the compressor station.
Immediately report all noticed faults to the head of the treatment facilities, the foreman.
The driver is prohibited from leaving work without handing over the shift.
Smoking at the station is allowed only in designated areas.
Store cleaning materials in metal boxes with a lid.
The driver must be able to provide first aid to the injured in an accident.
3a violation of the requirements of this manual, the driver is liable in the manner prescribed by law.
3.2.2 Safety requirements before starting work
Put on overalls.
Check the availability and serviceability of tools, inventory, fire-fighting equipment, working and emergency lighting, personal protective equipment, communication and signaling equipment.
Find out from the person handing over the shift about the condition of the working equipment.
Check the serviceability of the equipment by personal inspection of each compressor, electric motor, check the heating of the bearings, the presence of grease in them, the serviceability of the measuring instruments and valves.
Check the presence and serviceability of fences, protective devices and grounding.
3.2.3 Safety requirements during work
Before starting the compressor, check that the valves and valves on the outlet air line are open.
All work on the equipment should be performed with its complete shutdown and in strict accordance with the assignment.
Constantly check the heating of bearings, electric motors and monitor the presence of grease in the bearings.
Monitor the normal operation of equipment and exhaust ventilation, as well as control devices. Avoid deviations of the equipment operating modes from those specified in the operating instructions.
The driver has the right to make an emergency stop of the unit without prior notice to the administration in the following cases:
With strong vibration of the unit, threatening its integrity;
In the event of a breakdown of any part of the unit;
In case of an accident;
When a fire breaks out;
In the event of a lubrication system malfunction;
With unacceptably high heating of the bearings;
When abnormal noises appear in the unit.
3.2.4 Safety requirements in an emergency
In the event of an emergency (accident, fire, flooding of the station, etc.), the driver must:
De-energize the equipment;
Report the incident to the dispatcher on duty, your immediate supervisor;
If necessary, call the fire department (v. 01), ambulance (v. 03);
Provide first aid to victims;
Proceed to eliminate the emergency on their own.
3.2.5 Safety requirements at the end of work
Tidy up the used tools, devices and protective equipment and put them in their designated place.
Tidy up the workplace, clean the overalls from contamination.
Before eating, wash your hands with soap and water, after finishing work, take a shower. Overalls should be washed periodically.
3.3 Instruction on labor protection on electrical safety for non-electrical personnel
3.3.1 General safety provisions
Electrical equipment may be serviced by a person who is at least 18 years of age who has completed an introductory instruction in labor protection, initial instruction in the workplace, medical examination and training in the profession at the workplace upon admission to work.
Employees who have mastered the requirements of this instruction on electrical safety related to their work are assigned group 1 with registration in the journal of the established form.
Perform only the work that is given by the manager at the workplace (foreman, site manager, head of pumping stations, etc.), provided that you know safe ways to do it.
Know the meaning of signs and posters, warning, prohibiting, prescribing, indicating, as well as sound and light signaling operating at the facility.
Do not obstruct approaches to electrical installations, starters, circuit breakers and other switching equipment.
Do not touch broken electrical wires and electrical wires with damaged electrical insulation.
Do not open, turn on or touch with your hands or objects of electrical devices and electrical equipment, unless they are directly serviced.
It is forbidden to step on cables, electric welding wires, as well as allow vehicles to run over them.
Do not look into the arc with unprotected eyes when welding, as this can lead to eye disease.
Do not follow the instructions if they contradict the safety rules and their observance may lead to an accident.
Noticing a violation of safety rules for other workers or a danger to others, do not remain indifferent, warn the worker and the foreman about the need to comply with the requirements that guarantee safety.
Observe cleanliness at the workplace, production and household premises, on the territory of the enterprise. Follow the rules of personal hygiene.
Know the rules for providing first aid to victims and be able to apply them if necessary.
For violation of the requirements of this manual, non-electrotechnical personnel shall bear responsibility established by law.
3.3.2 Safety requirements before starting work
Before starting work, the employee must review:
Availability of grounding and its connecting contacts;
The presence of dielectric rugs near electrical equipment;
The presence of casings on rotating parts of the equipment;
Condition of cabinets, assemblies, etc. (doors must be locked);
Condition of dielectric gloves;
In the magazines at the workplace - additional orders on the procedure for carrying out work.
The state of electrical equipment should be noted in work logs at workplaces.
Make sure that fire-extinguishing equipment and first aid are ready in case of accidents.
3.3.3 Safety requirements during work
Do not go behind fences and follow the requirements of signs, safety posters posted by electrical personnel.
It is forbidden to unauthorizedly remove or move fences, signs, posters.
Make sure that the switching devices, alarms and interlocks are in good working order.
Check the health of lighting devices, electrical wiring, lamps and lamps. Adjust local lighting so that the work area is illuminated and the light does not dazzle the eyes.
Do not touch broken wires, as well as bare live parts of electrical installations (terminals, buses, etc.). Touching two wires is especially dangerous.
During work, non-electrical personnel should perform work related only to their direct production activities.
When a ground fault is detected, it is forbidden to approach the place of the fault at a distance of less than 4-5 meters in closed and less than 8-10 meters in open electrical installations.
3.3.4 Safety requirements in an emergency
If a malfunction is detected in electrical installations (sparking, flash, violation of insulation of wires, cables, etc.), as well as about live parts left unprotected, you must inform your manager.
It is necessary to immediately turn off the electrical equipment in the following cases:
Breakdown of any of the parts, when a malfunction is detected in the operation of mechanisms, electrical equipment;
An accident that happened to any of the service personnel;
Fire in the work area.
Noticing a fire, you must immediately inform the water utility dispatcher, call the fire department and start extinguishing the fire with the available primary fire extinguishing means.
To extinguish a fire in electrical installations, first of all, it is necessary to use carbon dioxide or powder fire extinguishers. Do not forget also the simplest fire extinguishing means, such as dry sand, asbestos or coarse-woolen cloth, which, when thrown onto a fire, can quickly extinguish the flame.
...Similar documents
Hazardous production factors at the workplace of the pump station operator. The harmful effects of microclimate parameters. Lack of natural light, insufficient illumination of the working area. Impact protection increased level vibration.
term paper, added 03/12/2011
Basic definitions and terms of labor safety, hazardous and harmful production factors. Identification, measurement and assessment of hazardous and harmful production factors in the workplace of an electronic engineer. Measures to improve working conditions.
term paper, added 08/08/2010
Study of natural side lighting in the workplace. Study of artificial lighting in the workplace. Study of the noise level in the workplace. Investigation of dustiness in the air in the workplace.
laboratory work, added 11/10/2003
Harmful factors in the workplace and their impact on the human body. Measures to reduce and eliminate the harmful effects of the environment of the workplace: standards of illumination and ionization of air in the room, organization of the worker's desk.
test, added 06/07/2011
Description of the welder's workplace. Harmful and hazardous production factors. Study of the requirements for preserving the life and health of an employee in the process of work. Maximum permissible concentration of harmful substances emitted during metal welding.
term paper added 06/09/2015
Hazardous production factors affecting the crane operator of the Komatsu D355C pipelayer, methods of their prevention. Research of the work process, identification of the causes of malfunctions leading to the failure of the machine. Building a "fault tree".
term paper added 03/14/2010
Identification of hazardous and harmful production factors at the workplace of the waterproofer. Determination of general organizational and technical measures to improve working conditions and increase the level of workplace safety. Calculation of the aspiration system.
term paper added on 05/11/2015
Harmful and dangerous factors arising in the process of injection molding: air pollution with dust and gases, noise and severity of the labor process. Introduction of local supply and exhaust ventilation to improve the air in the working area from increased dustiness.
thesis, added 10/13/2015
Hazardous and harmful production factors, their impact on the environment and assessment of its consequences. Labor protection at the workplace of a PC operator in the post office of FSUE "Russian Post". Lightning protection of buildings and structures, installation of lightning rods.
term paper, added 09/25/2014
Fundamental principles of the Constitution of the Russian Federation concerning labor issues. General characteristics of the cook's workplace, classification of hazardous and harmful production factors. The work of managers to ensure safe working conditions in the workplace.
RUSSIAN JOINT STOCK COMPANY "UES OF RUSSIA"
TYPICAL INSTRUCTIONS
LABOR PROTECTION FOR THE ENGINEER
COMPRESSOR UNIT
RD 34.03.252-93
UDC 658.382.3: 621.51
The validity period is set from 26.01.93.
Compiled by JSC "Firm for the adjustment, improvement of technology and operation of power plants and networks ORGRES"
Executors S.V. BOYTSOVA (Novgorodenergo), N.I. KUZMIN (Kamchatskenergo), M.V. A. A. A. A. A. A. A. A. A. A. A. CHURSINOVA, V.G. TIMASHOV (ORGRES)
Agreed with the All-Russian Committee "Electroprofsoyuz" (Resolution of January 14, 1993 No. 16)
Approved by the Department of Labor Protection and Safety of the Electricity Committee of the Ministry of Fuel and Energy of the Russian Federation on January 26, 1993.
Deputy Chairman I.A. NOVOZHILOV
This Standard Instruction (hereinafter referred to as the Instruction) provides labor protection requirements for the compressor installation operator.
These instructions are intended to develop local instructions taking into account the specific working conditions of the worker.
1. GENERAL PROVISIONS
1.1. The labor protection instruction is the main document that establishes the rules of behavior for workers in production and the requirements for the safe performance of work.
1.2. Knowledge of the Labor Protection Instructions is mandatory for workers of all categories and groups of qualifications, as well as their immediate supervisors.
1.3. The administration of the enterprise (shop) is obliged to create conditions at the workplace that meet the labor protection rules, provide workers with protective equipment and organize their study of this Labor Protection Instruction.
At each enterprise, safe routes must be developed and communicated to all personnel along the territory of the enterprise to the place of work and evacuation plans in case of fire and emergency.
1.4. Every worker is obliged:
comply with the requirements of this Instruction;
immediately inform your immediate supervisor, and in his absence - a higher supervisor about the accident that occurred and about all violations of the requirements of the Instruction noticed by him, as well as about malfunctions of structures, equipment and protective devices;
remember personal responsibility for non-compliance with safety requirements;
keep the workplace and equipment clean and tidy;
ensure the safety of protective equipment, tools, devices, fire extinguishing equipment and labor protection documentation at their workplace.
IT IS FORBIDDEN to execute orders that contradict the requirements of this Instruction and the "Safety Rules for the Operation of Electrical Installations" (PTB) - M .: Energoatomizdat, 1987.
2. GENERAL SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
2.1. To work for this working profession allowed persons at least 18 years of age who have passed a preliminary medical examination and do not have contraindications to perform the above work.
2.2. When hiring, a worker must undergo an induction training. Before being admitted to independent work, a worker must go through:
initial instruction at the workplace;
checking the knowledge of this Labor Protection Instruction; Instructions for providing first aid to victims of accidents during the maintenance of power equipment; on the use of protective equipment necessary for the safe performance of work; PTB for workers who have the right to prepare a workplace, carry out admission, be a work producer, supervisor and a member of a team in the amount corresponding to the duties of the responsible persons of PTB;
training in professional training programs.
2.3. Admission to independent work must be formalized by the appropriate order for the structural unit of the enterprise.
2.4. The newly hired worker is issued a qualification certificate, in which an appropriate entry must be made on checking the knowledge of the instructions and rules specified in clause 2.2, and the right to perform special work.
A qualification certificate for personnel on duty while on duty may be kept by the shift supervisor or with him in accordance with local conditions.
2.5. Workers who have not passed the knowledge test on time are not allowed to work independently.
2.6. A worker in the process of work must go through:
repeated briefings - at least once a quarter;
testing the knowledge of the Labor Protection Instructions and the current Instructions for providing first aid to victims of accidents during the maintenance of power equipment once a year;
medical examination - once every two years;
testing the knowledge of industrial safety for workers who have the right to prepare a workplace, carry out admission, be a work manufacturer, supervisor or a member of a team - once a year.
2.7. Persons who have received an unsatisfactory mark during the qualification test are not allowed to work independently and must be retested no later than one month.
In case of violation of safety rules, depending on the nature of the violations, an unscheduled briefing or an extraordinary test of knowledge is carried out.
2.8. In case of an accident, the worker is obliged to provide first aid to the injured person before the arrival of medical personnel. In the event of an accident with the worker himself, depending on the severity of the injury, he must apply for medical help to a health center or to provide first aid to yourself (self-help).
2.9. Each employee should know the location of the first aid kit and be able to use it.
2.10. If faulty devices, tools and protective equipment are found, the worker must inform his immediate supervisor.
DO NOT work with defective attachments, tools or protective equipment.
2.11. To avoid electric shock, do not step on or touch loose, dangling wires.
2.12. Failure to comply with the requirements of the Labor Protection Instruction for the worker is considered a violation of production discipline.
For violation of the requirements of the instructions, the worker is liable in accordance with applicable law.
2.13. When servicing a compressor unit, the following hazardous and harmful production factors may occur:
increased noise level;
increased vibration level;
moving mechanisms, rotating parts of the fan;
increased pressure of compressed air in the receiver;
increased voltage value in the electrical network.
2.14. To protect against the effects of hazardous and harmful factors, it is necessary to use appropriate personal protective equipment.
To protect the worker from an increased noise level at the workplace, it is necessary to use anti-noise protective equipment (headphones, earplugs, etc.) or to limit the time spent in the area of increased noise.
Increased pressure of compressed air in the receiver above the permissible one can lead to its rupture and injury to the operating personnel by fragments, therefore, if the pressure readings are higher than the permissible one, the compressor must be stopped immediately.
When the driver is near the rotating parts of the compressor, there should be no fluttering parts of clothing in order to avoid being caught by the rotating blades.
In order to avoid electric shock to the operator, it is necessary to have a grounding of the unit's frame. During work, the driver must use dielectric gloves, carpets, galoshes.
When you are in rooms with technological equipment (with the exception of control panels), you must wear a safety helmet with a chin strap.
In case of smoke or gas contamination of the room, a gas mask should be used.
2.15. The driver must wear protective clothing and must wear protective equipment issued in accordance with applicable industry regulations.
2.16. The following work clothing must be issued to the compressor operator in accordance with industry regulations:
overalls or cotton suit - for 12 months;
combined mittens - for 2 months.
Depending on the nature of the work and the conditions of their production, the driver is temporarily issued additional overalls and protective equipment for these conditions free of charge.
2.17. It is not allowed to use fire in the compressor room, enter with a lit cigarette, etc., use electric heating devices (electric stoves, etc.), and also store flammable liquids (kerosene, gasoline, etc.).
3. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS BEFORE STARTING WORK
3.1. The overalls used must be put in order: the sleeves must be fastened, the clothes must be tucked in so that there are no hanging ends, the hair must be removed under a tight-fitting headdress or mask. DO NOT roll up the sleeves of your workwear.
3.2. Check the presence and serviceability of instruments for monitoring air pressure, oil, temperature.
3.3. Check at the workplace the serviceability of tools, devices, the safe condition of the equipment.
Locksmith tools must meet the following requirements:
hammer strikers should have a smooth, slightly convex surface without skewing, chips, gouges, cracks and burrs;
hammer handles must not have cracks;
the impact tool must have a smooth occipital part, without cracks, burrs, work hardening and bevels;
the working surfaces of the wrenches should not have knocked down bevels, and the handles should not have a burr.
Files, scrapers and other tools should have handles with retaining rings.
3.4. Report the readiness to accept the shift to the superior duty personnel.
3.5. IT IS FORBIDDEN:
test the equipment before accepting the shift;
come to shift in drunk or drink alcohol during working hours;
leave the shift without registering the acceptance and delivery of the shift.
4. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS DURING WORK
4.1. While the compressor is running, you need to carefully monitor the operation of the devices and listen to the refrigerator for compressed air leaks.
4.2. When cleaning the premises, do not clean the equipment under pressure.
4.3. If oil and water leaks are found, oil gets on the foundation, it is necessary to identify and eliminate the causes of the leaks, remove the oil and water. Only cotton or linen rags may be used as cleaning materials, which should be stored in a special closed container.
4.4. The compressor must be stopped immediately in the following cases:
if the pressure gauges at any stage of the compressor show a pressure higher than the allowable (higher than the setpoints);
if the pressure gauge in the lubrication system shows pressure below the permissible lower limit;
when the cooling fan is turned off;
if you hear knocks, bumps in the compressor or engine, or a malfunction is detected that can lead to an accident;
if the temperature of the III stage of the compressor is higher than the temperature alarm setpoint;
if there is a smell of burning, smoke from a compressor or an electric motor;
with a noticeable increase in vibration of the compressor and electric motor.
After an emergency stop of the compressor, it can be put into operation with the permission of the person responsible for the safe operation of the compressor unit.
4.5. When servicing the compressor unit, it is prohibited:
place equipment and equipment not related to the compressor in the compressor unit room;
start up and operate a technically faulty compressor or with a faulty (missing) guard;
leave the operating compressor units unattended by the operating personnel;
store gasoline, kerosene and other flammable materials in the compressor unit;
repair and clean pressurized equipment and pipelines;
making an open fire in the compressor plant room;
operate a compressor with faulty safety valves, pressure switches and pressure gauges;
clean, wipe and lubricate rotating and moving parts of mechanisms, as well as climb over fences or reach behind them for lubrication and cleaning;
to shorten the route of bypassing equipment, jump or climb over pipelines;
lean on and stand on platform barriers, stair fences, protective covers for couplings and bearings, walk along pipelines, as well as on structures and ceilings that are not intended for passage through them;
stop manually rotating mechanisms;
open fittings without protective gloves;
step on the covers of manholes, wells, channels;
penetrate into hazardous areas (steam, water, oil leaks, gas leaks, fuel oil, cranes);
use kerosene, gasoline, acetone and other flammable substances to wipe equipment;
clean and replace burnt out lamps;
when wiping the outer surfaces of working mechanisms, wrap a cleaning material around your hand or fingers;
smoke throughout the compressor room.
4.6. Oil leakage to the foundation is not allowed. The cause of the leak must be repaired immediately.
4.7. Only cotton or linen rags may be used as a cleaning material.
4.8. When the temperature in the station room drops to 2 ° C, cooling water must be drained from the cooling systems of non-operating equipment, and the air cavities must be thoroughly purged. In the event of freezing in the air line or water separator, they should be rewarmed with steam or hot water.
4.9. It is FORBIDDEN when inspecting the compressor unit equipment to switch, remove posters or safety signs, fences and groundings installed during the preparation of the workplace, touch live parts, close and open valves, penetrate through permanent and temporary fences.
4.10. When performing repair work, it is FORBIDDEN:
to work on unstoppable equipment and mechanisms;
to carry out work without taking measures against erroneous switching.
4.11. Before disassembling the compressor and opening the interstage equipment, it is necessary:
disconnect the compressors from the existing collectors;
ensure the complete absence of overpressure in the compressor and interstage equipment;
ensure the absence of voltage in the electrical equipment and complete disconnection from the power supply system (posters should be posted on the starting device: "Do not turn on! People are working");
install plugs on the suction and discharge lines, turn off the purge and sampling lines for compressors operating on hazardous and toxic gases;
confirm by analyzing the quality of the blowing of the compressor and interstage equipment;
to protect areas of work and all openings;
check for the necessary scaffolding and scaffolds.
4.12. The shutdown of all vessels and other equipment under pressure must be done with two valves installed in series with a drainage device between them.
4.13. It is necessary to open and close valves and valves with special devices. It is FORBIDDEN to use levers (crowbars, pipes and other objects) for this.
IT IS FORBIDDEN to build up the key with a pipe or other key, as well as work with oily keys.
4.14. When working with attached and sliding ladders at a height of more than 1.3 m, it is necessary to use a safety belt attached to the structure of the structure or to the ladder, provided it is securely attached to the structure.
4.15. DO NOT place heavy parts on the edge of the workbench, use fragile stands and boxes, or place tools on the compressor unit.
4.16. IT IS FORBIDDEN for the driver to carry parts weighing more than 50 kg.
4.17. Before internal inspection, cleaning or repair of devices, they must be reliably disconnected from communications, completely freed from the working product.
4.18. During operation inside the apparatus, all hatches must be open and the entire apparatus must be continuously ventilated. There must be a companion outside the apparatus to monitor the state of those working inside the apparatus.
Work inside the apparatus is classified as hazardous work and must only be carried out with the permission of the person responsible for safe operation.
Cleaning of devices by burning is FORBIDDEN.
4.19. Working with random supports (boxes, barrels, boards, etc.) is PROHIBITED.
4.20. Protective goggles must be worn when using the impact tool to prevent particulate matter from entering the eyes.
4.21. When using a locksmith tool during repairs, the following requirements must be observed:
when unpressing or removing individual parts, special serviceable pullers must be used. If it is impossible to use them, it is necessary to use copper pads and pads;
when assembling assemblies and mechanisms with springs, devices must be used to ensure the impossibility of sudden action of the spring. The installation of compressed springs should also be carried out using special devices;
cleaning files from shavings should be done with a special brush;
when cutting metal with hand hacksaws, it is necessary to tighten and firmly fasten the hacksaw blade.
4.22. The tool in the workplace must be positioned so that it cannot roll or fall. It is prohibited to put the tool on the railing of fences or on the unenclosed edge of the scaffolding platform, scaffolds, as well as near open hatches and wells.
4.23. The production of work with the use of open fire and electric welding must be carried out in compliance with fire-prevention measures under the supervision of a responsible person, with the written permission of the chief engineer of the enterprise and a representative of the fire department.
5. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS AT THE END OF WORK
5.1. At the end of the shift, you must:
finish switching;
stop admission and registration of the end of work along the line;
all tools, fixtures, devices and protective equipment must be put in proper order and placed in special cabinets and racks designed for this purpose;
inform the host of the shift about all malfunctions and changes in the operation of the equipment that occurred during the shift;
report on the delivery of the shift to your superior duty personnel and draw up a list in the operational log;
take off overalls, put it and other personal protective equipment into the closet.
Quote: It is possible to get a disability gas seal from Kazakhstan at a discount in the amount of 220 hours, in this amount - the duration is to say the letters "minor" consequences. Therefore, accept the schedule of the certificate of staff reduction (from 2 months).
Will work 2 years in 11 months.
Article 10. Consideration of application for dismissal due to reduction of staff
Paid leave must be granted to the employee annually.
By agreement between the employee and the employer labor contract may be terminated even before the expiry of the notice of dismissal.
In cases where the employee's application for dismissal on his initiative (of his own free will) is due to the impossibility of continuing his work (enrollment in educational institution, retirement and other cases), as well as in cases of established violation by the employer labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, local regulations, the terms of a collective agreement, agreement or employment contract, the employer is obliged to terminate the employment contract within the time period specified in the employee's application.
(as amended by Federal laws from 22 08 2004 122-FZ, from 29 06 2015 176-FZ, from 02 11 2007 284-FZ)
If the amount is not very important to go to court with additional evidence.
You can apply to the Court with a Statement of Claim.
Article 3 of the Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation. Right to go to court
1. The interested person has the right, in accordance with the procedure established by the legislation on civil proceedings, to apply to the court for the protection of violated or disputed rights, freedoms or legitimate interests, including with a claim to award him compensation for violation of the right to legal proceedings within a reasonable time or the right to performance a court order within a reasonable time.
2. Waiver of the right to appeal to court is invalid.
3. By agreement of the parties, a dispute within the jurisdiction of the court arising from civil legal relations, prior to the adoption by the court of first instance of a court decision, which ends the consideration of the civil case on the merits, may be referred by the parties to the arbitration court, unless otherwise provided by federal law.
Article 151 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Compensation for non-pecuniary damage
If a citizen has suffered moral harm (physical or mental suffering) by actions that violate his personal non-property rights or encroach on the intangible benefits belonging to the citizen, as well as in other cases provided for by law, the court may impose on the violator the obligation of monetary compensation for the specified harm.
When determining the amount of compensation for non-pecuniary damage, the court takes into account the degree of guilt of the offender and other noteworthy circumstances. The court must also take into account the degree of physical and mental suffering associated with the individual characteristics of the citizen who is harmed.
Article 12.8. Driving a vehicle by a driver who does not have the right to drive a vehicle (with the exception of training driving) -
shall entail the imposition of an administrative fine in the amount of five thousand to fifteen thousand rubles.
(as amended by Federal laws from 22 06 2007 116-FZ, from 24 07 2007 210-FZ, from 23 07 2013 196-FZ)
(see text in previous edition)
10 2. 56
ConsultantPlus, 1992-2014
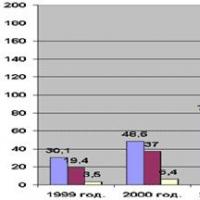 Coursework: Prospects for the Development of Electronic Money in Russia Circulation of Electronic Money
Coursework: Prospects for the Development of Electronic Money in Russia Circulation of Electronic Money Instant quality control throughout the entire winemaking process
Instant quality control throughout the entire winemaking process Reputation management: modern approaches and technologies
Reputation management: modern approaches and technologies Information about the Department of International Economic Relations Textbooks and teaching aids published abroad
Information about the Department of International Economic Relations Textbooks and teaching aids published abroad Practice report in an advertising agency
Practice report in an advertising agency The youngest and most successful businessmen in the world
The youngest and most successful businessmen in the world New promising professions: who to be in the 21st century Professions that appeared in the 20th 21st centuries
New promising professions: who to be in the 21st century Professions that appeared in the 20th 21st centuries